Interoperability is key to the growth of blockchain networks. However, most networks today operate independently and cannot exchange information. This is where Polkadot Bridge comes in.
So what is polkadot bridge?
Polkadot Bridge acts as a crucial connector, linking Polkadot with various blockchain networks like Ethereum, Avalanche, Cardano, and Binance Smart Chain. These bridges simplify the transfer of digital assets between these networks, improving interoperability within the blockchain ecosystem.
But there’s more. In this article, we’ll explore Polkadot Bridge, uncovering its role in enabling seamless asset transfers between Polkadot and Ethereum. We’ll also delve into different blockchain bridging methods, provide insights into setting up a Parity Bridge, and discuss practical use cases.
Let’s get started!
Contents
- 1 What are Blockchain Bridges?
- 2 What is Polkadot Bridge?
- 3 What Sorts of Bridges Are Various Networks Creating within the Polkadot Ecosystem?
- 4 Different Methods for Bridging Blockchains
- 5 How to Set Up and Run a Parity Bridge
- 6 Example Use Cases of Polkadot Bridge
- 7 Reach the Best Polkadot Blockchain Development Company Webisoft
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 FAQs
What are Blockchain Bridges?

Blockchain bridges, also known as cross-chain bridges, are tools that link separate blockchain networks, allowing them to exchange assets and information. This solves a significant issue in the blockchain world, the inability of different blockchains to interact with each other.
Through these bridges, assets can be moved and information shared across different blockchains, improving their functionality and usefulness. There are various ways to implement these bridges.
Some depend on intermediaries to oversee transfers, while others use advanced technologies like atomic swaps or smart contracts for secure, direct exchanges.
For example, if you want to move a digital coin from the Solana blockchain to the Ethereum system, the bridge changes the Solana coin into a format that Ethereum recognizes, called an ERC-20 token. This way, assets can move between blockchains
What is Polkadot Bridge?
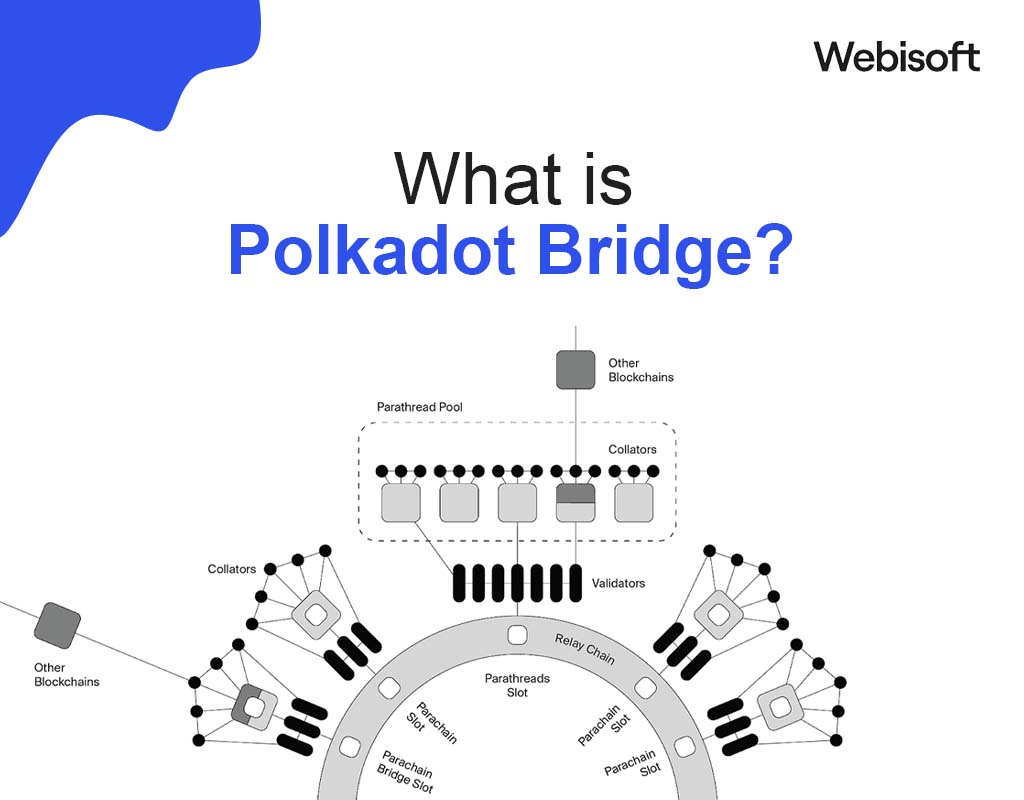
The Polkadot Bridge is a specific type of blockchain bridge within the Polkadot ecosystem, designed to connect Polkadot’s main network (the Relay Chain) with external blockchains, including both public and private networks.
