What Are AI Agents: Everything You Need to Know
- BLOG
- Artificial Intelligence
- October 13, 2025
You might wonder why everyone’s talking about AI agents, especially if you’re struggling with repetitive tasks, missing out on data-driven insights, or feeling overwhelmed by manual processes. AI agents are stepping in to solve these headaches by working smarter, not harder.
So what are AI agents? An AI agent is a software system that uses AI to understand its environment and make decisions. Agents take actions often without human intervention to achieve specific goals. They can analyze data, solve problems, and automate tasks based on rules or learned patterns.
But what makes AI agents truly powerful, and how are businesses using them to get real results? Keep reading to discover more.
Contents
- 1 What are AI Agents?
- 2 AI Agents vs. AI Assistants vs. Bots: What’s the Difference?
- 3 Build your AI agent by planning with Webisoft through their AI consultancy!
- 4 Types of AI Agents
- 5 AI Agent Frameworks
- 6 Key Features and Components of an AI Agent
- 7 Benefits of AI Agents
- 7.1 Saves Time by Automating Complex Work
- 7.2 Reduces Errors and Improves Accuracy
- 7.3 Works 24/7 Without Human Supervision
- 7.4 Frees Teams from Operational Burdens
- 7.5 Scales Effortlessly with Business Growth
- 7.6 Breaks Down Silos and Streamlines Collaboration
- 7.7 Enables Data-Driven Decision-Making
- 7.8 Improves Customer and Employee Experience
- 7.9 Reduces Costs Across the Board
- 8 How Do AI Agents Work?
- 9 The Role of Human-in-the-Loop in AI Agents
- 10 How Business Are Using AI Agents: Practical Use Cases
- 11 How AI Agents Can Transform Digital Strategy
- 12 The Hidden Challenges and Limitations of AI Agents
- 13 The Future of AI Agents: Multi-Agent Collaboration and Agentic Workflows
- 14 How to Bring AI Agents in Your Business
- 15 Build your AI agent by planning with Webisoft through their AI consultancy!
- 16 Conclusion
- 17 FAQs
What are AI Agents?
AI agents are smart digital partners, not just software that follows orders. You give them a goal, like “help customers” or “sort through all these emails,” and they use their own intelligence to find solutions and to reach your desired outcome.
An AI agent can make decisions, adjust to new situations, and learn from experience. Unlike traditional programs, they can handle complex tasks, such as answering tricky customer questions or automating entire workflows.
They use feedback and memory to get better over time, so they’re always improving. This means agents can help with multi-step jobs that usually need a real person.
AI Agents vs. AI Assistants vs. Bots: What’s the Difference?
When you first hear about AI agents, you may confuse them with AI bots or AI assistants. But what are AI agents, assistants, and bots? They are different from each other. Here’s a table of differences between these three AI-related facilities:
| Feature | Bots | AI Assistants | AI Agents |
| Autonomy | Low: Follows strict scripts and rules | Moderate: Needs user prompts, can handle basic automation | High: Operates independently after initial goal is set |
| Learning Ability | None: Can’t learn or adapt | Some: May improve responses based on user feedback | Strong: Learns from interactions, adapts to new situations |
| Complexity | Simple: Handles repetitive, predefined tasks | Moderate: Manages routine tasks, provides recommendations | Advanced: Handles multi-step, dynamic, and complex tasks |
| Decision Making | None: No real decision-making | Limited: Supports decisions with user input | Full: Makes decisions and takes actions autonomously |
| Human Oversight | Low: Needs minimal oversight | Moderate: Requires regular human input | Variable: Can run independently, but oversight is recommended |
| Memory | None: No memory of past interactions | Short-term: Session-based memory | Long-term: Remembers and learns from past interactions |
| Interaction Type | Transactional: Q&A, simple commands | Conversational: Natural language, two-way dialogue | Contextual: Understands and acts on nuanced, evolving requests |
| Best For | FAQs, basic customer service, simple workflows | Scheduling, reminders, quick info lookups, basic automation | Complex workflows, dynamic environments, multi-step processes |
| Examples | Website chatbots, order status bots | Siri, Alexa, Cortana, scheduling assistants | Autonomous customer support, supply chain optimization, sales |
When to Use Each: Key Business Implications
Now, you may want to know when you should use an AI bot, AI assistant, and AI agent in your business. Here’s the impact and usage of these AI services:
AI Bots
- When to Use: You need quick, reliable answers to common questions or simple, repetitive tasks.
