Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and Chainlink have emerged as significant digital game-changers. This article delves into the concept of Chainlink NFTs, their creation process, and potential applications.
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, are unique digital objects on a blockchain. Each NFT is distinguishable from another through a unique token ID and contact address.
Metadata such as images, videos, or other data can be attached to these tokens, representing unique digital objects. On the other hand, Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that provides real-world data to smart contracts on the blockchain.
It bridges off-chain and on-chain data, enabling smart contracts to interact with data outside their network. Chainlink NFTs have a wide range of potential use cases.
For instance, in blockchain games, when a player levels up, the metadata in the NFT can change to reflect the character’s growth. Similarly, NFTs can update their metadata when tokenizing real-world assets to reflect asset status changes.
This article explores the concept of Chainlink NFTs, their creation, and their potential applications.
Contents
What Are NFTs?

Non-Fungible Tokens, or NFTs, are unique digital assets on a blockchain. Each NFT is distinct, representing a specific item or content that cannot be interchanged with another.
This uniqueness sets NFTs apart from cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, where each token is identical to the next. NFTs are secured on the blockchain, a digital ledger that records transactions across numerous computers.
This ensures the authenticity and ownership of these digital assets. NFTs can represent various unique items or content, including digital artwork, music, and even real estate.
NFTs are a revolutionary concept in the digital world. It provides a way to prove ownership of digital assets. This is a significant shift from the traditional internet, where duplicating digital content is usually straightforward. With NFTs, digital content can have a verified owner, much like a physical object in the real world.
The uniqueness of NFTs is derived from the information stored in them. Each NFT contains metadata about the asset, such as the creator, owner, and ownership history. This metadata is what makes each NFT unique and non-fungible.
NFTs have generated new possibilities for digital artists and creators. They offer a new way to sell digital artwork and other unique digital content directly to consumers. It has the potential to disrupt traditional models of content distribution and ownership.
However, the use of NFTs is not without controversy. Some critics argue that NFTs contribute to commodifying digital culture and the environment due to the energy-intensive process of minting NFTs on the blockchain.
Despite these concerns, the popularity of NFTs continues to grow, with many seeing them as the future of digital content ownership and distribution. NFTs are unique digital assets that represent ownership of unique items or content.
They are secured on the blockchain, ensuring their authenticity and ownership. While they have opened up new possibilities for digital artists and creators, they have also sparked controversy and debate.
What is the Use of NFTs?
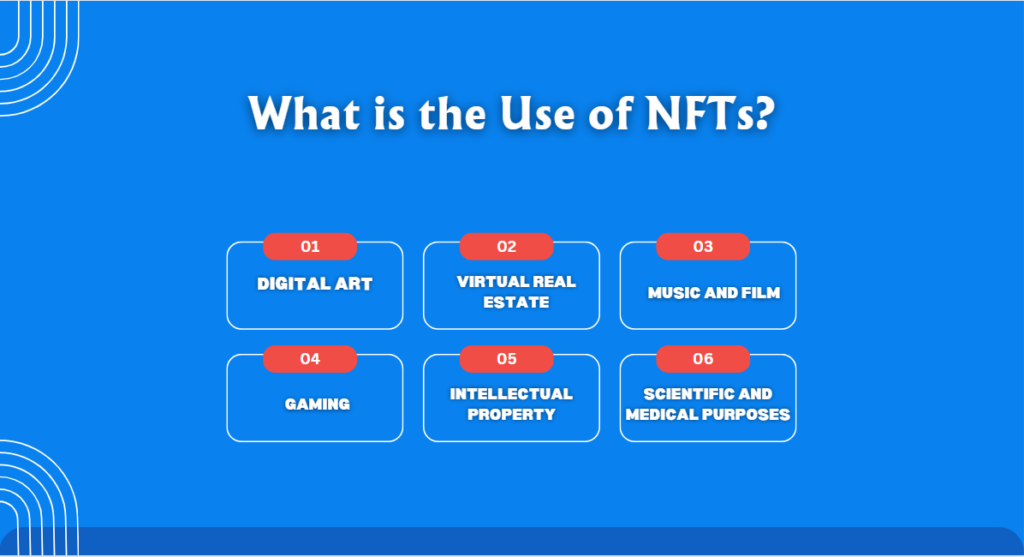
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, have many uses beyond digital collectibles. These unique digital assets, secured on the blockchain, have the potential to revolutionize various industries.
