Remember when we talked about Polkadot blockchain in one of our recent posts? Well, we briefly touched upon something called a Parachain.
If it’s been a while, let’s jog your memory a bit. Polkadot is this fantastic blockchain, renowned for its interoperability, which essentially means it can bring multiple blockchains together in a way that they can talk to each other. Parachains? They are these unique blockchains that plug into Polkadot and can have a friendly chat with Polkadot Network and other Parachains.
A fun fact about Parachain – the name isn’t random! ‘Para’ stands for parallel, symbolizing that a Parachain runs parallel to the Polkadot relay chain. This parallel operation allows a Parachain to process transactions concurrently with the Polkadot system, leading to a key advantage – scalability.
But that’s not all! A Parachain can not only interact with its Polkadot siblings (other Parachains), but it also shares the security blanket of the entire network.
In this post, we’ll be opening up the Pandora’s box of Parachains – exploring their benefits, potential applications, and, finally, how you can set a Parachain running on Polkadot. Buckle up and get ready for a deep dive into the Parachain universe!
Contents
- 1 What is Parachains?
- 2 Polkadot Parachain Characteristics
- 3 What are the Benefits of Parachains?
- 4 What is Parachain Consensus?
- 5 Making Sense of Parachain Types & Slot Allocation
- 6 How Parachains Work?
- 7 What can Parachains be Used for?
- 8 How to Run a Parachain on Polkadot?
- 9 How to Rent a Parachain: A Guide to the Process
- 10 Exploring Parachain Projects: Examples and Use Cases
- 11 What about Parathreads?
- 12 Acala Network: Stepping into Polkadot’s Parachain Ecosystem
- 13 Kusama Parachain Auctions: The Adventure Begins
- 14 The Growing Buzz Around Parachains: What’s Ahead?
- 15 What are the Fees and Costs of Running a Parachain?
- 16 Conclusion
- 17 FAQs
What is Parachains?
Parachains, short for parallelizable chains, are independent chains that run in parallel within the Polkadot network. They operate alongside the main Polkadot chain, known as the Relay Chain, and benefit from its security and consensus mechanism.

Parachains are designed to enhance the scalability, interoperability, and customizability of the Polkadot network. They provide a way to run multiple chains simultaneously, each with its own set of rules, logic, and functionalities. Parachains can be tailored to meet specific requirements and use cases, making them highly versatile and adaptable.
The Backbone of Parachains: Collators
Under the hood, parachains are maintained by a group of network maintainers known as collators. Think of collators as the hardworking conductors of this symphony, collecting user transactions from each parachain and creating proofs of state transition for Relay Chain validators.

In simpler words, they bundle up the parachain transactions into blocks (or parachain block candidates, to be precise), and then produce proofs based on these blocks for validators.
The Bridge to External Networks
An interesting feature of parachains is their ability to link up with other networks such as Bitcoin and Ethereum, courtesy of cross-network bridges. One example that stands out is Clover Finance.
This parachain uses a unique two-way peg system to effortlessly transport assets and data from the Polkadot Network to Bitcoin or Ethereum, and to other chains as well.
The Versatility of Parachains
One of the greatest strengths of parachains is their adaptability. They can be tailor-made to serve a wide variety of applications, including but not limited to:
- Decentralized Finance
- Decentralized Data Storage
- Internet of Things
- Identity Verification
- Gaming
- Credentials
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs)
- Oracles
- Digital Wallets
This versatility of parachains lets Polkadot build a truly dynamic digital asset infrastructure. The result? A network that provides the scalability, security and interoperability required to transform the blockchain’s potential into the next iteration of the Internet – Web 3.0.
Polkadot Parachain Characteristics
Parachains within the Polkadot ecosystem have some distinct characteristics:

Shared Security
Parachains leverage the security of the Polkadot Relay Chain through a shared security model.
The Polkadot network relies on a nominated proof-of-stake (NPoS) consensus mechanism, where DOT token holders elect validators to secure the Relay Chain. Validators play a crucial role in validating transactions and maintaining the overall security and integrity of the network.
The shared security model ensures that each parachain benefits from the robustness of the validator network. Validators secure the Relay Chain and the parachains connected to it.
This means that the security of a parachain is directly linked to the security of the entire Polkadot network. By sharing the security resources, parachains can focus on their specific functionalities and use cases while still enjoying high security.
Cross-Chain Communication
Parachains enable cross-chain communication and data sharing through the Polkadot Relay Chain. This interoperability feature allows different parachains to interact with each other seamlessly.
Parachains can exchange information, transfer assets, and collaborate on various functionalities without the need for complex bridges or intermediaries.
The Relay Chain acts as a communication hub, facilitating the exchange of data between parachains. This cross-chain communication unlocks new possibilities for collaboration and synergy between different blockchain networks.
It enables the transfer of assets from one parachain to another, opening up opportunities for decentralized finance, gaming, and other applications.
Upgradability
One of the key advantages of parachains is their upgradability without disrupting the entire network.
Parachains can be upgraded with new features, improvements, or bug fixes while maintaining compatibility with the existing network infrastructure. This allows for the continuous evolution and improvement of parachain functionalities over time.
The upgradability of parachains is facilitated by the modular architecture of the Substrate framework. Developers can introduce changes to specific modules or components of the parachain without affecting the overall network.
This flexibility ensures that parachains can adapt to changing requirements, incorporate new technologies, and address emerging challenges without sacrificing compatibility or security.
What are the Benefits of Parachains?
Parachains offer several benefits that enhance the capabilities of blockchain technology. Some of the key advantages include:

