Web3 stack is now a popular topic and making waves in the tech world. A surprising fact: over 60% of tech experts are now diving into Web3 projects.
So, what is this Web3 stack?
Simply put, it’s the technology behind decentralized apps on the blockchain. This contains things like smart contracts and decentralized finance platforms. The big deal about the Web3 stack is how it changes your internet experience – it’s more secure and transparent and gives you more control.
But it’s not all smooth sailing. Web3 stack faces challenges like handling a lot of users at once, exploring new regulations, and some complex tech stuff.
However, in this article, we will unpack all of this and more. We’ll explore the benefits and challenges of the Web3 stack in detail, helping you understand how it impacts you. Now, keep reading to get a clearer idea of this innovative technology.
Contents
- 1 Web3 Stack and Its Features
- 2 Web3 Tech Stack Overview
- 3 Components of Web3 Technology Stack
- 3.1 Layer 0 – Infrastructure: Building the Foundation of Web3
- 3.2 Layer 1 – Protocols: Powering the Decentralized Web
- 3.3 Layer 2 – Utilities: Empowering the Decentralized Web
- 3.4 Layer 3 – Services: Empowering dApp Creation and Management
- 3.5 Layer 4 – Applications: Enabling Decentralized App Experience
- 4 What Is the Web3 Stack for Developers?
- 5 The Development Environment in the Web3 Tech Stack
- 6 Explore the Comprehensive Web3 Development Offerings at Webisoft
- 7 Final Note
- 8 Frequently Asked Questions
Web3 Stack and Its Features
Web3 is a new way to use the internet that gives you more control over your identity and what you own online. Unlike the current internet, which a few big companies mostly control, Web3 spreads out control and uses blockchain technology. This makes the internet more secure and works better.
However, right now, the internet faces numerous problems, like data theft and being stuck with certain services. Web3 changes this by spreading out the power that big companies have. It ensures a better experience, safer data, and more reliable services.
Web3 Stack’s Key Features

The key features of the Web3 stack are:
- Decentralized Web Infrastructure: Web3 reduces the need for centralized servers. This makes the network stronger and less dependent on a single point of control.
- Ownership of Data, Content, and Platform: You get to own your data, content, and where it lives. Thus, you can control your digital stuff and decide how it’s used.
- Native Digital Payments: With Web3, you can make digital payments directly to others without middlemen. This is simpler and more direct.
- Self-Sovereign Identity: You can control your personal information and identity without relying on big companies.
- Trust-Less, Distributed, and Strong Infrastructure: Web3’s system is built to be reliable and secure, even if there are failures or attacks.
- Open, Public, Composable Back-End: Web3 supports an open system where different apps and services can work together easily.
Web3 Tech Stack Overview
Web3 tech stack is the engine behind the new phase of the internet, known as Web3. It is a version of the internet where you have more control over your data. This is what the Web3 technology stack offers.
However, a set of tools and technologies makes the internet decentralized. Unlike the old web, where big companies held most of the power, Web3 lets you and others share this control.
Moreover, this stack uses blockchain, the same technology behind cryptocurrencies. Blockchain platform is like a digital ledger that’s secure and transparent. Everyone can see what’s happening, but no one can tamper with the information. This makes Web3 reliable and safe.
Ethereum web3 stack is a popular example. It’s a platform where developers build open apps and run on blockchain. These apps, called DApps, give you new security and freedom online.
Components of Web3 Technology Stack

The layers are the key components of the Web3 technology stack. We’ll list them and then discuss each one in more detail below. Now take a look at the layers of the Web3 technology stack below:
- Layer 0 – Infrastructure: Building the Foundation of Web3.
- Layer 1 – Protocols: Powering the Decentralized Web.
- Layer 2 – Utilities: Empowering the Decentralized Web.
- Layer 3 – Services: Empowering dApp Creation and Management.
- Layer 4 – Applications: Enabling Decentralized App Experience.
Let’s explore these layers to understand how they contribute to the Web3 framework.