This bridge enables the transfer of data, assets, and smart contract instructions across Polkadot and other blockchains. It facilitates interoperability and communication between the Polkadot network and various blockchain environments.
Polkadot itself is a multi-chain framework that supports cross-chain transfers of any type of data or asset, not just tokens. This capability allows different blockchains to communicate and share information seamlessly.
What Sorts of Bridges Are Various Networks Creating within the Polkadot Ecosystem?

Let’s explore the different blockchain bridges being developed in the Polkadot ecosystem, supported by the Web3 Foundation Grants.
What Sorts of Bridges Are Various Networks Creating within the Polkadot Ecosystem.
| Network Bridge | Supported Networks | Key Features |
| Interlay | Bitcoin, Polkadot | Trustless bridge, minted PolkaBTC backed by Bitcoin (1:1), utilizes XCLAIM protocol. |
| Snowfork | Ethereum, Polkadot | General-purpose bridge, transfers Ethereum, ERC20 assets, supports cross-chain smart contracts. |
| Darwinia | Cross-chain | Noncustodial, permissionless, focuses on efficient cross-chain token transfers. |
| Centrifuge & ChainSafe | Multi-directional | Modular, asset-agnostic, facilitates fungible and non-fungible token transfers. |
| ChainX | Bitcoin, Substrate | Crypto asset exchange platform, bridges Bitcoin to substrate-based chain, PoS consensus. |
| Bitfrost | EOS networks | Trustless bridge, enables cross-chain asset transfers for EOS networks. |
Interlay: A Trustless Link with Bitcoin
Interlay is working on a trustless bridge between Bitcoin and Polkadot. It’s still in the beta test phase, but the promise is fascinating.
They offer users the ability to mint assets on Polkadot, backed by Bitcoin on a one-to-one ratio. These assets, known as PolkaBTC, unlock Bitcoin’s liquidity for Polkadot’s decentralized finance. The XCLAIM protocol ensures that this bridge is trustless, permission-less, and censorship-resistant.
Snowfork: Bridging Ethereum and Polkadot
Snowfork has developed a general-purpose bridge between Ethereum and Polkadot. This bridge is more than just an asset mover; it allows the transfer of Ethereum, ERC20 assets, and arbitrary data over to Polkadot.
In addition, it supports cross-chain smart contract calls, amplifying its utility in the blockchain ecosystem.
Darwinia: The Cross-Chain Bridge Hub
Known as the cross-chain bridge hub, Darwinia has designed a noncustodial and permissionless bridging protocol.
Their protocol focuses on the efficient and cost-effective decentralization of cross-chain tokens, emphasizing cross-chain crypto-asset transfers. Their integration of optimistic verification mechanisms further enhances the protocol’s capabilities.
Centrifuge and ChainSafe: The ChainBridge Collaboration
In a joint effort, Centrifuge and ChainSafe have constructed ChainBridge. This modular, asset-agnostic, multi-directional bridge allows Centrifuge to transfer both fungible and non-fungible tokens between chains.
