Blockchain manufacturing is emerging as a game-changer in an era where transparency, efficiency, and traceability are paramount.
By leveraging blockchain technology’s decentralized and immutable nature, the manufacturing industry is witnessing a huge shift in how it operates and delivers value.
Enter the era of blockchain manufacturing. Technology transcends traditional boundaries. Decentralized ledgers replace siloed information. Immutable records ensure trust. Transparency is no longer a dream.
Traceability becomes a tangible reality. Efficiency gains momentum. Collaboration finds new meaning. Manufacturers embrace blockchain’s potential. Supply chains transform. Processes become streamlined.
Stakeholders connect on common platforms. Information flows without barriers—trust rebuilds. Quality assurance strengthens. Costs reduce. Delivery timelines shorten. Customer satisfaction grows.
This article discusses the intricate workings of blockchain manufacturing, unravelling its components, processes, and the profound impact it has on the supply chain.
Contents
- 1 Blockchain Manufacturing: How It Can Shape the Industry?
- 2 How Does the Manufacturing Industry Work Today?
- 2.1 Lack of Transparency: A Persistent Challenge
- 2.2 Quality Assurance: A Daunting Task
- 2.3 Delayed Processes: The Time Trap
- 2.4 Raw Material Procurement: The Beginning
- 2.5 Design and Development: The Creative Phase
- 2.6 Production: Where Magic Happens
- 2.7 Quality Control: The Gatekeeper
- 2.8 Logistics: The Journey to the Customer
- 2.9 Sales and Marketing: The Customer Connection
- 2.10 After-Sales Service: The Continuing Relationship
- 2.11 Technology Integration: The Future Beckons
- 2.12 Sustainability: A Responsibility to Embrace
- 2.13 Globalization: A World of Opportunities and Challenges
- 3 Blockchain – Reinventing the Manufacturing Supply Chain
- 3.1 Stakeholders Involved in the Blockchain System
- 3.2 Step 1: The merchant places the manufacturing order
- 3.3 Step 2: The manufacturing company receives the order
- 3.4 Step 3: The suppliers receive the order
- 3.5 Step 4: Logistic service provider adds parcel details to the blockchain
- 3.6 Step 5: Order received by the manufacturer
- 3.7 Step 6: The merchant receives the order
- 4 Blockchain: A Transformative Technology
- 5 What Are the Challenges and Solutions of the Million-Dollar Manufacturing Industry?
- 5.1 1. Challenge: Lack of Transparency
- 5.2 2. Challenge: Quality Assurance Issues
- 5.3 3. Challenge: Inefficient Processes
- 5.4 4. Challenge: Supply Chain Complexity
- 5.5 5. Challenge: Sustainability Concerns
- 5.6 6. Challenge: Globalization and Regulatory Compliance
- 5.7 7. Challenge: Customer Expectations and Satisfaction
- 6 Final Thoughts
Blockchain Manufacturing: How It Can Shape the Industry?
Manufacturing complexity grows with global markets. Stakeholders demand transparency. Technologies evolve, but challenges remain. E-commerce’s rise amplifies the need for traceable supply chains.
Blockchain in manufacturing companies emerges as a solution. A promise to redefine blockchain solutions for manufacturing awaits. Globalization fuels manufacturing’s intricate web. Processes intertwine, creating a maze. Stakeholders struggle to navigate.
Traditional methods falter. Transparency has become a rare commodity. Traceability turns into a Herculean task. E-commerce adds another layer of complexity. The solution seems elusive.
So, what is blockchain? Blockchain is key. Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger. Alterations become impossible. Fraud diminishes. Transparency reigns supreme. Stakeholders gain real-time insights.
Decision-making accelerates. Efficiency reaches new heights. Suppliers find solace in the blockchain. Raw material tracking simplifies.
Quality verification becomes effortless. Procurement aligns with demand. Waste minimizes. Sustainability goals align. Profits increase.
