Social media has become an essential part of the digital era, connecting people globally and enabling instant information sharing. It allows users to stay updated on current events, discover new products, promote businesses, and more. However, these benefits come with the risk of compromising user data privacy.
Senator Durbin highlighted this concern during the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal, emphasizing the need to evaluate the limits of privacy in the name of global connectivity. Web 2.0 social media platforms leverage user data and monitor user actions to provide personalized experiences.
This article explores the social graph definition and advantages of the web3 social graph over Web 2.0 social graphs.
Contents
What is a Social Graph?
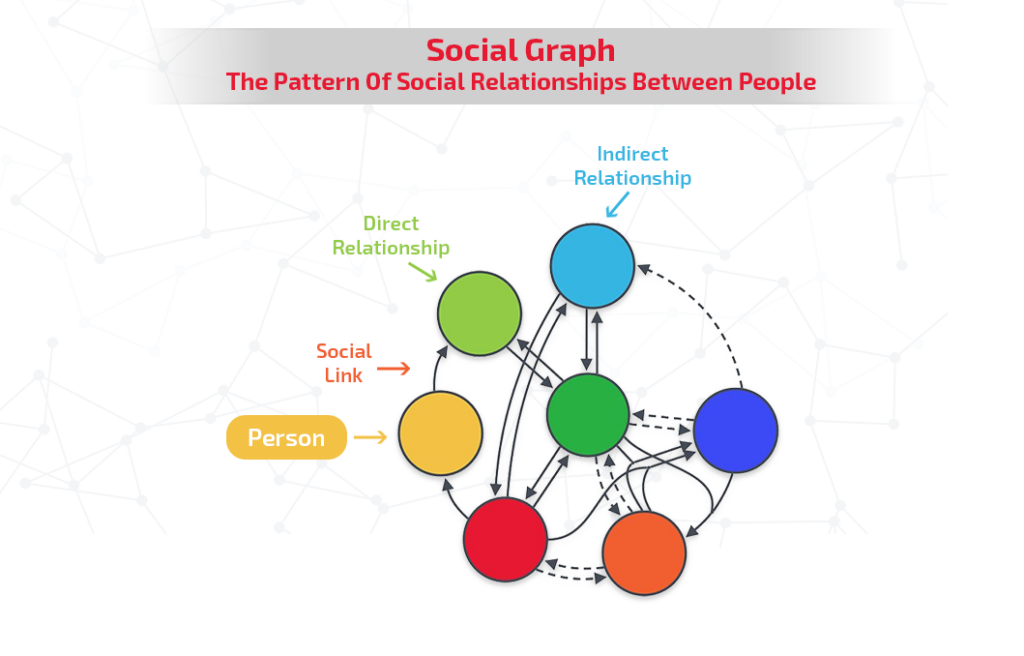
A social graph represents the intricate network of relationships individuals form within an online social platform. It visualizes the connections among users, groups, and organizations within the digital social network.
When users create accounts on platforms like Facebook and engage with content or follow others, a curated feed of their activities is generated. This personalized feed is recommended to users each time they visit the platform, contributing to the expansion of their social graph.
By liking or commenting on posts, users continually add to their social graph, forming a complex web of connections and data.
The Rise of the Social Graph – An Excellent Data Model
Although the concept of a social graph existed for some time, it gained widespread attention when Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg reintroduced it at the Facebook F8 conference on May 24, 2007.
Zuckerberg discussed policy changes aimed at enhancing the web experience by documenting Facebook members’ connections and relationships through the social graph. Since the Facebook F8 conference, the social graph has become a fundamental aspect of every major social media platform.
When new users register and join a social media application, the platform proactively suggests people they may know based on the provided registration information.
The platform learns about users’ preferences by recommending relevant topics and recording their interactions, such as browsing activity, likes, comments, and more. This user-centric social graph encompasses users’ interests, interpersonal relationships, and even living habits.
Benefits of the Social Graph
The social graph brings significant advantages to social media platforms like Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, and TikTok.
- It enables the platforms to document all your activities once you join, including tracking your friends, calls, texts, and shared events.
- These details are organized and interconnected, making the platforms more powerful.