Layer 0 – Infrastructure: Building the Foundation of Web3
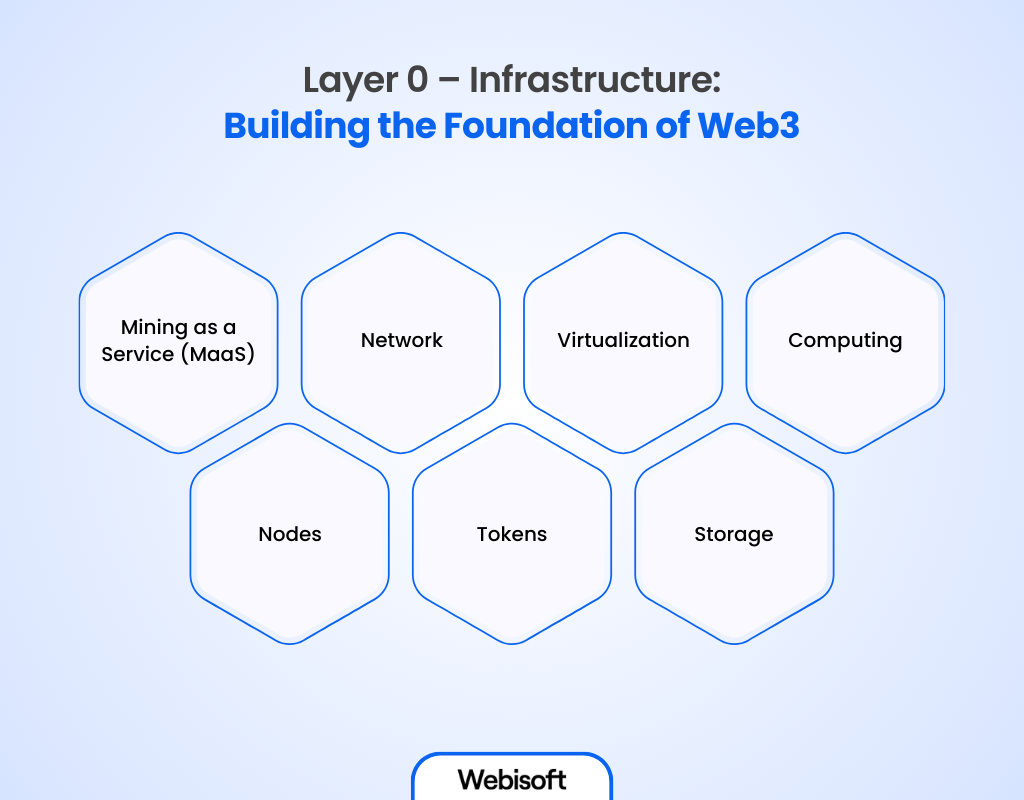
At the core of the web3 stack lies the infrastructure layer. It forms the foundation for all other components.
However, this layer primarily comprises the underlying blockchain architecture upon which the entire web3 ecosystem is built. Within this layer, several key elements serve crucial functions:
Mining as a Service (MaaS)
Mining has become a prominent topic in the crypto world. And the decentralized web requires mining as a service.
Various companies offer mining as a service (MaaS) to investors and individuals seeking to engage in large-scale mining operations. Decentralized web uses this emerging business strategy.
Network
The network of the web3 stack operates in a distributed manner. It eliminates the need for a central authority. This decentralized network ensures privacy for every user. Moreover, it functions similarly to a blockchain network but with enhanced scalability.
The Web 3.0 stack can run its web3 browser, which can also be distributed. This network enables the decentralized execution of blockchain applications. It aligns with the structure of dApps (decentralized applications).
Virtualization
Virtualization involves creating virtual resources such as desktops, servers, operating systems, storage, and networks. It transforms traditional computing by enabling more manageable and scalable workloads.
While virtualization has existed for years, its full potential is being realized with the new web3 blockchain structure. Virtualization can be implemented across various layers of the web3 stack, operating at the system, hardware, and server levels, reshaping our current perspectives.