Logistics companies see transformation too. Shipment tracking evolves. Real-time updates become standard. Lost parcels become history. Customer trust strengthens. Revenues grow.
Quality assurance teams benefit as well. Product inspections streamline. Standards compliance verifies easily. Quality becomes consistent. Customer expectations meet. Brand reputation enhances.
Merchants or purchasing companies gain control. Order placements become transparent. Manufacturing aligns with demand. Deliveries become predictable. Customer satisfaction soars. Business thrives.
E-commerce finds a reliable ally in blockchain in traceability. Product origin verifies. Fake products eliminate. Customer trust builds—sales increase. Returns reduce. Profit margins expand.
Challenges persist, but solutions emerge. Smart contracts in manufacturing are not a panacea. Implementation requires careful planning. Collaboration with technology experts is essential. Alignment with business goals is crucial. Risks exist, but mitigation strategies work.
How Does the Manufacturing Industry Work Today?
Manufacturing stands as a pillar of modern economies. Complexity defines its nature. Multiple parties engage in a dance of creation. Interconnected steps form a delicate ballet. Raw materials transform into products.
Each stage demands precision. Coordination and trust become essential—flaws mar this intricate system.
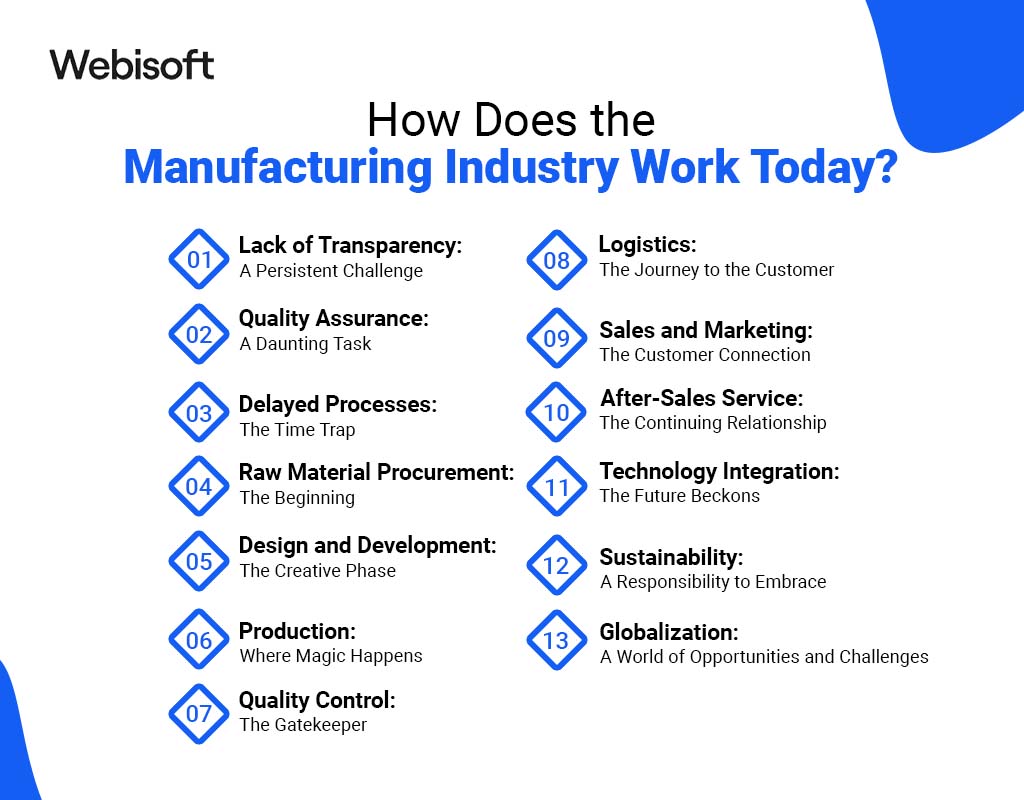
Lack of Transparency: A Persistent Challenge
Transparency remains elusive in traditional manufacturing. Information hides in isolated silos. Stakeholders struggle to access vital data. Mistrust brews. Inefficiencies multiply.