- Business Impact: Cuts costs on routine customer service, speeds up basic workflows, and frees up staff for more complex issues.
- Example: A bot on your website answers FAQs about shipping or returns; no human needed.
AI Assistants
- When to Use: You want to automate everyday tasks but still need a human touch or quick access to information.
- Business Impact: Increases productivity and helps employees manage calendars, emails, and simple research. Great for teams that need support, not replacement.
- Example: An AI assistant schedules meetings, manages your inbox, or reminds you of deadlines.
AI Agents
- When to Use: You need to automate complex, multi-step processes or make smart decisions without constant human input.
- Business Impact: Drives efficiency at scale, handles dynamic situations, and reshapes new challenges. Ideal for sales, support, logistics, and operations where flexibility and intelligence matter.
Example: An AI agent manages your entire customer support workflow, like tagging, routing, drafting replies, and escalating only when necessary. Or, it optimizes your supply chain by predicting demand and rerouting shipments in real time.
Build your AI agent by planning with Webisoft through their AI consultancy!
Schedule an AI strategy and consultation – Build a secure & scalable AI agent today!
Types of AI Agents

Depending on the types of AI agents, their working purpose may vary. Here are the agent types categorized by their operational purpose:
By Decision Logic and Autonomy
Simple Reflex Agent
Responds to current input using fixed rules, ignoring past events. Acts instantly but can’t adjust to new situations. For example, a thermostat turns on heat if the temperature drops below a set point.
Model-Based Reflex Agent
Uses an internal model to track environment changes, making more informed decisions. For instance, a robot vacuum remembers cleaned areas and avoids repeating them.
Goal-Based Agent
This agent plans actions and evaluates options to achieve specific targets, like a navigation system. It analyzes different paths to find the fastest route for your journey.
Utility-Based Agent
A utility-based agent aims to maximize value or minimize risk. It makes decisions similar to a self-driving car choosing the safest and most efficient path.
Learning Agent
A learning agent improves by gaining experience and feedback. It adapts its behavior, just as a recommendation engine personalizes suggestions as it learns your preferences.
By Behavior and Initiative
Proactive Agent
A proactive agent anticipates needs before you ask. It uses predictive analytics to act ahead, such as scheduling maintenance when it forecasts equipment failure.
Reactive Agent
A reactive agent responds instantly to triggers. It doesn’t plan or remember, like a chatbot that answers customer questions as soon as they are typed.
By Structure and Functionality
Hybrid Agent
A hybrid agent blends features from different agent types. It can plan, learn, and react, much like a self-driving car that reroutes, learns from mistakes, and stops for obstacles.
By Interaction and Collaboration
Collaborative Agent
A collaborative agent works together with others. It helps achieve shared goals, such as warehouse robots that cooperate to fulfill customer orders.
Multi-agent System
A multi-agent system involves multiple agents interacting. They may cooperate or compete, for example, AI agents in traffic management coordinating to optimize the flow of vehicles.
AI Agent Frameworks
An AI agent framework is a structured toolkit or platform that helps you quickly build and manage smart, autonomous agents. It’s the backbone for developing AI systems that can reason, learn, and act on their own.
Its main task is to provide ready-made components, rules, and integrations so you don’t have to start from zero every time you want to create a new AI agent.
AI Agent Framework Examples

Here are some popular AI agent frameworks that businesses often opt for:
AutoGen
Built for multi-agent conversations, AutoGen lets agents with different roles, like researcher, planner, or executor, work together to solve complex tasks. It supports easy switching between large language models and offers a no-code interface for quick prototyping.
LangChain
Focused on integrating language models into applications, LangChain helps agents process and respond to natural language, connect to databases, and use external tools.
CrewAI
Designed for multi-agent teamwork, CrewAI assigns specialized roles to agents, supports flexible tool integration, and allows for parallel task execution, ideal for research and content generation.