Computing
Computing in the web3 stack connects the power of multiple computers collaborating on solving a single problem. This collaborative approach enhances efficiency and saves time. Problems are divided into smaller parts distributed across the network, and a group of computers works together to solve them.
These computers are connected through the network, facilitated by a lightweight software program, to collectively tackle the problem.
Nodes
Nodes play a vital role in the decentralized web, serving as interaction points within the network. They route internet traffic to its destination and track each transaction. It enables real-time updates and decision-making.
As every node holds the same information, the loss of any node has minimal impact on the network. This design ensures the resilience and strength of the web3 stack.
Tokens
Tokens form an integral part of the infrastructure layer in the web3 stack. They are essential assets within the decentralized web system, allowing users to access various features offered by the network.
These tokens are tradable and transferable assets, facilitating interactions within the infrastructure layer of the web3 stack.
Storage
The new web3 infrastructure introduces decentralized storage, offering a more secure environment. Blockchain technologies have brought about the concept of decentralized cloud storage. It is more cost-effective, resilient, and widely distributed than existing centralized cloud solutions.
This decentralized storage solution within the infrastructure layer ensures the safekeeping of users’ data without relying on a trusted third party.
Layer 1 – Protocols: Powering the Decentralized Web
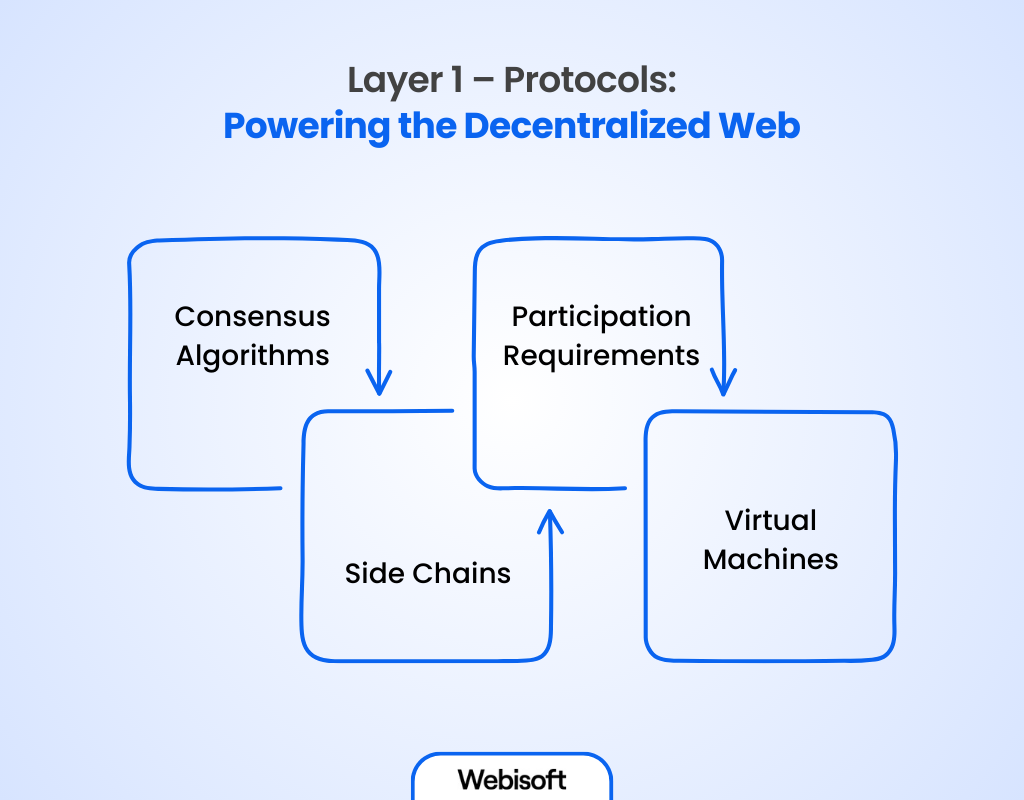
The protocols layer within the Web 3.0 stack contains a range of essential elements, including consensus algorithms, protocols, participation requirements, and virtual machines.