Collaboration suffers—innovation stalls. Growth becomes stunted. A solution seems distant. Yet, hope glimmers in emerging technologies.
Quality Assurance: A Daunting Task
Quality assurance presents another hurdle. Products traverse multiple stages. Ensuring consistent quality proves cumbersome. Standards vary.
Compliance becomes a maze. Inspections slow down processes. Errors slip through. Customers receive subpar products. Reputations tarnish. Trust erodes. The quest for quality turns into a battle.
Delayed Processes: The Time Trap
Time is of the essence in manufacturing. Manual processes dominate the landscape. Delays become the norm. Costs soar. Deadlines miss.
Customers grow impatient. Competitors gain an edge. Efficiency dwindles. Profits shrink. The industry cries for innovation. A revolution in process management is overdue.
Raw Material Procurement: The Beginning
Manufacturing starts with raw materials. Procurement demands careful planning. Suppliers must align with demand. Quality checks are vital. Costs need optimization.
Sustainability calls for attention—delays in procurement ripple through the system. Production schedules falter. The entire chain feels the impact. A seamless start is crucial.
Design and Development: The Creative Phase
Next comes design and development. Creativity meets technology—engineers craft blueprints. Designers envision aesthetics. Prototypes come to life. Testing ensures functionality. Revisions refine the product.
Collaboration between teams is key. Time management becomes essential. Innovation thrives or dies here.
Production: Where Magic Happens
Production is the heart of manufacturing. Machines roar to life. Raw materials transform—assembly lines buzz with activity. Workers wield tools with skill.
Quality checks intervene. Efficiency is paramount. Waste minimization is vital. Coordination between stages ensures flow. A single hiccup can disrupt everything.
Quality Control: The Gatekeeper
Quality control stands as a gatekeeper. Rigorous inspections take place. Standards guide the process. Compliance is non-negotiable. Errors get detected. Corrections happen.
Rejections protect the brand. Customer satisfaction becomes the goal. Quality control is not just a stage; it’s a commitment.
Logistics: The Journey to the Customer
Logistics orchestrates the product’s journey. Warehouses store the goods. Transportation plans unfold. Routes optimize. Shipments track in real-time.
Delays get managed. Customers await their products. Logistics is not just delivery; it’s a promise kept.
Sales and Marketing: The Customer Connection
Sales and marketing build customer connections. Products find their audience. Marketing campaigns ignite interest—sales teams close deals. Customer feedback loops back.
Improvements happen. Relationships grow. Loyalty builds. The cycle continues. Manufacturing is not just about products; it’s about people.
After-Sales Service: The Continuing Relationship
After-sales service extends the relationship. Customers seek support. Repairs happen. Replacements fulfil promises.
Feedback guides future improvements. Loyalty strengthens. Trust deepens. The manufacturing journey does not end with a sale; it evolves.
Technology Integration: The Future Beckons
Technology integration points to the future. Automation promises efficiency. Artificial intelligence guides decisions. Data analytics offers insights. Collaboration tools connect teams. Innovation accelerates. Costs reduce.
Quality improves. Delivery speeds up. Customer satisfaction reaches new heights. The future of manufacturing is not a destination; it’s a journey.
Sustainability: A Responsibility to Embrace
Sustainability is a growing concern. Materials must be sourced responsibly. Waste must be minimized. Energy efficiency is vital. Emissions need reduction.
Compliance with regulations is mandatory. Social responsibility guides actions. Sustainability is not just a trend; it’s a duty.
Globalization: A World of Opportunities and Challenges
Globalization opens new horizons. Markets expand. Opportunities multiply. Challenges also grow. Regulations vary. Competition intensifies. Cultural nuances matter. Adaptation becomes key. Globalization is not just an opportunity; it’s a complex puzzle.