1. Digital Art
One of the most prominent uses of NFTs is in digital art. Artists can mint their artwork as NFTs, providing blockchain-backed proof of ownership.
This not only allows artists to sell their work directly to consumers without the need for intermediaries, but it also ensures the authenticity and uniqueness of the artwork.
High-profile auctions of NFTs linked to digital art have received considerable public attention, with some pieces selling for millions of dollars.
2. Virtual Real Estate
NFTs are also making waves in the virtual real estate market. Platforms like Decentraland allow users to buy, sell, and trade parcels of virtual land as NFTs.
This virtual land can then be developed and monetized, much like real-world real estate.
3. Music and Film
The music and film industries are also exploring using NFTs. Musicians can tokenize their music and sell it directly to fans as NFTs, providing a new revenue stream that bypasses traditional music distribution platforms.
Similarly, filmmakers can tokenize movie scenes and sell them as collectibles.
4. Gaming
In the gaming industry, NFTs can represent in-game assets, such as weapons, outfits, or characters.
These assets and properties can be bought, sold, or traded on the blockchain, giving gamers ownership and control over their in-game items.
5. Intellectual Property
NFTs can use to represent intellectual property rights ownership. This could revolutionize how intellectual property is managed and monetized, providing creators with greater control and transparency.
6. Scientific and Medical Purposes
NFTs have been proposed for scientific and medical purposes. Suggestions include turning patient data into NFTs, tracking supply chains, and minting patents as NFTs.
In conclusion, the uses of NFTs are vast and varied. We expect to see even more innovative applications of these unique digital assets as technology evolves.
However, it’s important to note that the NFT market is still in its early stages and comes with challenges and risks, including copyright enforcement, market volatility, and environmental impact.
What are Chainlink Oracles?
Chainlink oracles serve as a bridge between the blockchain and the real world. They are a crucial component of the Chainlink network, a decentralized oracle network that securely connects smart contracts to real-world data, events, and payments.
Smart contracts, while powerful, are limited in their functionality due to their inability to interact with data outside the blockchain. This is where Chainlink oracles come in.
They provide a secure and reliable way for smart contracts to interact with external data. This enables smart contracts to function in a way that’s responsive to real-world events and conditions.
Chainlink oracles fetch data from various external sources, validate it, and then relay it to the smart contract on the blockchain. This process is decentralized, meaning multiple independent oracles provide data.
This decentralization ensures the reliability and accuracy of the data, as it reduces the risk of a single point of failure. Chainlink oracles can connect to any API, allowing smart contracts to interact with a wide range of real-world data.
This includes everything from price feeds and weather data to IoT sensor data. This flexibility is one of the key strengths of Chainlink oracles. Furthermore, Chainlink oracles are not limited to fetching data.
They can also send data, enabling smart contracts to trigger real-world events. For example, a smart contract could use a Chainlink oracle to send a payment via a traditional payment system once certain conditions are met.
In conclusion, Chainlink oracles are a powerful tool that extends the capabilities of smart contracts. Securely connecting smart contracts to real-world data creates more complex and valuable decentralized applications.
As the blockchain space continues to evolve, the role of Chainlink oracles will likely become increasingly important.
What are Dynamic NFTs?
Dynamic NFTs, or dNFTs, are revolutionizing the digital asset landscape. Unlike static NFTs, these tokens can adapt and evolve in response to external data or events.
This unique characteristic is made possible by Chainlink oracles, which provide the necessary real-world data or trigger the events that the NFT responds to.
A dynamic NFT is essentially an NFT that can change based on external conditions. This change often refers to alterations in the NFT’s metadata triggered by a smart contract.
The smart contract encodes automatic changes, instructing the underlying NFT about when and how its metadata should change. For instance, consider a dynamic NFT representing a digital artwork.
This artwork could change based on the weather, time of day, or even the artist’s mood. The possibilities are endless, limited only by the imagination and creativity of the NFT creator.
The potential use cases for dynamic NFTs are vast. Generative NFT art projects often have some traits. These traits are kept within an NFT. These metadata, alongside an IPFS, link to an image or video corresponding to the NFT’s traits.
In a dynamic NFT, these traits can change based on external conditions. This functionality can be handy for character progression in blockchain games. When a player starts a game with a playable NFT character, the NFT has base stats reflected in its metadata. As the player levels up, the metadata in the NFT changes to reflect the character’s growth.
