Living in an era where our digital lives cross paths with our physical selves, managing personal identity information has become a matter of great concern. From online shopping to joining new social media platforms, our personal details make endless journeys across the vast digital landscape.
Given this, wouldn’t it be great to have control over our own digital identities? To keep them secure, private, and in our hands? Enter Hyperledger Indy, an innovative technology reshaping the concept of digital identity.
With its decentralized approach, it hands the control back to us, the users. Let’s dive deeper into how this transformative solution is redefining the future of identity management.
Contents
- 1 The Importance of Identity Management
- 2 A Look Back at Identity Management: The Early Days
- 3 Re-thinking Identity Management: A Look at Centralization
- 4 Possible Drawbacks of Centralized Identity Systems
- 5 The Power of Decentralized Identity Management
- 6 Taking Control: Self-Sovereign Identity Management via Hyperledger Indy
- 7 The Role of Indy CLI in Hyperledger Indy Operations
- 8 The Nuts and Bolts: How it All Works
- 9 Ensuring Privacy: Off-Ledger Interactions
- 10 Leveraging Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Verifiable Claims with Hyperledger Indy
- 11 Paving the Way for Interoperability in Identity Across Distributed Ledger Technologies
- 12 Key Components in a Hyperledger Indy-Based Identity Solution
- 13 Recovering Compromised DIDs
- 14 Final Words
The Importance of Identity Management

In our digitally dominated era, we willingly share our personal details for a myriad of activities. Whether it’s for buying the latest gadget, exploring fresh knowledge, executing financial dealings, or engaging on social platforms.
So, it’s undeniable how critical identity management has become.
Rising Concerns in Our Online Society
As our engagement with the digital realm grows, we’re facing a rise in problems such as data theft and loss. In truth, most digital interactions ask us to reveal personal details to use a service.
Unknown Storage
Picture this: each time you share details online, they’re logged in countless, unseen databases across the internet. Often, this identifiable information is shared without our approval, stored in locations unbeknownst to us.
This lack of control can expose us to significant threats should these databases be compromised. The core of the issue lies in the fact that our identities are managed in a centralized manner, leaving us with little to no control.
Blockchain for Identity Management
But what if we told you there was a way to reclaim control over your digital identity? Studies show that blockchain technology could be our savior, eliminating the need for centralized authorities.
Hyperledger’s Indy: A New Hope for Identity Management
Recognizing the need for solutions in this space, Hyperledger introduced a groundbreaking project, Indy. Their aim? To empower individuals with blockchain-based digital identities, giving control back where it belongs – in your hands.
A Look Back at Identity Management: The Early Days

Casting our minds back to the dawn of identity management, we find that a centralized body had the reins of identity data.
The Age of Federal Identity
Federal identities, introduced in this era, allow users to utilize a singular identity for multiple purposes, provided they have the user’s permission. However, this model wasn’t without its flaws.
Given the centralized approach to data storage, these federal identities were anything but transparent to their holders.
The Emergence of User-Centric Identities
After the downfall of the federal identity concept, attention shifted toward user-centric identity. The idea was simple yet powerful: Give identity holders control over their digital identities.
However, this solution too had its pitfalls. User-centric identities were still tethered to a register that could potentially cut off access to a user’s identity without their knowledge or consent.
The Birth of Self-Sovereign Identity
Given the limitations of previous systems, a new solution emerged, called self-sovereign identity. Instead of leaving digital identity to third parties, this system put it back in the hands of owners.
For an identity to be truly self-sovereign, the underpinning infrastructure should veer towards decentralization rather than merely being distributed.
One such platform that exemplifies this decentralized approach is Hyperledger Indy. Designed specifically for decentralized identity, it presents an interesting case study.
Re-thinking Identity Management: A Look at Centralization

Originally, the internet was crafted as a direct connection web, facilitating peer-to-peer interactions without the need for a middleman. But as the landscape changed and the web leaned towards privatization, things took a different turn.
Third-party intermediaries sprouted up, gradually embedding themselves as crucial components of our online infrastructure. These controlling figures could control and monitor online identities, as well as manage access to the world wide web, thanks to a centralized identity system.
It might seem efficient on the surface, but it gives these authorities unfettered access to vast quantities of personal information.
This data is stored on servers that aren’t immune to hacking threats. The congregation of sensitive data in the hands of a few can significantly amplify the risk of future data breaches.