Rivet
A drag-and-drop workflow builder that lets you design, test, and establish agentic workflows without writing code, making it accessible for non-developers.
Botpress
An open-source framework for building chatbots and conversational agents, with tools for natural language understanding and easy deployment.
AutoGPT
Turns GPT-based models into goal-driven, self-planning agents that can operate with minimal supervision. This autonomous AI agent is perfect for experimental or semi-automated workflows
Key Features and Components of an AI Agent
When we talk about an AI agent platform, the components are the core parts, like perception and reasoning, that make the agent work. They form the foundation for building smart, adaptable AI agent systems. The core features and components are as follows:
| Component | What It Does | Resulting Features |
| Perception | Gathers data from the environment (sensors, APIs, inputs) | Data intake, context awareness, input handling |
| Reasoning | Analyzes info, makes decisions, plans next steps | Decision-making, problem-solving, logic, planning |
| Learning | Adapts and improves from experience | Continuous improvement, personalization, adaptation |
| Memory | Stores and retrieves past info and context | Recall, personalization, context-aware actions |
| Action | Executes tasks or changes in the environment | Task automation, output generation, execution |
Benefits of AI Agents

AI agents do more than just automate tasks; they solve real business problems, save money, and make your operations faster, smarter, and more reliable at every turn. Here are the benefits of AI agents:
Saves Time by Automating Complex Work
AI agents handle multistep, repetitive, or logic-heavy tasks without needing constant human input. For example, they can process procurement orders, analyze supplier bids, or route customer service tickets, all while you focus on higher-value work.
Reduces Errors and Improves Accuracy
AI agents can self-examine their output, spot gaps, and correct mistakes. Hence, they can maintain high accuracy levels, especially in data-driven tasks like invoicing, compliance checks, or code generation. The result is fewer costly errors and more reliable results.
Works 24/7 Without Human Supervision
AI agents don’t sleep. They keep running processes, answering customer questions, and managing workflows around the clock, so your business stays responsive and operational at all hours, even outside standard office times.
Frees Teams from Operational Burdens
By taking over routine, cross-functional tasks, AI agents let your team focus on innovation, strategy, and creative problem-solving instead of getting bogged down in operational details.
Scales Effortlessly with Business Growth
AI agents can handle increased workloads instantly, without extra training or new hires. Whether you’re processing more orders, supporting more customers, or expanding into new markets, your agents adjust with you.
Breaks Down Silos and Streamlines Collaboration
AI agents connect different departments and systems, sharing data and automating workflows that would otherwise require manual handoffs. This reduces bottlenecks and makes cross-functional projects run smoother.
Enables Data-Driven Decision-Making
They analyze large datasets in real time, spot trends, and generate actionable insights. This helps you make informed decisions, whether you’re optimizing supply chains, forecasting demand, or identifying new sales opportunities.
Improves Customer and Employee Experience
By delivering fast, accurate, and personalized responses, AI agents make interactions smoother for both customers and employees. They remember preferences, provide timely support, and help resolve issues faster, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Reduces Costs Across the Board
With automation, error reduction, and 24/7 availability, AI agents cut operational expenses. You spend less on labor, overtime, and manual corrections while getting more done.
How Do AI Agents Work?