The manufacturing industry is a dynamic landscape. Interconnected steps form a complex system. Multiple parties engage in a coordinated dance. Transparency, quality assurance, and efficiency define success.
Challenges persist, but solutions emerge. Innovation guides the way. Technology fuels growth. Sustainability shapes the path. People remain at the core. Manufacturing is not just an industry; it’s a world in itself.
Blockchain – Reinventing the Manufacturing Supply Chain
A new era dawned in manufacturing. Blockchain emerges as a transformative force. Supply chains witness a revolution. Traditional methods give way to innovation. Transparency, efficiency, and trust redefine the landscape. Let’s explore this exciting journey.
Stakeholders Involved in the Blockchain System
- Merchants or purchasing companies: They initiate the manufacturing order, setting the process in motion.
- Manufacturing company: Responsible for producing the goods as per the order specifications.
- Suppliers: Provide the necessary raw materials and components for smart contracts in manufacturing.
Logistics Company: Manages the transportation and delivery of goods.

The blockchain system brings these stakeholders onto a common platform, enabling seamless communication, transparency, and efficiency.
Step 1: The merchant places the manufacturing order
A new journey begins with the merchant. Specific goods are needed. An order takes shape. Details are meticulously crafted. Specifications are defined. Quantities are determined. Delivery timelines are set.
The blockchain comes into play. Transparency and traceability become the watchwords. The order records on the decentralized ledger.
Every detail is visible to stakeholders. Mistrust vanishes. Clarity prevails. The process kicks off with confidence—a new era in manufacturing dawns.
Step 2: The manufacturing company receives the order
The manufacturing company springs into action. The order arrives. Specifications are reviewed. Quantities are noted. Timelines are assessed. Feasibility is evaluated. The blockchain ensures transparency.
Confirmation happens on the decentralized ledger. All parties gain a clear understanding. Requirements are no longer ambiguous. Expectations align. The process moves forward.
The manufacturing company becomes a pivotal player. Commitment to quality and timelines defines success. The journey gains momentum.
Step 3: The suppliers receive the order
Suppliers are the next link. Notification of the order arrives. Raw materials are needed. Procurement begins. Quality is paramount. Sustainability is considered. Costs are optimized.
The blockchain records every transaction. Transparency extends to the supply chain. The origin of the materials is clear. Quality checks are verifiable.
Trust builds among stakeholders—efficiency gains pace. Delays minimize. The process flows smoothly. Suppliers become essential collaborators. The manufacturing vision takes shape.
Step 4: Logistic service provider adds parcel details to the blockchain
Logistics orchestrates the next phase. Goods are ready for shipment. Parcel details become crucial. Tracking numbers are generated. Shipment dates are set. Delivery addresses are confirmed.
The blockchain, in traceability, securely records everything. Transparency reaches a new level. Real-time tracking becomes possible. Stakeholders stay informed. Delays are managed proactively.
Customer expectations are met. Logistics is not just about transportation; it’s about keeping promises. The journey continues with precision.
Step 5: Order received by the manufacturer
The manufacturer takes centre stage. The order is received. Production planning begins. Raw materials are procured. Machines are prepared. The workforce is mobilized. Quality standards are set. Every stage of manufacturing is crucial.
The blockchain records the entire process. Transparency extends to production. Efficiency is monitored. Quality is assured. Timelines are adhered to. The manufacturer is not just a producer; it’s a creator. The product comes to life.
Quality assurance teams benefit as well. Product inspections streamline. Standards compliance verifies easily. Quality becomes consistent. Customer expectations meet. Brand reputation enhances.
Merchants or purchasing companies gain control. Order placements become transparent. Manufacturing aligns with demand. Deliveries become predictable. Customer satisfaction soars. Business thrives.
Step 6: The merchant receives the order
The final step unfolds. Goods are shipped to the merchant. The entire journey is traceable. The blockchain provides unparalleled transparency. Every stage is visible. Confidence in the process grows. The merchant receives the goods.