Possible Drawbacks of Centralized Identity Systems
There are several potential issues and challenges you might encounter when relying on a centralized identity management model:
1. Transparency at Stake
Recent years have seen a surge in privacy infringement incidents that put a spotlight on the lack of transparency within these systems. Events like the Cambridge Analytica debacle, DeepMind’s unauthorized sharing of patient data, and the fines imposed on Facebook by Spain and France offer evidence of this concern.
Spain’s Data Protection Authority (AEPD) accused Facebook of bypassing privacy rules for the sake of advertising. Similarly, France’s Commission Nationale de l’Informatique et des Libertés (CNIL) alleged that Facebook failed to disclose the way user data was shared and monitored by advertisers.
In most of these privacy infringement scenarios, the owners of the identity are left in the dark about how and where their personal information is utilized.
A Matter of Control
Another downside is the lack of control you have over your own data. Say you decide to delete your Facebook account. Even then, your data isn’t wholly erased. It’s an alarming situation where, despite the data being yours, you lack the power to fully delete it.
2. The Digital Dilemma: Identity Theft

Did you know that our digital identities are under constant threat? Just imagine – with each day that goes by, the Breach Level Index tells us a whopping 7,125,940 records are snatched up.
Break it down, and you get a staggering 296,914 records stolen every hour, or 4,949 records per minute. This scary rate of data theft is a testament to the ease and speed at which cybercriminals can infiltrate networks and snatch away our information.
The No Global Identity Issue
Let’s think about this – how many times have you had to provide the same set of documents for things like your driver’s license, passport, or PAN card? It’s a repetitive, long-winded process that has us confirming our authenticity over and over.
It’s a hassle for us, and for the verifying entities too. As it stands, we’re lacking a global identity solution, a single ID that can confirm who we are and check our backgrounds completely.
The Heavy Price of Identity Management
Consider this – the identity management process involves several key players. These are the companies doing the verification, the individuals needing verification, and the entities that must authenticate users. Right now, the cost of identity management is sky-high for everyone involved.
Consider the “Know Your Customer” (KYC) companies. They’re swamped with verification requests from a host of organizations, from banks to hospitals to insurance providers and immigration offices.

The sheer demand leads to an overburdened system that requires more resources. These extra costs are then passed down to us in the form of hidden processing fees.
A global survey on KYC challenges tells us that the average annual global spend on KYC alone stands at an eye-watering $48 million. Plus, the study shows it takes a lengthy 26 days on average to onboard a user and a further 20 days to update their records.
So, it’s clear – our current identity management system is a hefty financial burden for every single party involved.
The Power of Decentralized Identity Management
Imagine this scenario: You’re moving to a new country and need to apply for a variety of services like an electricity connection, driver’s license, voting rights, and entertainment packages.

The Challenge of Identity Verification
Each of these services requires you to verify your identity. You’ll have to set up separate accounts with every service provider and keep track of a complex mess of names, credentials, and other logins. Sound familiar?
Unleashing the Potential of Blockchain and Cryptography
Decentralized identity management could be the answer we’re all seeking. It leverages cutting-edge blockchain and cryptography technologies to streamline this complex process.
An Emphasis on Confidentiality and Security
At its heart, this decentralized ecosystem focuses on maintaining confidentiality. It uses cryptographic solutions to manage passwords and keys, boosting security and privacy for the identity owner.
But the benefits don’t stop there – it also simplifies the authentication process for those entities doing the verifying.
Trust in Immutability
Thanks to the immutable nature of records stored on a distributed ledger, it’s virtually impossible for hackers or unauthorized entities to tamper with or steal personal information.
Control Rests with the Identity Owner
The best part? Each authorized entity needs the identity owner’s consent to access their personally identifiable information (PII).
And with PII not centrally stored and every node on the blockchain-based identity platform holding a copy of the ledger, there’s no single point of failure.
The Self-Sovereign Identity Model
All this makes it clear that a self-sovereign identity based on a decentralized model can offer strong privacy protection. But how does this all fit into the bigger picture?
Let’s dive deeper into how Hyperledger Indy can empower users with a unique and robust identity management solution. Stay tuned!
Taking Control: Self-Sovereign Identity Management via Hyperledger Indy
With Hyperledger Indy at your disposal, you’re armed with the power to construct a resilient, scalable, and highly secure solution for self-sovereign identity management. What’s more, Hyperledger facilitates the storage of identities in a location that’s accessible for edits or removals.