These components shape the functioning and capabilities of the decentralized web. Let’s explore the key aspects of this layer:
Consensus Algorithms
Consensus algorithms play a vital role in ensuring agreement among nodes in a blockchain network. They enhance network efficiency and add a layer of reliability. The following consensus algorithms are available within the web3 stack:
- ASIC-optimized Proof of Work (PoW)
- ASIC-resistant PoW
- PoW and PoS (Proof of Stake) with fallback
- Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET)
- Proof of Space and Time (PoST)
- Braided PoW
- Casper TFG Proof of Stake (PoS)
- Hybrid PoS/PoW
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
- Proof of History (PoH)
- Byzantine Agreement with Leader Election (BA⋆)
- Stellar Consensus Protocol
- Ripple Consensus Protocol
- Leader-Centered Blockchain Consensus
Side Chains
Side chains offer an innovative mechanism that enables the transfer of tokens and assets between different blockchains. They hold great potential for developers, allowing them to create decentralized applications without impacting the main chain.
Side chains function as independent cells within a separate blockchain network, ensuring their own security. Compromises in one side chain affect only that specific side chain, safeguarding the entire ecosystem.
Participation Requirements
The participation requirements refer to the different types of blockchain networks in the web3 stack. The decentralized platform of the web stack examples primarily consists of two infrastructure types:
- Public/Permissionless Blockchain: These open networks allow anyone to participate without restrictions.
- Private/Permissioned Blockchain: These are networks with restricted access, where participants require permission to join and engage with the network.
Virtual Machines
Virtual machines play a crucial role in maintaining security and executing code from various computers within the network. Different blockchains employ different types of virtual machines and state transition machines. Here are notable examples:
- Ethereum 1.0, Wanchain, Hashgraph, Ethermint, and others utilize the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
- Solana and Cardano utilize direct LLVM exposure.
- Ethereum 2.0, EOS, Dfinity, and Polkadot use the Web Assembly Virtual Machine (WASM).
- Kadena, Corda, Tezos, and Rchain have their own state transition machines.
The protocols layer of the web3 stack forms the backbone of decentralized web operations, enabling secure consensus, efficient participation, and effective code execution.
Layer 2 – Utilities: Empowering the Decentralized Web
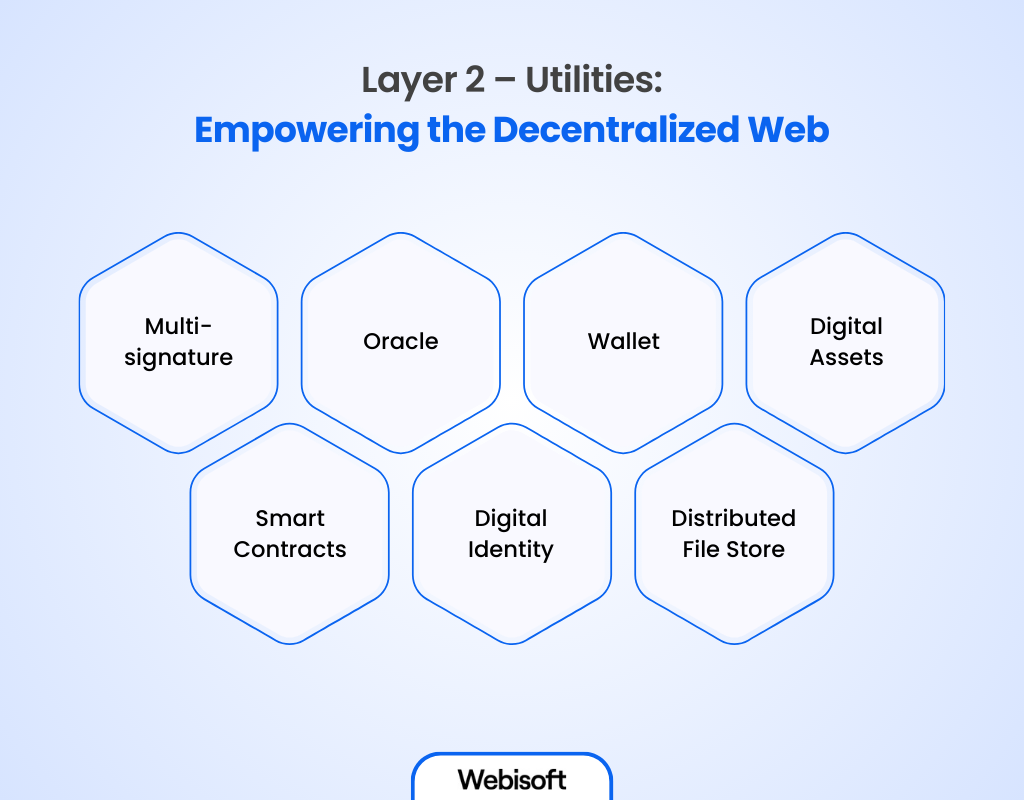
The utility layer within the web3 stack has different essential components that contribute to the functionality and effectiveness of the decentralized web. Let’s explore the key elements of this layer:
Multi-signature
Multi-signature functionality plays a crucial role in the web3 stack, providing enhanced transaction security. Each transaction requires a unique signature from multiple users before it can be sent.
Users can determine the number of signatures or requirements needed before creating an address. This technology, pioneered by BitGo, is widely adopted within the web3 architecture due to its importance in ensuring secure transactions.
Oracle
Oracles act as data feeds that support smart contracts within the blockchain network. They serve as intermediaries that gather real-world information and transmit it to smart contracts, enabling access to external data sources.
Since blockchain networks are typically isolated from the outside world, oracles bridge this gap by providing the necessary information to execute smart contracts effectively. Without oracles, the proper functioning of the web3 stack is compromised.
Wallet
Wallet programs play a crucial role in the web3 stack by storing users’ public and private keys. They facilitate communication with various blockchain networks and enable users to track their digital assets. It includes popular cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin.
Digital Assets
Digital assets form an integral part of the web3 stack and primarily contain cryptocurrencies used within the ecosystem. However, they can also extend to include images, multimedia, and textual contracts that are stored and exchanged digitally.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are agreements between parties that are executed automatically based on predefined rules. Transactions occur seamlessly once the conditions outlined within the smart contract are met.
With smart contracts, there is no need for intermediaries or higher authorities, as the process is entirely automated.
Digital Identity
In the web3 technology stack, digital identity assumes paramount importance as users remain interconnected online.
A digital identity serves to define and authorize individuals where necessary. Users can have multiple digital identities across different platforms. It ensures privacy and security in the decentralized web.
Distributed File Store
The distributed file store provides a server-based location for data storage. This process offers convenience, allowing data to be accessed as easily as from a local computer. To access the server, authentication is required, ensuring that authorized clients have full control over their data.
The utility layer in the web3 stack plays a crucial role in enhancing security. It enables seamless transactions and facilitates the storage and management of digital assets within the decentralized web.
