In the digital age, contracts are evolving. Ricardian contracts, a blend of traditional and smart contracts, lead this evolution.
They offer a human and machine-readable solution. Also, they provide a secure and efficient way of conducting transactions on the blockchain.
This article explores Ricardian contracts’ intricacies, workings, and potential to revolutionize blockchain transactions.
Contents
- 1 What Are Ricardian Contracts System?
- 2 What Does Ricardian Contracts Contain?
- 3 How Does A Ricardian Contract Work?
- 4 What Is Ricardian’s BowTie Model?
- 5 Signing And Intent of A Ricardian Contract
- 6 What Are The Characteristics of A Ricardian Contract?
- 7 What Are The Benefits Of A Ricardian Contract?
- 8 Ricardian Contract VS. Smart contract
- 9 EndNote
- 10 FAQ
What Are Ricardian Contracts System?
Ricardian contracts are a unique type of contract. They were first proposed by Ian Grigg in 1995. These contracts serve as a bridge between legal agreements and digital protocols.
They can execute automatically once certain pre-conditions are met. Moreover, they are more than just a set of trading intentions. They are a blend of a legally binding document and a software-executable format.
This dual nature offers a high level of security through cryptographic identification. It also provides a legal framework for dispute resolution, a feature absent in smart contracts.
What Does Ricardian Contracts Contain?

A Ricardian contract is a detailed document that encapsulates all the elements necessary for a legal agreement.
It’s a comprehensive tool that ensures clarity and transparency in transactions. Let’s delve deeper into its components:
1. Parties
One of the fundamental elements of a Ricardian contract is the clear identification of the parties involved. The contract explicitly states the number of parties partaking in the agreement.
It goes beyond just mentioning the parties; it also identifies who they are. This includes their legal names, roles in the agreement, and representatives, if any.
This clear identification of parties eliminates ambiguity and ensures that all parties know their roles and responsibilities.
2. Time Is An Element
Another crucial component of a Ricardian contract is the time element. The contract outlines its validity period, providing a clear timeline for the agreement.
This could be for a specific duration, such as a year or a month, or indefinite, lasting until certain conditions are met or events occur.
This time element provides a clear timeframe for the execution of the contract, ensuring that all parties are aware of the duration of their obligations.
3. Creating Blockchain Exceptions For Various Possibilities
Life is unpredictable, and a Ricardian contract takes this into account. The contractual contract includes provisions for unforeseen circumstances and blockchain transactions. For example, it considers what happens if one of the parties dies or becomes incapacitated.
It outlines the steps to be taken in such scenarios, ensuring the agreement adapts to changing circumstances. This flexibility is a crucial strength of contract Ricardian, making them a reliable tool in uncertain times of payment system.
4. Ito Network Conditions
Last but not least, a Ricardian contract can contain any conditions and if/then clauses as required. The form contract conditions outline the specific circumstances under which the full contract is to be executed.
They could include performance metrics, payment terms, or any other conditions relevant to the agreement. These if/then clauses provide a clear roadmap for the execution of the live contracts and smart contracts.
How Does A Ricardian Contract Work?

Ricardian contracts are a unique blend of the legal and digital worlds. They operate by linking these two realms through a process involving a hash function.
This process is a key component of how Ricardian contracts work, ensuring a clear separation between the issuance and execution of transactions.
The separation enhances security and ensures the integrity of the smart contract. Let’s delve deeper into this process:
1. Transactions Must Be Issued And Executed Separately
In a Ricardian contract, the issuance and execution of transactions are two distinct steps. The contract outlines all the rules and conditions of an agreement.
This includes the obligations of each party or users, the conditions under which the contract is to be executed, and the consequences of non-compliance.
This clear distinction between the issuance and execution system of transactions ensures that all parties know their written responsibilities. It also provides a clear roadmap for the execution of the contract, reducing the potential for disputes while taking legally actions.
2. A Ricardian Contract’s Hash Is Referred To As A Hash
A vital feature of a Ricardian contract is the use of a hash. The contract is signed using a standard digital signature.
This signature is then hashed, creating a unique identifier for the contract. Acceptance of the contract refers to this hash, not the contract itself.
This ensures that the contract cannot be altered once signed. It also provides a secure way of verifying the authenticity of the contract.
3. Private Keys Are Used to Sign A Ricardian Contract By the Parties Involved
The signing of a Ricardian contract involves the use of private keys. The contract provider’s signature is appended to the document using their private key. This creates a legally enforceable offer.
The use of private keys ensures the security of the contract. It also provides a clear record of who has agreed to the contract, providing a transparent chain of accountability.
What Is Ricardian’s BowTie Model?