Upon specifying a location for identities, the Hyperledger Indy platform grants it a name that’s recognizable on a global scale. Want to access the identity data? No problem. Indy is your guide, pointing you straight to the data storage details.
Let’s dive a little deeper and discuss the roles of the key players in a self-sovereign identity management solution:
Identity Provisioning
Unlike other models, self-sovereign identity management doesn’t center around a singular identity provider. Instead, there exists a well-structured standard for creating, revoking, and sharing identities—all while respecting the owner’s consent.
The Owners of Identity
Owners in this system are equipped with unique identities, verified via their distinct public/private key pairs. This identity structure of Hyperledger leans on a distributed ledger, governed by the central actors in identity management.
Validating Identity
Here’s where it gets interesting: Identity validators aren’t centralized authorities. They’re trusted individual parties with the ability to affirm identities using their private keys.
For outside parties, identity verification is possible using the public keys of these validators.
The Users of Identity
These are the individuals who harness the distributed ledger of identities. They extract identities and independently confirm their authenticity.
The Role of Indy CLI in Hyperledger Indy Operations
Let’s take a moment to unpack something pretty essential – Indy CLI. Now, you might be wondering, “What’s the big deal with this?” Well, in the context of Hyperledger Indy, it’s a really crucial piece of the puzzle.
Indy CLI is your command-line tool, your interface, if you will, for interacting directly with the Hyperledger Indy. It’s like your personal remote control that allows you to navigate the Indy environment with ease.
With it, you can manage decentralized identities, handle transactions, or even play around with various components of the Indy ecosystem.
In a nutshell, the Indy CLI makes your life a whole lot simpler when it comes to operating within the Hyperledger Indy framework. Isn’t that handy?
The Nuts and Bolts: How it All Works
Let’s get into the nitty-gritty of how the Hyperledger indy process unfolds —
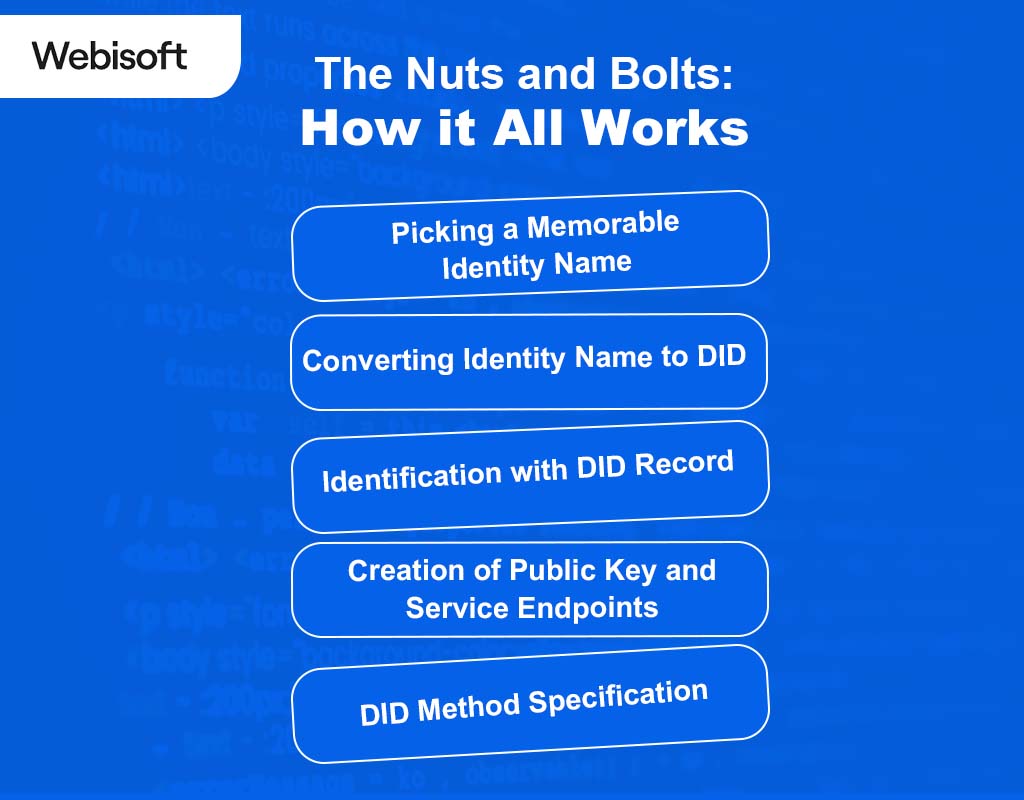
1. Picking a Memorable Identity Name
First off, users get to choose a name for their identity that’s easy to remember.