It’s open-source, inviting other teams to leverage it to build bridges, facilitating a more interconnected project ecosystem.
ChainX: Crypto Asset Exchange and Bridge Building
ChainX, a crypto assets exchange platform, is building bridges to several networks. They’ve already constructed a bridge between Bitcoin and a substrate-based chain. This bridge is uniquely managed by validators staked in ChainX’s PoS consensus, adding an extra layer of security by controlling a Bitcoin multi-sig wallet.
Bitfrost: Trustless Transfers for EOS Networks
Bitfrost has successfully developed a bridge for the EOS networks. This bridge provides trustless cross-chain asset transfers by implementing on-chain light nodes and Merkle tree verification.
Different Methods for Bridging Blockchains

When it comes to blockchain, bridging is where the magic happens. It’s a key feature of the Polkadot platform, letting it play nice with other blockchain networks such as Cardano, XDC, Ethereum, and many more.
But how does Polkadot build these decentralized and trustless bridges? Let’s dig into some of the specifics.
Using Pallets for Bridging
One method involves the use of bridge pallets. They’re used in substrate-based chains to bridge the gap in cross-chain communication.
An example would be the bridge between the Kusama bridge and Polkadot networks, as they’re both parachains and use a substrate.
A substrate pellet can be employed to receive messages on the Polkadot ecosystem from a network that isn’t a parachain. This substrate example can then be rolled out on the Polkadot in the form of a system-level parachain or a parachain operated by a community.
When we’re dealing with independent non-substrate chains, we use bridging contracts to bridge the gap in cross-chain interaction. Here’s how that works.
Using Smart Contracts
In cases where a chain doesn’t use a substrate, we can deploy smart contracts on the non-substrate blockchain to build the bridge. Take the Ethereum mainnet for example. It has a bridging smart contract that triggers ETH transactions based on the Cross-chain Message Passing (XCMP) messages it receives.
Thanks to Turing-complete smart contract languages, Polkadot can be effectively bridged with any other blockchain with smart contract capabilities.
Look at Ethereum’s Parity bridge for instance. It’s made up of two smart contracts, each deployed on their respective blockchains, allowing for the transfer of values between chains.
When ETH is deposited into the contract of the main chain, it creates a balance in the denomination of ERC-20 tokens on the Ethereum sidechain. Conversely, depositing ERC-20 tokens back into the side chain contract can release ETH on the main chain.
Adopting Higher-Order Protocols
When other bridging options are off the table, we can turn to higher-order protocols such as XCLAIM. This requires any asset that can be swapped to be backed by collateral that has a higher value than the swappable assets.
Bitcoin is a great example of a network well-suited for higher-order protocols because it lacks smart contract capabilities and is a non-substrate network.
In addition, there are three specific ways to bridge Polkadot and Substrate chains to the Ethereum chain:
- Substrate EVM Module
- Polkadot<-> Ethereum Public Bridge
- Substrate<->Parity Ethereum (Openethereum) Bridge
Now that we have a handle on the methods for bridging, let’s move on to how to install and run Parity bridges. Stick around for that in the next section!
How to Set Up and Run a Parity Bridge

To build Parity bridges, we use a combination of Substrate pallets, and libraries to create relayers for on-chain communication and run three bridge nodes for testing. Let’s learn how to install and get one of these Parity bridges up and running.