Layer 3 – Services: Empowering dApp Creation and Management
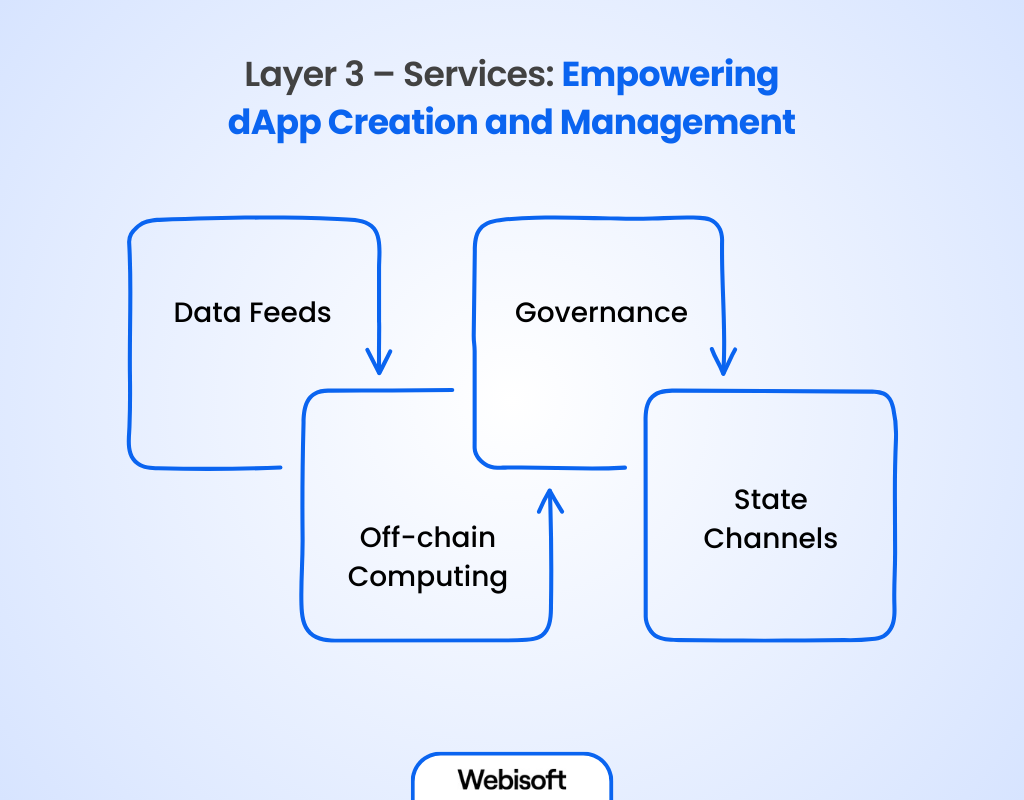
The services layer within the web3 stack is instrumental in providing the essential tools for creating and managing decentralized applications (dApps). This layer has various components that enable efficient dApp development. Let’s explore the key elements of this layer:
Data Feeds
Data feeds, also known as web feeds, play a vital role in the web3 stack by facilitating the reception of updated data from reliable sources. In the new technology stack, these decentralized data feeds are utilized to keep the information of nodes up to date.
Off-chain Computing
Off-chain computing refers to processes that occur outside the blockchain application stack. It offers cost-effectiveness and efficiency compared to on-chain computing.
By using off-chain computation, data integrity is ensured, and privacy is enhanced. All these make it an ideal foundation for decentralized app development. This approach resembles a virtual memory system.
Governance
Governance plays a critical role in the infrastructure of the web3 stack, eliminating the need for human management. Developers can utilize decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) for their projects, which operate through smart contracts.
DAOs are based on the principles of decentralization within the blockchain technology stack. It enables autonomous decision-making processes.
State Channels
State channels establish bidirectional communication between two peers through transactions. Each user must sign the transactions with their private keys to ensure authorization and authentication.
These channels are accessible only to the participating parties and have a limited timeframe within which they are available. However, it disappears after the predefined period. The services layer of the web3 stack provides essential functionalities for the development and management of dApps.
Layer 4 – Applications: Enabling Decentralized App Experience
The applications layer within the web3 stack contains crucial elements such as dApp browsers, application hosting, user interfaces, and decentralized applications (dApps). Let’s explore the key components of this layer:
The dApp Browser
The dApp browser serves as the uppermost layer of the web3 stack, allowing users to access decentralized applications. Traditional browsers lack the necessary infrastructure to browse these emerging decentralized applications.
Specialized dApp browsers, such as MetaMask, provide fully-featured desktop browsers with user interfaces, enabling access to both the web3 and regular web.