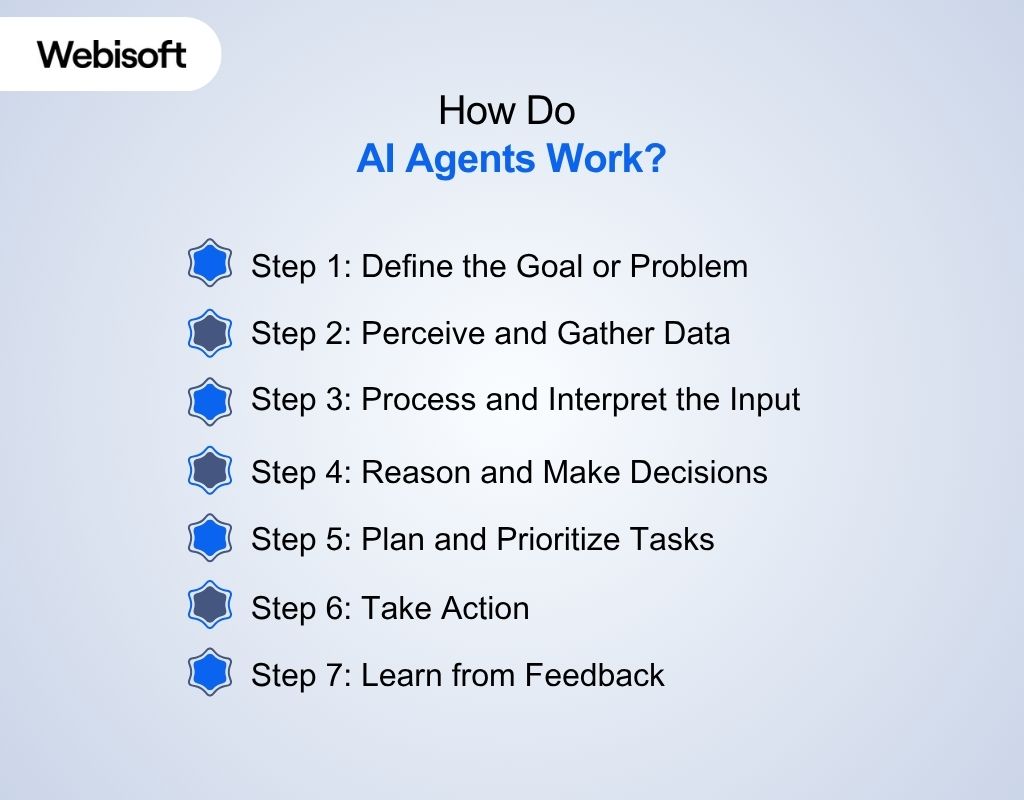
Understanding the working of AI agents is necessary to understand what are AI agents and how they simplify business operations. Here’s how an AI agent works in step-by-step:
Step 1: Define the Goal or Problem
Every AI agent starts with a purpose. You tell it what you want, like answering customer questions, scheduling appointments, or analyzing data. This sets the direction for everything that follows.
Step 2: Perceive and Gather Data
The agent collects information from its environment. This could be a chat message, a sensor reading, or a new entry in a database. It’s like the agent opening its eyes and ears to see what’s happening.
Step 3: Process and Interpret the Input
Raw data isn’t enough. The agent needs to make sense of it. It uses tools like natural language processing or image recognition to turn noise into actionable insights.
Step 4: Reason and Make Decisions
Now, the agent thinks about what to do. It might break the goal into smaller tasks, check its memory for past experiences, or consult rules and logic. This is where the agent’s intelligence kicks in.
Step 5: Plan and Prioritize Tasks
The agent maps out a plan. It figures out what steps to take, in what order, and which tools or systems to use. It’s like a project manager organizing a team.
Step 6: Take Action
With a plan in place, the agent carries out the necessary actions, like sending a response, updating a record, or triggering another process. This is where the real work happens.
Step 7: Learn from Feedback
After acting, the agent checks the results. It learns from what worked and what didn’t, updating its knowledge and improving for next time. This feedback loop keeps the agent getting smarter
The Role of Human-in-the-Loop in AI Agents
AI agents are powerful, but they’re not perfect. That’s where human-in-the-loop (HITL) comes in. HITL means humans stay involved, not as observers only, but as partners who step in when things get tricky or the stakes are high.
Practical Frameworks for Human-AI Collaboration
Businesses use HITL frameworks to keep automation sharp and safe. Here’s how it usually works:
Escalation Paths
When an AI agent isn’t sure what to do or if a decision is sensitive, it automatically directs the case to a human. For example, a customer support agent might send a tricky request to a real person instead of guessing.
Feedback Loops
Every time a human intervenes, the AI learns from it. This feedback makes the agent smarter over time. It’s like having a coach review your work and give you tips for next time.
Approval Workflows
Some tools let you set up rules so AI agents need human approval for certain actions. For example, before a chatbot offers a refund, a manager might have to sign off.