- The benefits of the social graph vary for the platforms themselves, users, and third parties.
- Platforms can personalize user experiences and monetize the data.
- Users receive personalized content and advertisements based on their interests.
- Third parties, such as advertisers, can leverage the social graph to target specific audiences and deliver personalized recommendations.
- The social graph plays a crucial role in enhancing the functionality and effectiveness of social media platforms.
Benefits of the Social Media Platform
A rich social graph empowers social media platforms like Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, or TikTok.
- These platforms meticulously document users’ activities, including their friend’s lists, calls and texts, and shared event attendance.
- By organizing and connecting this information in a structured manner, platforms can personalize user experiences, fostering greater user engagement and loyalty.
- Social media platforms can monetize the social graph by selectively selling user data to third parties and advertisers. For instance, Facebook generated an average revenue of $50.25 per user in the U.S. and Canadian market during Q2 2022.
Benefits for Users
Despite potential privacy concerns, users benefit from the social graph through personalized experiences. The social graph enables platforms to understand users’ preferences and recommend content, advertisements, and products tailored to their individual interests.
By sharing more details with the platform, users can enjoy increasingly personalized experiences.
Benefits for Third Parties
Third parties, such as advertisers, companies, and brands, leverage the social graph to identify the right audience for their products and services. By utilizing the social graph, these entities can target and promote their offerings to specific users, increasing the likelihood of user engagement and purchase decisions.
For example, TripAdvisor employs Facebook’s social graph to prioritize reviews from people users know, ensuring that those reviews appear prominently when users search for recommendations related to restaurants, hotels, or resorts.
In summary, the social graph plays a pivotal role in mapping online relationships within social media platforms. It benefits the platforms themselves, users through personalized experiences, and third parties by facilitating targeted advertising and recommendations.
However, users should remain mindful of potential privacy implications associated with the social graph.
Problems of Web 2.0 Social Graph
The social graph is a model that represents social relations between entities. It is essentially a representation of a social network, where the term “graph” is derived from graph theory. The social graph is often described as “the global mapping of everybody and how they’re related.
However, several issues have arisen with the current implementation of the social graph, particularly the one owned by Facebook. For instance, a social networking service is currently unaware of the relationships formed between individuals on a different service.
This results in an online experience that is not seamless, but rather fragmented due to the lack of an openly available graph between services. Moreover, existing services define relationships differently.
1. Invasion of User Privacy
The Web 2.0 social graph poses serious concerns regarding user privacy. Social media platforms extensively monitor user behavior and collect their data, which is then sold to third parties for profit.
In the second quarter of 2022, Facebook (now Meta) earned a staggering $28.15 billion in ad revenue, highlighting the substantial monetary value derived from user data.
2. Centralized Data Storage and Data Leakage
A critical issue with Web 2.0 social graphs lies in centralized data storage. User data on existing social media platforms is stored in centralized databases, making it vulnerable to data breaches and leaks.
Unnecessary data collection and storage practices expose the social media ecosystem to fraud and irreversible damage. The infamous case of Cambridge Analytica’s acquisition of personal data from the Facebook social graph for political advertising serves as a prominent example.
3. Data Ownership
Companies that own social media platforms exercise control over each user’s social graph. Users must agree to the platform’s terms and conditions, relinquishing ownership of their data.
This poses a threat to individuals as platforms hold the right to information and can arbitrarily ban users based on their opinions or deemed inappropriate content.
The Web 2.0 social graph primarily benefits the platform, utilizing users’ social behavior to generate value while restricting users’ rights solely to utilizing the platform as a social tool.