Another case where metadata changes are helpful is in the tokenization of real-world assets, where many changing metrics are often required.
For example, an NFT representing a property could reflect its maintenance history, age, market value, and more. They are tokenizing these changing assets. Therefore, it requires NFTs that can update with changing metadata.
How to Create Dynamic NFTs using Chainlink Oracle?
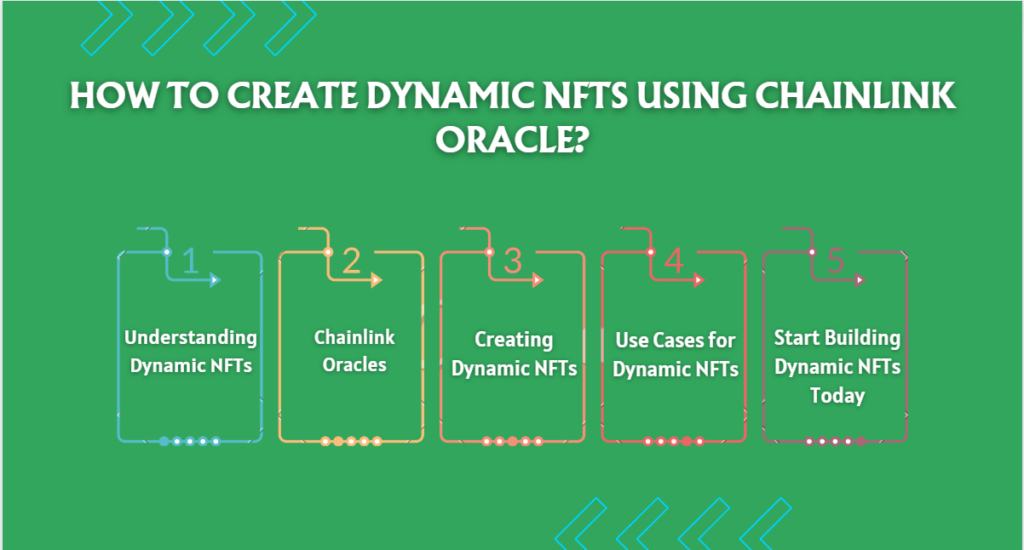
Creating dynamic NFTs using Chainlink Oracle involves steps that leverage the power of Chainlink’s decentralized Oracle network.
This process is designed to securely and reliably connect your NFTs to external data and systems. Here’s a detailed guide on how to create dynamic NFTs using Chainlink Oracle:
1. Understanding Dynamic NFTs
Dynamic NFTs are a step beyond traditional NFTs. They are perpetual smart contracts. It uses oracles to communicate with and react to external data and systems.
This allows the NFT to use external data/systems for minting/burning NFTs, trading peer-to-peer, and checking state.
2. Chainlink Oracles: The Key to Dynamic NFTs
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network. It reliably and securely connects smart contracts to external data and systems.
Using different independent oracles to verify data and aggregate data from multiple sources. Chainlink’s Oracle framework enables customers to source and deliver data to their smart contracts.
3. Creating Dynamic NFTs: A Simple Framework
Creating dynamic NFTs involves using Chainlink oracles to connect your NFT to external data sources. This could include IoT data, web APIs, or other data providers. Chainlink’s Oracle makes it possible to create dynamic NFTs that react to real-world data.
4. Use Cases for Dynamic NFTs
Dynamic NFTs have many use cases. They can be used in multiplayer online games to mint rare in-game items as NFTs. The ownership of NFT allows special privileges within the game.
Chainlink oracles can transfer ownership, use data to create NFTs, t and settle competition outcomes by assigning value to the assets.
5. Start Building Dynamic NFTs Today
Suppose you are a blockchain project looking to support NFTs, a Dapp looking to upgrade to dynamic NFTs. or a startup/enterprise looking to branch into this exciting new market.
In that case, you can start building dynamic NFTs today using Chainlink’s robust Oracle network.
Creating dynamic NFTs using Chainlink Oracle is a process that requires a good understanding of how Chainlink oracles work and how they can be used to connect your NFTs to external data sources.