Quality is verified. Quantities are checked. Delivery timelines are met. Customer satisfaction becomes the ultimate goal. The merchant is not just a buyer; it’s a partner in success. The journey concludes with fulfilment.
The six steps in blockchain-enabled manufacturing form a symphony. Each step plays a vital role. The merchant initiates the process. The manufacturing company shapes the vision. Suppliers provide the building blocks.
Logistics ensures a smooth journey. The manufacturer crafts the product. The merchant concludes the process. Transparency, efficiency, quality, and collaboration define this new era.
Challenges exist, but solutions are at hand. Technology guides the way. Innovation fuels growth. Trust builds among stakeholders. A new way of manufacturing is not just a concept; it’s a reality.
Blockchain: A Transformative Technology

Blockchain stands as a transformative technology. Decentralized ledgers redefine transparency. Smart contracts automate agreements. Real-time tracking builds trust. Collaboration among stakeholders grows.
Efficiency reaches new heights. Costs reduce. Quality improves. Customer satisfaction soars. Innovation thrives. Growth accelerates—a new era in manufacturing beckons. Blockchain is not just a technology; it’s a revolution.
The Future: A World of Possibilities
The future of manufacturing is exciting. Blockchain opens new horizons. Traditional methods give way to innovation. Silos break down. Collaboration flourishes. Efficiency becomes the norm. Quality is consistent. Customer satisfaction defines success. Sustainability aligns with profitability.
Global reach becomes possible. Challenges are met with solutions. Growth is fueled by technology. People, processes, and technology align. A world of possibilities is not just a vision; it’s the future of manufacturing.
What Are the Challenges and Solutions of the Million-Dollar Manufacturing Industry?
The manufacturing industry stands as a giant. Its value reaches millions of dollars. Innovation drives growth. Technology fuels efficiency. Global reach expands opportunities. Yet, challenges persist. Problems plague processes.
Efficiency falters. Quality suffers. Transparency becomes elusive. Blockchain manufacturing emerges as a savior. Solutions unfold—a new era beckons. Let’s delve into the challenges and solutions.

1. Challenge: Lack of Transparency
Transparency is a vital need. Traditional manufacturing often falls short. Information hides in silos. Stakeholders struggle to access data. Mistrust brews.
Collaboration suffers. Decisions delay. Costs escalate—growth stunts. A solution seems distant. The challenge is real. The impact is profound. A new approach is needed.
Solution: Blockchain’s Decentralized Ledger
Blockchain offers a way out. Its decentralized ledger changes the game. Every transaction is recorded transparently. Alterations become impossible. Mistrust vanishes. Collaboration flourishes. Decisions accelerate.
Costs reduce. Growth gains momentum. Transparency is not just a feature; it’s a promise fulfilled. The challenge of transparency finds its match.
2. Challenge: Quality Assurance Issues
Quality assurance is a complex task. Standards vary across stages. Compliance becomes cumbersome. Inspections slow down processes. Errors slip through.
Customers receive subpar products. Reputations tarnish. Trust erodes. The quest for quality turns into a battle. The challenge is daunting. The solution must be robust.
Solution: Streamlined Quality Assurance through Blockchain
Blockchain simplifies quality assurance. Every step is recorded on the decentralized ledger. Compliance verifies easily. Standards uphold. Errors are detected early. Rejections minimize. Customer satisfaction soars.
Quality becomes a consistent promise. The challenge of quality assurance meets its solution. Blockchain is not just a technology; it’s a quality guardian.
3. Challenge: Inefficient Processes
Inefficiency haunts traditional manufacturing. Manual processes dominate. Delays become the norm. Costs soar. Deadlines miss.
Customers grow impatient. Competitors gain an edge. Efficiency dwindles. Profits shrink. The challenge of inefficiency looms large. The solution must be transformative.