Installation Process
To kick things off, you’ll need both a stable and a nightly Rust. The nightly Rust is crucial for developing the Web Assembly (WASM) runtime for bridge nodes. To get WASM support up and running, punch in these commands:
rustup install nightly
rustup target add wasm32-unknown-unknown –toolchain nightly
With that done, you can build and test the repo with the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/paritytech/parity-bridges-common.git
cd parity-bridges-common
cargo build –all
cargo test –all
You also have the option to create the repo using the Parity CI Docker image. Just use this command:
docker pull paritytech/bridges-ci:production
mkdir ~/cache
chown 1000:1000 ~/cache # processes in the container run as “nonroot” user with UID 1000
docker run –rm -it -w /shellhere/parity-bridges-common
-v /home/$(whoami)/cache/:/cache/
-v “$(pwd)”:/shellhere/parity-bridges-common
-e CARGO_HOME=/cache/cargo/
-e SCCACHE_DIR=/cache/sccache/
-e CARGO_TARGET_DIR=/cache/target/ paritytech/bridges-ci:production cargo build –all
#artifacts can be found in ~/cache/target
Understanding the High-Level Architecture
The Parity bridge repo consists of support for bridging two foreign chains using a mix of Substrate pallets and relayers. In simple terms, a bridge chain follows the consensus of an independent foreign chain.
For instance, let’s imagine we’re bridging two substrate chains, X and Y. The X chain should be capable of receiving Y headers and verifying their integrity.
This is done with a runtime module specifically designed to monitor the GRANDPA block finality. However since the two blockchains can’t communicate directly, they need an external service, known as the relayer, to interact.
The relayer subscribes to the X chain headers with the help of the Remote Procedure Call (RPC) and submits these headers to the Y chain for validation.
Laying Out the Project
The project is organized as follows. It includes nodes (the actual blockchain), modules required to build the blockchain’s runtime and relays that pass on messages between two chains.
├── bin // Node and Runtime for the various Substrate chains
│ └── …
├── deployments // Useful tools for deploying test networks
│ └── …
├── diagrams // Pretty pictures of the project architecture
│ └── …
├── modules // Substrate Runtime Modules (a.k.a Pallets)
│ ├── grandpa // On-Chain GRANDPA Light Client
│ ├── messages // Cross Chain Message Passing
│ ├── dispatch // Target Chain Message Execution
│ └── …
├── primitives // Code shared between modules, runtimes, and relays
│ └── …
├── relays // Application for sending headers and messages between chains
│ └── …
└── scripts // Useful development and maintenance scripts
Getting the Bridge Running
When it comes to connecting the bridge relay node, it’s done with the RPC interface of the nodes on every side of the bridge. You can run bridges in one of two ways:
- Creating and running from the source
- Running a docker-compose setup
Running from the Source
Start by building the nodes and the relay with these commands:
# In parity-bridges-common folder
cargo build -p x-bridge-node
cargo build -p y-bridge-node
cargo build -p substrate-relay
Launching the Dev Network
To show how to relay communication between two substrate chains (X and Y chains), we’ll launch a dev network. For this, we’ll use two nodes, two relayers for relaying the headers, and two more relayers for relaying the messages.
Running from Local Scripts
Begin by firing up the two substrate nodes with these commands:
# In ‘parity-bridges-common’ folder
./deployments/local-scripts/run-x-node.sh
./deployments/local-scripts/run-y-node.sh
Next, run the header relayers:
./deployments/local-scripts/relay-y-to-x.sh
./deployments/local-scripts/relay-x-to-y.sh
This is when you’ll see the relayer giving headers from the Y substrate chain to the X substrate chain. The header relayer logs will look something like this:
# Header Relayer Logs
[y_to_x_Sync] [date] DEBUG bridge Going to submit finality proof of y header #147 to x
[…] [date] INFO bridge Synced 147 of 147 headers
[…] [date] DEBUG bridge Going to submit finality proof of y header #148 to x
[…] [date] INFO bridge Synced 148 of 149 headers
Finally, you need to run the message relayers:
./deployments/local-scripts/relay-messages-y-to-x.sh
./deployments/local-scripts/relay-messages-x-to-y.sh
And there you have it! That’s how you install and run a Parity bridge. Enjoy your cross-chain communications!
Example Use Cases of Polkadot Bridge

As blockchain technology continues to grow, the significance of interoperability is becoming increasingly clear.
At the forefront of this development is the Polkadot cross chain bridge, which aims to connect different blockchain networks to work together seamlessly. One of the key features enabling this interoperability is the Polkadot Ethereum bridge.