Guide to the Web3 Social Graph
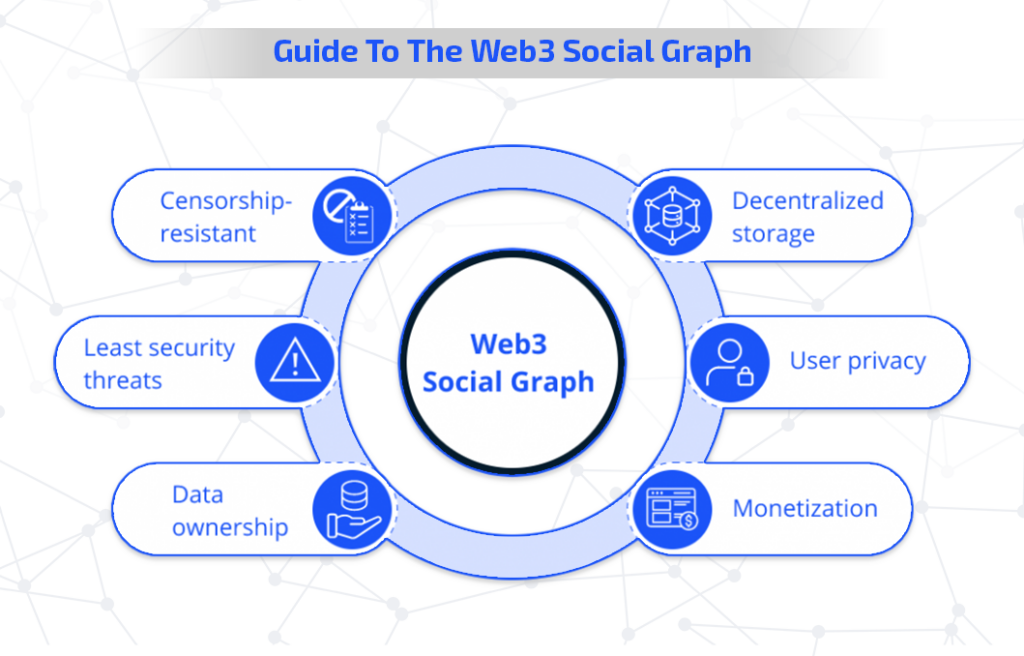
The introduction of web3 aims to decentralize social media and restore data ownership to users. By leveraging blockchain technology and on-chain identities, users regain control over their social graph data, shifting power from social media giants
Users now have the authority to grant or deny data access to others and can even monetize their data, similar to web 2.0 platforms.
Web3 social graph eliminates data barriers, enabling users to effortlessly switch between social platforms while preserving their identity and history. Additionally, the web3 social graph ensures transparency and tamper-proof data.
Information such as transactions, participation in DeFi projects, and more is visible through the user’s wallet address. With a single address, users can access multiple applications, and their behavior across platforms is recorded, safeguarding their data from external parties.
Web3 Social Graph vs. Web 2.0 Social Graph
Web 2.0 is the current version of the internet, which is characterized by user-generated content and the rise of social media platforms. In the Web 2.0 era, data and content are centralized, meaning they are controlled by a small group of companies, often referred to as “Big Tech”.
The social graph in Web 2.0 is largely controlled by these companies, who determine how users connect and interact with each other on their platforms.
Web3, on the other hand, is a proposed new iteration of the internet that incorporates concepts such as decentralization, blockchain technologies, and token-based economics.
The social graph in Web3 would be decentralized, meaning that no single entity would control how users connect and interact with each other. This could potentially lead to more user autonomy and privacy, as well as new forms of online interaction and economy.
However, the concept of Web3 is still in its early stages and has been met with both enthusiasm and skepticism. Critics have expressed concerns over issues such as the centralization of wealth, loss of privacy due to more expansive data collection, and the difficulty of regulating a decentralized web.
Some also argue that Web3 is more of a buzzword or marketing term than a tangible reality at this point.
| Aspect | Web 2.0 social graph | Web3 social graph |
| Data storage | Centralized storage | Decentralized and distributed storage |
| User privacy | Has least user privacy | Offers maximum user privacy |
| Data control | Data is controlled by social media platforms | Data is controlled by users themselves |
| Data ownership | Social media platforms own user data | Users own their own data |
| Transparency | No transparency exists | It is transparent |
| Monetization | Social media platforms can sell data to third parties | Users have the right to monetize or not monetize their data |
| Data vulnerability | Has high chances of data leakage and security threats | Least prone to data leakage and security threats |
Please note that this table is based on the provided information and may not encompass all aspects or details of Web 2.0 and Web3 social graphs.