Solution: Automation through Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are blockchain’s magic. Agreements turn into code. Execution becomes automatic. Delays diminish. Costs shrink. Efficiency reaches new heights. Manual interventions reduce.
Processes speed up. The challenge of inefficiency finds its answer. Automation through smart contracts is not just innovation; it’s a revolution.
4. Challenge: Supply Chain Complexity
Supply chain complexity adds to challenges. Multiple parties engage. Coordination becomes difficult. Delays ripple through the system. Costs escalate.
Customer satisfaction suffers. The challenge of supply chain complexity is intricate. The solution must be comprehensive.
Solution: Blockchain-Enabled Supply Chain Management
Blockchain transforms supply chain management. Transparency extends to suppliers. Procurement aligns with demand. Quality verifies effortlessly. Costs optimize. Sustainability aligns. Waste minimizes. Profits increase.
Coordination becomes seamless. The challenge of supply chain complexity meets its solution. Blockchain is not just a connector; it’s a supply chain orchestrator.
5. Challenge: Sustainability Concerns
Sustainability is a growing concern. Materials must be sourced responsibly. Waste must be minimized. Energy efficiency is vital. Emissions need reduction. Compliance with regulations is mandatory.
Social responsibility guides actions. The challenge of sustainability is urgent. The solution must be responsible.
Solution: Blockchain for Sustainable Manufacturing
Blockchain supports sustainability. Materials are sourced responsibly. Waste minimizes. Energy efficiency improves. Emissions reduce. Compliance verifies. Social responsibility guides.
Sustainability is not just a trend; it’s a duty fulfilled. The challenge of sustainability finds its answer.
6. Challenge: Globalization and Regulatory Compliance
Globalization opens new horizons but adds challenges. Regulations vary across regions. Compliance becomes complex.
Cultural nuances matter. Adaptation becomes key. The challenge of globalization and compliance is multifaceted. The solution must be adaptable.
Solution: Blockchain for Global Reach and Compliance
Blockchain enables global reach. Markets connect. Regulations align. Compliance verifies across regions. Cultural nuances navigate. Opportunities multiply.
Challenges manage. Global reach is not just an opportunity; it’s a complex puzzle solved. The challenge of globalization and compliance meets its match.
7. Challenge: Customer Expectations and Satisfaction
Customer expectations are ever-evolving. Satisfaction becomes a moving target. Quality, timelines, and transparency define success. Meeting customer expectations is a constant challenge. The solution must be customer-centric.
Solution: Blockchain for Customer-Centric Manufacturing
Blockchain builds customer trust. Quality assures. Timelines meet. Transparency builds confidence. Customer satisfaction reaches new peaks. Loyalty strengthens. Growth accelerates.
Customer-centric manufacturing is not just a goal; it’s a reality achieved. The challenge of customer expectations finds its solution.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain manufacturing is more than a technological innovation; it’s a strategic approach to transforming the manufacturing industry. By embracing this technology, businesses can unlock unprecedented transparency, efficiency, and collaboration levels.
Webisoft specializes in implementing blockchain solutions tailored to your manufacturing needs. Contact us today to explore how blockchain manufacturing can elevate your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does blockchain improve supply chain management?
Blockchain supply chain management improves by providing a transparent and unalterable record of all transactions. It enables real-time tracking, reduces fraud, and streamlines processes through automation.
What are the benefits of blockchain in manufacturing?
The benefits of blockchain in manufacturing include increased transparency, improved quality assurance, reduced costs, and enhanced collaboration among stakeholders.
How can I implement blockchain in my manufacturing process?
Implementing blockchain in manufacturing requires careful planning, collaboration with technology experts, and alignment with business goals.
It involves selecting the right blockchain platform, integrating it with existing systems, and training the team.
What are the potential risks of blockchain in manufacturing?
Potential risks include technological complexity, integration challenges, regulatory compliance, and stakeholder resistance. Proper planning, expert guidance, and stakeholder buy-in can mitigate these risks.