How Business Are Using AI Agents: Practical Use Cases
AI agents are transforming business operations across industries. Here are some use cases of AI agents examples, from automating tasks to improving productivity and unlocking new efficiencies:
- Predictive Maintenance: Monitors equipment, predicts breakdowns, and schedules repairs to prevent costly downtime.
- Quality Control: Inspects products for defects on assembly lines using vision-based systems.
- Inventory and Logistics Optimization: Analyzes demand, manages stock, and optimizes delivery routes for smooth supply chains.
- Production Scheduling: Adjusts schedules based on resources, ensuring factories run efficiently.
- Diagnosis and Treatment: Analyzes patient data to help doctors diagnose and recommend treatments.
- Revenue Cycle Management: Automates billing, claims, and payment reconciliation for faster revenue cycles.
- Risk Management: Analyzes data for risk assessments and regulatory compliance.
- Customer Onboarding: AI agents verify identities, handle KYC checks, and simplify account setup.
- Order and Shipping Management: AI agents place orders, track shipments, and update customers for a smooth experience.
- HR Support: It helps HR with policy questions, onboarding, and automating repetitive tasks.
- Employee Productivity: AI agents assist with scheduling, reminders, and communication for better team organization.
- Lead Generation: Builds and qualifies lead lists, sends personalized messages, and analyzes competitor activity.
- Autonomous Vehicles: AI agents power self-driving vehicles, analyzing sensor data to move safely and efficiently.
How AI Agents Can Transform Digital Strategy
What are AI agents for business? It can be a game-changer for transforming digital strategy and growing your business. Here’s how:
- Automate Complex Tasks: AI agents handle data analysis, campaign optimization, and reporting without manual intervention.
- Real-Time Insights: They process large volumes of data quickly, delivering actionable insights as trends emerge.
- Personalize Customer Experiences: AI can customize marketing messages, recommendations, and offers based on individual user behavior.
- Optimize Campaigns: AI agents adjust ad targeting, content, and budgets in real time for better results.
- Competitor Analysis: They track competitors’ moves, pricing, and content strategies, providing a competitive edge.
- Easy Operations: AI automates routine processes in marketing, sales, and customer service, freeing up human teams for strategy and creativity.
- Improve Decision-Making: With data-driven recommendations, businesses can make smarter, faster decisions.
- Drive Innovation: AI agents help identify new opportunities, predict trends, and support product development.
- Support Multi-Channel Strategies: They manage and optimize digital touchpoints across websites, social media, and email.
- Improve Efficiency and Agility: Businesses become more responsive to market changes and customer needs.
The Hidden Challenges and Limitations of AI Agents

AI agents strengthen business workflow, but real challenges like reliability, integration, and costs affect success. Knowing what are AI agents and their challenges helps set realistic expectations for AI-driven transformation.
Reliability and Trust Issues
AI agents can sometimes get things wrong or make up information, which makes it hard for people to trust them. This is especially a problem when important decisions are at stake and users expect accurate, consistent results.
Integration and Human Oversight
Connecting AI agents to existing business systems isn’t always smooth. Data can be stuck in different places, making integration tough. People still need to check the AI’s work, catch mistakes, and provide context that the AI might miss.
Data Quality, Bias, and Knowledge Gaps
AI depends on good data to work well. If the data is bad or biased, the AI’s decisions will be too. AI also struggles to understand insider knowledge that isn’t written down, and hidden biases in training data can lead to unfair outcomes for customers or employees
Cost and Resource Considerations
Using AI isn’t cheap. It requires investment in technology, experts, and ongoing maintenance. There are also extra costs for keeping data secure, following regulations, and making sure the AI stays up to date and useful. This all adds up to a big commitment for any business.
The Future of AI Agents: Multi-Agent Collaboration and Agentic Workflows
The future of AI agents is moving beyond single-purpose automation to multiple agents collaborating, communicating, and managing tasks together. So, what are AI agents getting into in the future?
Multi-Agent Collaboration:
- AI agents work together, sharing data and context to solve complex problems.
- Specialized agents focus on different tasks, communicating and coordinating in real time.
Agentic Workflows:
- Workflows become goal-driven and adaptive, not just scripted or rule-based.