Benefits of Web3 Social Graph
Web3 social graphs offer significant advantages over Web 2.0 social graphs. Let’s explore the benefits:
- Decentralization: Web3 social graphs are decentralized and distributed among multiple blockchain nodes. This decentralized structure enhances resilience and reduces dependence on a single authority.
- Self-sovereignty: Users have sole control and ownership of their data within Web3 social graphs. They can choose whether to share their data with third parties, empowering them with greater autonomy.
- Privacy: Web3 social graphs provide maximum privacy by offering self-sovereign identities to users. Users have greater control over their personal information and can decide who has access to it.
- P2P sharing: Users, as data owners, can directly share their social graphs with anyone they choose. This peer-to-peer sharing eliminates intermediaries and facilitates secure data exchange.
- Data portability: With Web3, data and social graphs can seamlessly move across blockchain platforms without the need for data rebuilding at each step. This enhances flexibility and interoperability.
- Freedom of choice: Web3 empowers users with the freedom to choose applications, community cultures, and policies that align with their preferences. Users can tailor their digital experiences according to their individual needs and desires.
Web3 social graphs offer advantages such as decentralization, self-sovereignty, privacy, P2P sharing, data portability, and freedom of choice. These benefits foster a more user-centric and robust social graph ecosystem within the Web3 paradigm.
The Existing Social Graph in Web3 Projects
Web3 has given rise to several innovative social graph projects. Let’s take a look at some of the existing initiatives:
1. Lens Protocol
Developed by the Aave team, Lens Protocol is a user-owned, decentralized social graph that can be integrated into any application. Built on the Polygon Proof-of-Stake blockchain, it offers modularity, allowing for the addition of new features while ensuring the immutability of user-owned content and social relationships.
Lens Protocol empowers creators to take ownership of their content and eliminates concerns about content loss.
2. CyberConnect
Launched in September 2021, CyberConnect is a decentralized social graph protocol that enables dApps to establish network effects and create personalized social experiences for users.
It fosters decentralization, self-sovereignty, and censorship resistance within web3 social networks. CyberConnect is openly accessible, and it operates as a multi-chain and multi-platform social graph protocol.
3. DeSo
DeSo, known as the decentralized social blockchain, is a layer 1 blockchain designed to decentralize social media platforms and support storage-heavy applications.
It grants users control over their social graphs and facilitates seamless portability of information, NFTs, content, and coins across different applications. No external party possesses exclusive access to a user’s social graph.
DeSo assigns each user a “DeSo identity” akin to Metamask on Ethereum, enabling easy login to DeSo ecosystem apps and enhancing content and data portability.
4. 5 Degrees
5Degrees, developed by the TokenPocket wallet, is a social graph protocol based on the ERC-1155 token standard. It constructs a social relationship network infrastructure by creating profile NFTs using core user data.
This protocol aims to enhance the connectivity and interactivity among users within the web3 social graph ecosystem.
In summary, these existing web3 social graph projects, including Lens Protocol, CyberConnect, DeSo, and 5Degrees, offer decentralized, user-owned, and interoperable solutions that empower individuals, facilitate content ownership, and foster the growth of vibrant social graph communities within the web3 landscape.
Conclusion
In the current landscape, the need for a revamped social graph is evident. Web3 social graphs provide a promising solution, countering the exploitation of user data by major social platforms. With user-centric control and ownership, web3 social graphs address concerns of data privacy, portability, and security threats.
By introducing web3 social graphs, the entire ecosystem can be reconstructed into a more effective and user-oriented model. Embracing the principles of decentralization and self-sovereignty, web3 social graphs pave the way for a more transparent, secure, and empowering social graph framework.
For those committed to fostering a more secure and privacy-centered digital future, it’s clear that web3 social graphs represent the next evolutionary step. Webisoft, as a forward-thinking technology company, is positioned at the forefront of these advancements.
Are you interested in capitalizing on the power of web3 social graphs for your business or project? Now is the time to act. Reach out to the Webisoft team today to explore how we can help you build your decentralized and user-centric social graph. Let’s together pioneer the next wave of digital transformation and secure a more transparent, empowered future for all.