Other notable dApp browsers include Trust Browser and Cipher, which offer similar functionalities and empower users to explore and engage with decentralized applications.
Application Hosting
Application hosting is a crucial layer responsible for hosting dApps. Once downloaded through the dApp browser, the hosting process makes the applications available through cloud storage for execution.
The distributed network influences Software as a Service (SaaS) to host the applications. It ensures easy access and integration across various devices. This layer provides a risk-free hosting environment with minimal maintenance requirements.
Decentralized Applications
dApps are a pivotal component of the web3 stack. They transform the traditional centralized application through blockchain technology advancements. These applications enable peer-to-peer connectivity through a server network on the blockchain.
Building hearty dApps necessitates the integration of external data, computation, monetization, and file storage. The technology stack within the web3 ecosystem facilitates the development of this layer, empowering the creation of decentralized applications.
What Is the Web3 Stack for Developers?
Web3 technology reshapes the way developers create applications. In this section, we’ll take you through the key components of the Web3 tech stack for developers. Those are:
Blockchain
Blockchain is the core of Web3, acting like a secure, digital record-keeping system. It’s essential for building safe and decentralized apps.
For you, as a developer, it means working with systems like Ethereum’s Web3 stack. It is crucial for creating secure applications spread across many computers.
Smart Contracts
Smart Contacts are automated contracts. They’re coded to execute certain actions under specific conditions on the blockchain.
However, smart contracts in the Web3 development stack are key to making decentralized apps that are both efficient and reliable.
Development Environments
In Web3, development environments come with specialized tools for blockchain app development. For example, Ethereum’s Web3 stack environments are designed specifically for working with blockchain technology.
Testing Frameworks
The testing framework is crucial to make sure your app works right. Web3 testing frameworks let you check your smart contracts and apps in a safe space. They help find and fix problems, making your app more reliable.
File Storage
In Web3, file storage is different from traditional storage methods. It uses decentralized networks for more secure and distributed storage. This part of the Web3 tech stack means your app’s data isn’t kept on just one server. Thus, it becomes safer and more accessible.
User Identity Management
User identity management is about how users control their data. Web3 changes the game by giving users more power over their information. In the Web3 technology stack, you’ll create systems that let users manage their identities securely and privately.
UI/UX Components
In Web3, UI/UX components need to be easy to use but also able to handle complex decentralized tech. The right UI/UX design in the Web3 frontend stack is crucial for a good user experience.
The Development Environment in the Web3 Tech Stack

In Web3 development, the environment you work in is crucial. Each blockchain, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, has its own unique setup. Now, take a look at the development environment in the Web3 tech stack:
Bitcoin Web3 Development Environment
The Bitcoin environment focuses on cryptocurrency transactions. It’s simpler than other platforms in the web3 tech stack.
While it doesn’t support complex applications or smart contracts, it’s great for projects that need secure digital currency exchanges. Working in Bitcoin’s environment means you’re dealing with a straightforward and secure system. But it’s not suited for more complex applications.
Ethereum Web3 Development Environment
Ethereum’s environment is more versatile, especially for creating complex decentralized apps and smart contracts. It supports different programming languages, making it a flexible choice in the web3 development stack.
However, this environment is part of the Ethereum web3 stack, popular for its adaptability and widespread use. As a developer, this gives you a broader range of project possibilities.
The Testing Environment for Web3 Apps
Testing your applications is a must in Web3 development. The testing environment is designed to test your decentralized apps and smart contracts in conditions that mimic real-world scenarios.
However, this is a key part of the web3 technology stack. It helps you ensure that your apps are effective and free from glitches. By using this environment, you can fine-tune your apps to be strong and user-friendly.
Explore the Comprehensive Web3 Development Offerings at Webisoft

Webisoft, a leading web3 development company, specializes in creating interactive and cutting-edge web3 solutions. Using blockchain, AI, NFT, and other advanced technologies, our experienced team of web3 developers offers numerous services.