2. Converting Identity Name to DID
This name is then transformed into a unique key known as a “DID” (short for Decentralized Identifiers) on the ledger. The details linked to this key are referred to as DDO (DID Descriptor Objects). When you put a DID and DDO together, you get a DID record.
3. Identification with DID Record
Using this DID record, users can be identified on the distributed ledger. To ensure top-level security, the private keys of an identity owner cryptographically safeguard each DID record.
4. Creation of Public Key and Service Endpoints
Next, a public key that corresponds to the key pair is generated in the DDO, complete with a key description. The DDO also includes a range of service endpoints for interaction with the identity holder.
5. DID Method Specification
Finally, each DID come with a DID method specification. This essentially lays out the rules for how a DID is registered, updated, resolved, and revoked on a specific ledger or network.
Ensuring Privacy: Off-Ledger Interactions
Now, keep in mind that while our ledger is public, we absolutely don’t want any personally identifiable information (PII) hanging out there for all to see.
To make sure we keep our privacy intact, only the following items are stored on the public ledger —
Item 1: DIDs
These are your Decentralized Identifiers, and they’re unique for every pair.
Item 2: Public Keys
These handy keys make it possible for encrypted interactions to take place with the identity owner.
Item 3: Service Endpoints
These facilitate communication with the identity owner via an associated agent.
Item 4: Proofs
Think of these as zero-knowledge proofs or hashed artifacts. They enable identity owners, validators, and other parties to verify the validity period of certain information, without revealing the specifics of that information.
Leveraging Zero-Knowledge Proofs and Verifiable Claims with Hyperledger Indy
Hyperledger Indy steps up with intrinsic support for Zero-knowledge proofs, adding an extra layer of protection against unwarranted exposure of identity attributes.
A verifiable claim comes into play when dependent parties need to validate the information of identity holders. These claims can be filed against distinctive DID pairs recorded on the ledger, endorsed with the issuer’s private key, and authenticated with the issuer’s public keys.
Off-ledger agents are equipped to handle claim exchanges and verification, using service endpoints identified in the DDO.
But what happens when verifiable claims don’t meet the truth test? Indy has an answer: Zero-knowledge proofs.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs: The Invisible Shield
Zero-knowledge proofs empower identity owners to verify the ownership of a credential without revealing the credential itself, courtesy of anon cred (short for anonymous credentials).
Consider the case of a candidate sharing their college education details (claims) with a potential employer. Here’s how the process might unfold:
Setting the Stage
The authority in charge of education certificates lays the groundwork by creating public keys, claim schema, and a cancellation registry entry on the ledger.
Claim Issuance
The authority presents the candidate with a verifiable claim, affirming successful completion of graduation through DID A.
The Proof
The candidate offers proof of a subset of his claim—only the information he selects—to the organization where he’s seeking employment via DID B. This proof also attests that his claim hasn’t been revoked by the identity validator.
Verification
The organization is then able to ascertain the authenticity of the candidate’s educational certificates, all without having to contact the identity validator.
Paving the Way for Interoperability in Identity Across Distributed Ledger Technologies
In today’s digital age, it’s common for individuals to juggle multiple accounts across various social media platforms—Google, Facebook, Twitter, and the list goes on. It implies having a host of different credentials just to gain access to each of these accounts.
It’s not unusual for the same user attributes to pop up across different identity providers. The result? A not-so-seamless process when it comes to managing these identity attributes.
Some services may require gathering identity information from diverse sources. Say, your date of birth from one account, contact number from another, and so on. At present, users must cherry-pick attributes from a range of identity providers to unlock many digital services.
Clearly, what’s needed is a secure, interoperable, private, and universally accessible protocol for identities.
Here’s a look at the tools that were devised to ensure interoperability in identities across distributed ledger technologies —
DIDs: Decentralized Identifiers
These unique identifiers can work across different systems without the need for a centralized authority. With the ability to link to service endpoints and public keys, and given their pairwise pseudonymous nature, DIDs can thwart correlation while upholding privacy.