Use Cases of Dynamic NFTs
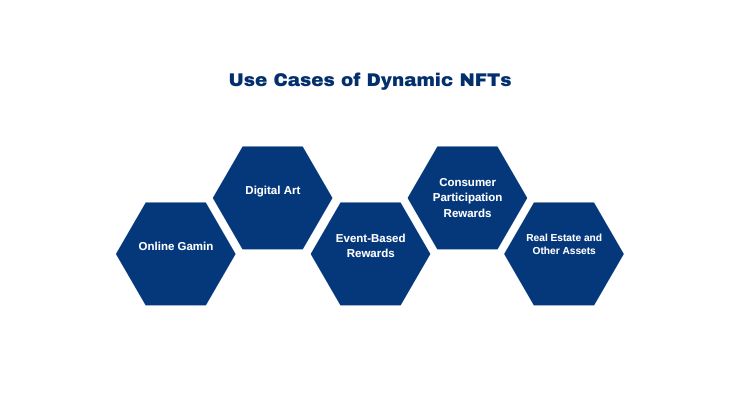
Dynamic NFTs have different potential use cases. Here are some of the most promising applications:
1. Online Gaming
In online gaming, dynamic NFTs can represent in-game items that change based on players’ actions or real-world events.
For instance, a weapon in a game could become more powerful as a player achieves higher levels, or a character’s appearance could change based on real-world weather data. This adds a new level of interactivity and immersion to games.
2. Digital Art
In the art world, dynamic NFTs can represent digital artworks that change over time or in response to external data.
An artist could create a piece that evolves with time or changes in response to social media trends, stock market fluctuations, or other real-world data. This opens up different new possibilities for artistic expression and audience engagement.
3. Event-Based Rewards
Dynamic NFTs could also be used to create event-based rewards. For example, a music festival could issue NFT tickets that change based on the performances a ticket holder attends, creating a unique digital memento of the event.
Similarly, a sports team could issue NFTs that change based on the outcome of games, creating a dynamic digital collectible for fans.
4. Consumer Participation Rewards
Businesses could use dynamic NFTs to reward consumer participation. For example, a coffee shop could issue an NFT loyalty card that changes based on the number of purchases a customer makes.
As the customer reaches certain milestones, the NFT could evolve, perhaps even unlocking special rewards or privileges.
5. Real Estate and Other Assets
Dynamic NFTs could also be used to represent ownership of real-world assets like real estate. These NFTs could change based on factors like property value fluctuations, renovations, or changes in ownership.
This would provide a dynamic digital asset representation that reflects its current status and history.
In conclusion, dynamic NFTs have the potential to revolutionize a wide range of sectors by providing a new form of digital asset that can interact with real-world data and evolve.
NFT Services Offered by Webisoft
Webisoft stands at the forefront of the NFT revolution, offering a comprehensive suite of services. These services serve different needs in the NFT space.
1. NFT Creation Webisoft excels in the creation of NFTs. They assist in transforming digital assets into unique, blockchain-secured NFTs. Whether it’s digital art, music, or virtual real estate, Webisoft can help tokenize it.
2. Marketplace Development Webisoft also specializes in the development of NFT marketplaces. These platforms facilitate the buying, selling, and trading of NFTs. Webisoft ensures these marketplaces are secure, user-friendly, and efficient.
3. NFT for Gaming The gaming industry is ripe for NFT integration. Webisoft helps game developers incorporate NFTs into their platforms. This could mean tokenizing in-game items or creating game mechanics based on NFT ownership.
4. Custom NFT Solutions Every client has unique needs. Webisoft understands this and offers custom NFT solutions. They work closely with clients to understand their requirements and deliver tailored NFT services.
5. NFT Consultation Navigating the world of NFTs can be complex. Webisoft offers consultation services to guide businesses and individuals. Their experts can advise on NFT strategy, legal considerations, and more.
Webisoft’s expertise in blockchain technology and digital assets makes it a reliable NFT partner. Whether you’re an artist looking to tokenize your work, a business exploring NFTs for customer engagement, or a game developer wanting to integrate NFTs, Webisoft has the services to assist you. Their commitment to quality, security, and customer satisfaction makes them a top choice for NFT services.
Final Note
Chainlink NFTs represent an exciting development in the world of digital assets. Connecting NFTs to real-world data opens up a world of possibilities for digital assets that can change and evolve over time.
Whether in gaming, art, or any other field, the potential applications of Chainlink NFTs are vast and exciting.