Let’s explore the categorized web3 development services that Webisoft provides:
1. Custom dApp Development
The skilled web3 developers at Webisoft excel in Rust, Solidity, Golang, and frameworks like Substrate and Brownie. With a focus on interoperability, security, and scalability, they create personalized web3 applications that meet specific client requirements.
2. DeFi Development
Enterprises can benefit from DeFi consulting and end-to-end development services offered by Webisoft.
Our dedicated DeFi developers specialize in building custom DeFi solutions. Those include DeFi dApps, layer2 solutions, automated market makers (AMM), non-custodial wallets, and DeFi exchanges across multiple blockchains.
3. Metaverse Development
Webisoft pioneers innovative metaverse development by connecting the power of blockchain, AR, VR, 3D reconstruction, and emerging technologies.
Our web3 developers create immersive 3D spaces, NFT marketplaces, and other components that generate real business value within metaverse environments.
4. NFT Marketplace
Webisoft designs and builds NFT marketplaces that facilitate live auctions and NFT trading in a realistic 3D environment. They offer ready-to-deploy NFT marketplace solutions. The solutions can be customized and seamlessly integrated into web3 projects, reducing time-to-market.
5. Smart Contract Development
Web3 developers at Webisoft utilize the web3 ecosystem’s public, open-source, and composable back-end.
Using it, we develop highly secure, reliable, and upgradable smart contracts based on current web3 standards. The flexibility to modify contract code while maintaining its original integrity ensures adaptability to evolving needs.
6. Web3 Gaming Development
Webisoft’s web3 developers possess Unity and Unreal Engine 5 game development tools expertise. They create innovative games, including “play to earn” and NFT-based multiplayer experiences.
7. Multi-chain Solutions
Webisoft offers fully interoperable multi-chain web3 solutions encompassing dApps. These solutions enable users to access different web3 platforms and engage in seamless trading activities.
Our web3 developers can integrate APIs, Oracle, and DAO into multi-chain solutions, enhancing transparency and automation.
8. Native Payment Solutions
Web3 developers at Webisoft craft advanced digital wallets compatible with various web3 platforms. These wallets facilitate the storage and management of native currencies. Moreover, they empower users to access web3 applications across different blockchains.
9. Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
Webisoft’s SSI system ensures users have freedom and autonomy within a secure environment. Our web3 developers create wallets and credentials that allow users to authenticate their identity in decentralized ecosystems.
However, ready to explore the future of web3 development? Look no further than Webisoft! With our skilled developers proficient in blockchain, AI, NFTs, and more, we offer a range of perfect web3 solutions.
Whether it’s custom dApp development, DeFi solutions, metaverse innovation, NFT marketplaces, or smart contract creation, Webisoft is at the forefront of web3 technology.
Final Note
In conclusion, Web3 is changing how we use the internet. It gives you more control and ownership. The Web3 stack includes everything from the basic infrastructure to applications and access points. This tech is always growing and changing.
Web3’s flexibility lets developers create new and innovative uses for the internet. Even though the basic structure of Web3 stays the same, the projects and opportunities it offers will keep changing. So, we can look forward to a future full of new possibilities and big changes.
However, at Webisoft, we’re excited to be part of this journey. If you’re ready to step into the transformative world of Web3, Webisoft is here to guide you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Web3 Full Stack?
Web3 full stack includes all the tools for creating decentralized apps on the blockchain. It covers everything from the blockchain itself to the user interface. Moreover, it focuses on secure and user-driven applications.
What is the Social Stack of Web3?
The social stack of Web3 is for building decentralized social platforms. It focuses on user data ownership and community-led governance, moving away from traditional, centralized social media models.
What is the Difference Between Web 2 and Web3 Technology Stack?
The main difference is that Web2 uses centralized servers controlled by companies, while Web3 is decentralized, spreading data across many places. Web2 holds user data, but in Web3, you control your own data. Web2 focuses on ads and data selling for money, whereas Web3 allows direct user monetization.