Picture it this way: Individuals can have hundreds, or even thousands, of DIDs, each symbolizing diverse digital relationships.
We live in an era where user-controlled, secure digital identities are imperative. Meet Webisoft – a team that’s not only familiar with this critical concept but also champions it. Our goal is to create safer, more secure digital experiences by using Hyperledger Indy’s power.
DDOs: Making Connections
Think of DDOs as JSON objects that lay bare the service endpoints and public keys needed to interact with the entity pinpointed by the DID.
Verifiable Claims: Proof in the Pudding
These are interoperable and standardized, and when paired with zero-knowledge proofs, they allow for minimal disclosure while ensuring authenticity.
Key Components in a Hyperledger Indy-Based Identity Solution
Let’s delve into the integral components that come into play when crafting an identity solution on top of the Hyperledger Indy Platform.
1. Cryptography
First up is the role of cryptography. Hyperledger Indy relies on zero-knowledge cryptography. It’s a cool concept where one party can demonstrate to another that they know the value of ‘X’, without giving away any additional information beyond the fact they know ‘X’.
2. The Role of Nodes
Nodes are another key component in this Hyperledger. They can be sorted into simple nodes, master nodes, and full nodes. In layman’s terms, a node is just a computer carrying out transactions on the blockchain network.
When we talk about a ‘full node’, we’re referring to a client that maintains a complete copy of the blockchain on the network. Master nodes, on the other hand, enable decentralized governance.
To achieve consensus in the Hyperledger Indy-based identity solution, these nodes use a mechanism known as Redundant Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
3. Redundant Byzantine Fault Tolerance (RBFT)
RBFT is basically an upgraded version of Plenum Byzantine Fault Tolerance. It works by running multiple instances of a BFT protocol in parallel, where each instance has a primary replica.
All protocol instances order requests, but only the master instance executes them in an efficient manner.
4. The Ledger
At the heart of Hyperledger, all is the ledger. Supported by a Merkle tree, it’s replicated across all the nodes in the network.
5. State and Storage
The state in Hyperledger Indy is managed in a similar way to Ethereum, using Patricia Trie. This is a blend of Merkle Trie and Radix Trie, used for data storage.
Each node’s storage is implemented using leveldb, a key/value database that offers an ordered mapping from string keys to string values. In this setup, DIDs are stored as state variables, each with its own value.
Recovering Compromised DIDs
Let’s say, in a worst-case scenario, your identity is lost or stolen. You’d like to know that you can reclaim it, right? Well, good news! You can do exactly that by reaching out to an identity provider with proof of your identity.
Since all the data is stored on a distributed ledger, your decentralized identity can be reissued.
Identity validators can spring into action and re-validate your identity using the biometric data stored on the ledger. You, as the identity owner, get verified, and voila! Your lost decentralized identity is recovered.
Why Choose Hyperledger Indy?
You might be thinking, “Okay, I get that a decentralized identity management solution can be built using various blockchain platforms, but why should I choose Hyperledger Indy?”
Let us explain some of the standout features that make it an excellent choice:
Feature 1: User-Controlled Exchange of Verifiable Claims
Even though the Hyperledger Indy public network is open to everyone, the only one who can permit an identity to be validated is the identity holder. That’s you!
Feature 2: Accessible Provenance for Trusted Transactions
Indy is a universal platform that enables the exchange of trusted claims, providing reliable provenance.
Feature 3: Privacy on the Public Ledger
One unique and crucial aspect of Indy’s architecture is its focus on “Privacy by Design.” Privacy isn’t an afterthought; it’s built right into the design from the start.
Final Words
Throughout this discussion, we’ve navigated the world of digital identity, a world where control, privacy, and security take center stage. We’ve seen how Hyperledger Indy is revolutionizing this space with its decentralized model. Thus allowing us to dictate how and where our personal information is used.
From understanding its innovative approach to the recovery of compromised identities and privacy by design, it’s clear that Hyperledger Indy isn’t just a platform—it’s a promise.
A promise to usher in a new era of identity management, where the power rests where it should – in our hands.Ready to take control of your digital identity with a solution that prioritizes security and user control? It’s time to connect with Webisoft for developer hire. We offer robust, user-centric identity management solutions powered by Hyperledger Indy. Don’t let your data float aimlessly in the digital sphere.