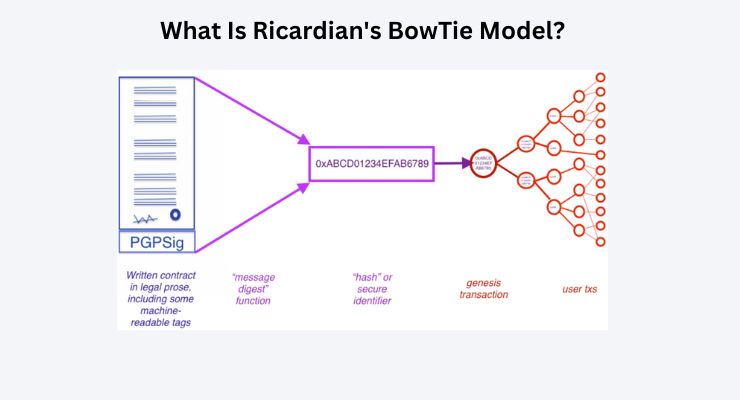
The Ricardian BowTie model is a mechanism that separates the agreement of the parties involved in a transaction. It does this based on the time and domain of trade.
It uses a hash to connect the legal domain and the accounting world in every transaction.
The creation and settlement of the legal contract result in a central parent document. This document defines every aspect of the agreement.
Signing And Intent of A Ricardian Contract
The signing of a Ricardian contract typically involves the use of a private key. The original offeror’s signature is affixed to the document. This creates a legally binding offer for the assets mentioned in the document.
Subsequent involvement in the contract, such as payments, refers to a hash identifier from the signed original document. This indicates intent and establishes a covert signature over the contract.
What Are The Characteristics of A Ricardian Contract?
Ricardian contracts stand out due to their unique features. These features make them a powerful tool in the digital world. Let’s explore these characteristics in detail:
- Human-parsable: Ricardian contracts are designed to be easily understood by humans. They are written in clear, simple language, making them accessible to all parties involved.
- Printable: Despite being digital, Ricardian contracts can be printed. This allows a physical copy to be kept for reference or legal purposes.
- Programmatically parsable: Ricardian contracts are not just for humans. They are also designed to be read and understood by machines, making them ideal for automation and digital processes.
- Comprehensive: Ricardian contracts contain all necessary information in a single document. This includes the parties’ signatures, the agreement’s terms, and any other relevant details.
- Legally binding: Ricardian contracts are not just digital agreements.
- Securely identifiable: Each Ricardian contract is securely identifiable. This is achieved through the use of cryptographic techniques, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of the contract.
- Backed by a robust Private Key Infrastructure: Ricardian contracts are backed by a robust Private Key Infrastructure. This ensures the contract’s security and the parties’ privacy.
- Unmodifiable: Once signed, a Ricardian contract cannot be modified by anyone other than the legal issuer or contract parties. This ensures the integrity of the contract.
- Accessible: Ricardian contracts can be written and used by anyone. There is no need for allocations in restricted areas, making them a democratic tool for digital agreements.
What Are The Benefits Of A Ricardian Contract?
Ricardian contracts offer a host of benefits. These benefits make them a powerful tool in the blockchain platform. Let’s explore these benefits in detail:
- Legally-enforceable exchange of assets: Ricardian contracts enable the legally-enforceable exchange of real assets and rights on the blockchain platform. This was previously impossible with Smart Contracts.
- Efficiency in dispute resolution: Ricardian contracts save time, money, and effort. They do this by providing a clear, legally binding agreement that can be referred to in disputes.
- Increased transparency: Ricardian contracts increase transparency in the blockchain network. They do this by providing a clear record of all transactions and agreements.
- Potential for convergence: Ricardian contracts demonstrate the potential for convergence between blockchain and smart contract features and traditional legal agreements. This opens up new possibilities for digital agreements.
Ricardian Contract VS. Smart contract
While Ricardian contracts and Smart contracts share some similarities, they are fundamentally different. A Ricardian contract records the intentions and actions of a specific contract, whether it has been performed or not.
In contrast, a Smart contract is a digital agreement that can be automatically executed. However, not every Ricardian contract is a Smart contract, and no basic Smart contract is a Ricardian contract.
| Features | Smart Contracts | Ricardian Contracts |
| Versatility | They are not Ricardian Contracts. | A Ricardian Contract can also be a Smart Contract. |
| Flow | Automate actions on the blockchain-based applications | It is also capable of automating activities on blockchain-based systems. |
| Validity | Not a legally binding document | A legally binding document or agreement |
| Purpose | Execute the terms of an agreement | Stores the terms of an agreement as a legal document. |
| Readability | Smart contracts are only machine-readable. | Ricardian Contracts are both machine and human-readable. |
EndNote
Ricardian contracts represent a powerful new form of code that can significantly influence blockchain network trading. They make it safer and more transparent.
They synchronize the legal agreement and contract provisions with machine-readable code for execution on the blockchain network. They can enhance the clarity of legal contracts between multiple parties.
They save time, money, and effort by reducing the likelihood of conflicts. When combined with Smart Contracts, they can also trigger functions and activities.
FAQ
What Is A Ricardian Contract?
A Ricardian contract is a digital agreement that is both human and machine-readable.
It combines the best of traditional contracts and smart contracts, providing a secure, transparent, and efficient way of conducting transactions on the blockchain.
How Does A Ricardian Contract Work?
Ricardian contracts link the legal and digital realms through a hash function. This ensures a clear separation between the issuance and execution of transactions, enhancing security.
What Are The Benefits Of A Ricardian Contract?
Ricardian contracts enable the legally-enforceable exchange of real assets and rights on the blockchain platform, save time, money, and effort in dispute resolution, and increase transparency in the blockchain network.