Now, let’s explore some real-world applications and example use cases that highlight the power and potential of the Polkadot Bridge.
Bridging Polkadot and Ethereum
Dr. Gavin Wood detailed three potential pathways to connect the Polkadot and Substrate ecosystem with Ethereum in his 2019 speech. So what are these bridges?
- Bridge between Polkadot and Ethereum Public
- Bridge connecting Substrate and Parity Ethereum (now Open Ethereum)
- The Substrate EVM module
All these bridges offer unique ways for these two significant blockchain platforms to interact and work together.
Connecting Bitcoin and Polkadot
Have you ever thought about how cool it would be to transport your Bitcoin assets over to Polkadot?
Well, Interlay has. This team has developed a specification for a Bitcoin bridge built on the XCLAIM framework. This protocol forms a two-way bridge between Bitcoin and Polkadot.
BTC holders can “teleport” their assets to Polkadot, creating PolkaBTC. Those with PolkaBTC can burn it to retrieve BTC on the Bitcoin chain, making it an intriguing process.
The Bitcoin bridge, as per the specification, consists of two distinct components:
- The XCLAIM component – takes care of all accounts holding PolkaBTC.
- The BTC-Relay – checks and confirms the Bitcoin state whenever a new transaction pops up.
Reach the Best Polkadot Blockchain Development Company Webisoft
Webisoft is known as a top-notch cross chain bridge development service provider and there are several good reasons for that:
Expertise in Polkadot Ecosystem
Webisoft has a deep understanding of the Polkadot system. This expertise helps us create and apply solutions in the Polkadot ecosystem, making it easier for decentralized apps (dApps) to work together and grow.
Customized Blockchain Solutions
We offer specialized services for blockchain development that can be customized to fit the specific needs of different businesses. This includes creating smart contracts, building unique dApps, and integrating blockchain into existing systems – all designed to match each client’s particular requirements.
Innovative Approach
Our team is dedicated to staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and innovative strategies. This ensures that the blockchain projects we work on for our clients are not only current but also give them a competitive advantage in their industries.
Proven Success
Webisoft has a strong track record of delivering excellent results. We’ve completed many successful projects and have satisfied clients who can vouch for our ability to provide high-quality and impactful blockchain solutions. This demonstrates our reliability and expertise in the field.
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explored Polkadot Bridge, revealing how it facilitates smooth asset transfers between Polkadot and Ethereum. We’ve also covered various blockchain bridging methods, shared insights on setting up a Parity Bridge, and discussed practical use cases.
Looking ahead, cross-chain interoperability is the future of blockchain technology. As the blockchain ecosystem continues to expand, secure bridges like Polkadot will play a crucial role in enabling communication between different chains and facilitating composability.
Ready to build cross-chain applications? Get in touch with Webisoft today and let us help you maximize the power of Polkadot Bridge and seamlessly integrate cross-chain functionality into your projects.
FAQs
How to do cross chain bridge development?
To develop a cross-chain bridge, you’ll need blockchain development expertise, especially in the blockchain networks you aim to connect. Then, follow these steps: design the bridge logic, create smart contracts, set up validators, and thoroughly test for security and functionality.
How secure are cross-chain transfers facilitated by Polkadot Bridge?
Cross-chain transfers via Polkadot Bridge are designed with security in mind, but users should exercise caution. Ensure you follow best practices and verify the trustworthiness of the bridge you are using to minimize security risks.
Is Polkadot Bridge compatible with all blockchain networks?
Polkadot Bridge is designed to connect with various blockchain networks, but it’s compatibility may vary. Ensure that the specific network you want to connect with supports Polkadot Bridge for seamless asset transfers.
What are some use cases of polkadot?
Polkadot has a wide range of use cases, including facilitating cross-chain communication, enabling interoperable decentralized applications (dApps), and supporting blockchain scalability. It also plays a crucial role in DeFi, NFTs, and governance systems.