- AI systems can dynamically adjust strategies and actions as business needs change.
Emerging Trends:
- Agents use APIs, direct messaging, and communication languages to interact seamlessly.
- Decision-making and control are distributed across multiple agents through decentralized task management.
What’s Next for Businesses and Technology Leaders:
- Invest in frameworks and platforms that support multi-agent collaboration.
- Prioritize strong data governance and security for agentic systems.
- Bring up human-AI teamwork for optimal results.
- Prepare for faster innovation, deeper insights, and greater operational efficiency.
- Stay ahead by adjusting flexible, adaptive workflows that keep pace with digital transformation.
How to Bring AI Agents in Your Business
So, now you know what are AI agents and how they can help in business growth. Interested in bringing AI agents into your business? But how to create an AI agent?
First, you need to understand the AI technologies and in which sector you want to implement the agent. If you have skills in coding, then you can build your own AI agent through arranging the necessary tech stacks and knowledge.
After building the agent, you need to train the AI agent to be fit for the task it’s built for. Additionally, you also need to train your human agents to adjust to the AI agent so that they can take over or assist the agent to provide the best response.
In case you want to go for developing a custom AI agent, you should rely on professional developers. They’ll handle the tasks of building the agent and integrating it into your business.
Webisoft’s Role in Building AI Agents for Your Business

Partnering with professionals minimizes risk and increases positive outcomes for your business. Here’s how you can get help from Webisoft for AI services:
AI Strategy and Consulting
Webisoft assesses your business needs, identifies the best AI opportunities, and recommends the right agent type, technology stack, and integration approach for your objectives.
Custom AI Model Development
Webisoft designs and builds AI models specifically customized to your business challenges and needs. They also showcase AI agent project examples that highlight how these solutions are applied in real scenarios.
Seamless Integration with Your Systems
Webisoft connects AI agents with your existing business tools, data sources, and workflows.
Advanced AI Capabilities
Webisoft implements agents with contextual understanding and multi-modal input (text, voice, image), enabling features like document search, predictive analytics, and generative AI for richer business insights. These capabilities also enhance personalized AI experiences for end-users, making interactions more natural and engaging.
LLM and RAG Solutions
Webisoft fine-tunes large language models (LLMs) for your industry or use case and builds retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) chatbots for accurate, up-to-date answers.
Continuous Improvement and Maintenance
They monitor agent performance, provide regular updates, and offer ongoing troubleshooting, optimization, and scaling support as your business grows.
Security and Compliance
Webisoft applies strong encryption and privacy controls to protect your data, meets industry regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, and audits and monitors agent actions for transparency and accountability.
Get started with the process of building an AI agent by booking a quote at Webisoft for AI consultancy today!
Build your AI agent by planning with Webisoft through their AI consultancy!
Schedule an AI strategy and consultation – Build a secure & scalable AI agent today!
Conclusion
So, what are AI agents and how do they work? In summary, an AI agent is like a smart system that autonomously performs tasks and makes decisions using artificial intelligence, and different types of agents in AI showcase how these systems vary in design and application.
They reshape, learn, and integrate with various tools and data, offering businesses dynamic, context-aware solutions.
By integrating these advanced facilities, organizations can simplify workflows, increase efficiency, and solve complex challenges with greater speed and accuracy with the help of real-world applications of AI agents.
FAQs
Here are some commonly asked questions regarding what are AI agents by people:
Is ChatGPT an AI agent?
No, ChatGPT is not an AI agent. It’s a powerful language model that generates responses based solely on the prompts it receives. It doesn’t have goals, it doesn’t act on its own, and it doesn’t interact with its environment unless directly instructed.
In contrast, a true AI agent can make decisions, take actions, and pursue objectives without constant user input.
ChatGPT is reactive, not autonomous, which is the core difference between a chatbot like this and an actual AI agent.
Are AI agents the same as employees?
No, AI agents are not employees but rather digital partners that augment human work by automating complex or repetitive tasks. It is more like a very advanced tool. Just like the computer when it was first introduced for the public.
Are AI agents safe to use?
With proper security, privacy controls, and compliance measures, AI agents can be deployed safely across various industries