Scalability
Parachains allow for horizontal scalability, enabling multiple chains to run simultaneously. This increases the overall transaction throughput of the network.
Interoperability
Parachains can communicate and share data with each other through the Relay Chain. This fosters collaboration and the seamless transfer of assets between different chains.
Customizability
Each parachain can have its own set of rules, logic, and functionalities, making it suitable for specific use cases. Developers have the freedom to create tailored solutions without compromising on security.
What is Parachain Consensus?
Parachain consensus refers to the mechanism by which agreement is reached on the validity of transactions and the state of the parachain. In Polkadot, the Relay Chain utilizes a shared security model called nominated proof-of-stake (NPoS).
Validators are elected by DOT token holders to secure the Relay Chain and validate transactions across all parachains. This consensus mechanism ensures the integrity and security of the entire network.
Making Sense of Parachain Types & Slot Allocation
Alright, so you’ve got your parachain ready. But it needs a home, right? That’s where the concept of slots comes in. Parachains need to nab one of the limited slots (rumored to be around 100) to be part of the Polkadot system. The good news? These slots are set to increase over time gradually.

Exploring Common Good Parachains
Some slots are special, set aside for parachains that serve the greater good of the entire Polkadot ecosystem – the Common Good Parachains. They usually fall into one of two types: system-level chains or public utility chains.
These lucky parachains don’t need to compete in the parachain auctions. Instead, they’re granted slots by the on-chain governance system. This privilege is not eternal, though. It can only be taken away through governance.
Unveiling Parachain Auctions
Most parachains, however, have to fight it out in the parachain auctions. They can either place their bids using Polkadot’s (DOT) or Kusama’s (KSM) native tokens, or crowdsource these tokens through something called crowdloans.
In the latter case, DOT holders can contribute their tokens to the parachain in exchange for certain rewards.
Now, for parachains that don’t fit the common-good criteria and wish to be continuously part of the system, they can lease a slot on the Relay Chain.
But winning a parachain slot auction comes with a price – teams need to put a substantial amount of DOT or KSM on the line for the lease duration, which can be up to two years, divided into three-month periods.
Understanding Crowdloans
Some parachains have come up with a smart way to raise the stake for the auction bid – crowdloans. Here, DOT or KSM holders can back their preferred projects.
Now, since these contributors miss out on staking rewards during the lease, the parachains decide how to compensate for this loss. The beauty of crowdloans is that it’s arguably a safer and fairer model for token distribution.
Instead of giving up their tokens for good, users let their tokens be temporarily reserved. This ensures that the project teams are kept on their toes to deliver, while reducing the risk exposure for users.
How Parachains Work?
Now, what sets Polkadot and Kusama networks apart from say, Ethereum? Well, the former are more like superhighways that let both tokens and information flow freely.

On the other hand, on Ethereum, decentralized applications are confined to the framework set by its blockchain. But here’s where Polkadot and Kusama up the game. They empower developers to build their own unique blockchains.
And these personalized blockchains, or parachains, aren’t just unique for namesake. They can be tailored with their own features, like block times, fees for transactions, reward mechanisms for mining, and governance systems.
What’s more, while enjoying this customization, parachains also reap the benefits of Polkadot and Kusama network’s sturdy security, maintained by what’s called the Relay Chain.
Instead of depending on their personal squad of validator nodes, parachains are kept up and running by collator nodes. These nodes not only store the full history for each parachain but also bundle up parachain transaction data into blocks for the Relay Chain.
What can Parachains be Used for?
Parachains have a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the use cases include:

Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Parachains offer a powerful platform for hosting decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols. DeFi aims to transform traditional financial systems by providing open, transparent, and permissionless financial services.
Parachains enable secure and transparent financial transactions without the need for intermediaries such as banks or financial institutions.
DeFi on parachains enables users to engage in various financial activities like lending, borrowing, trading, and yield farming. Smart contracts handle these operations autonomously, eliminating intermediaries and reducing costs. The decentralized nature ensures secure and censorship-resistant transactions.
Supply Chain Management
Parachains have the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by enabling transparent and auditable tracking of goods and products.
In traditional supply chains, tracking and verifying the authenticity of products can be challenging and susceptible to fraud. Parachains address these issues by providing a tamper-proof and transparent infrastructure for supply chain management.
Through the use of unique identifiers and blockchain technology, parachains can create an immutable record of every step in the supply chain. This record includes information such as the origin of raw materials, manufacturing processes, transportation, and final delivery.
By leveraging parachains, businesses and consumers can verify the authenticity and integrity of products, reduce fraud, and enhance trust in the supply chain.
Gaming and NFTs
Parachains offer a secure and efficient infrastructure for decentralized gaming platforms and non-fungible tokens (NFTs). The gaming industry has seen a rapid rise in the adoption of blockchain technology, and parachains provide an ideal environment for hosting decentralized games.
With parachains, game developers can create unique gaming experiences, leveraging the security, transparency, and interoperability provided by the Polkadot network. Parachains enable the ownership and trading of in-game assets as NFTs, allowing players to truly own their digital assets and transfer them seamlessly across different games and platforms.
NFTs, in particular, have gained significant attention in recent years. Parachains facilitate the creation and trading of NFTs, which represent unique digital assets such as artwork, collectibles, or virtual real estate.
By utilizing parachains, artists, creators, and collectors can benefit from the decentralized and transparent nature of NFTs, fostering a vibrant digital art and collectibles market.
How to Run a Parachain on Polkadot?
Running a parachain on Polkadot involves several significant steps:
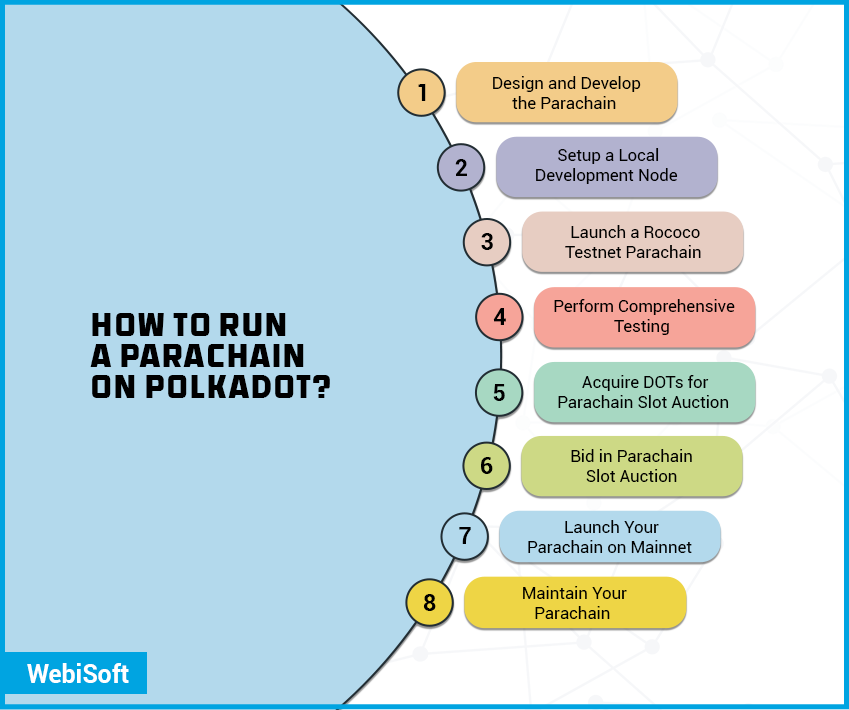
Design and Develop the Parachain
This involves designing your application and developing the parachain using the Substrate framework. Substrate is a modular framework that allows you to create your blockchain, developed by Parity Technologies, the team behind Polkadot.
You can customize your chain for your use case, and then connect it to the Polkadot network as a parachain.
Setup a Local Development Node
You should setup a local Polkadot node for testing. To do this, you can follow the Polkadot build guide on their official website or GitHub repository.
Launch a Rococo Testnet Parachain
Rococo is a Polkadot testnet specifically designed for testing parachains. Registering your parachain on Rococo is an essential step for testing how your chain interacts with the Polkadot relay chain and other parachains.
Perform Comprehensive Testing
Ensure that your parachain operates correctly in a multi-chain environment on the Rococo testnet. Test the functionality of your chain thoroughly, including transaction processing, consensus mechanism, interaction with the Relay Chain and other parachains, and any custom functionality you’ve built.
Acquire DOTs for Parachain Slot Auction
Polkadot uses an auction mechanism to allocate parachain slots, and this requires DOT tokens. You can acquire DOT tokens through public sale, private sale, or on the open market. Ensure that you have enough DOTs to bid for a slot.
Bid in Parachain Slot Auction
When you’re ready, you can bid in the parachain slot auction. If you win the auction, your chain can be connected to the Polkadot network as a parachain for the duration of the slot lease.
Launch Your Parachain on Mainnet
After winning the slot auction, you can launch your parachain on the Polkadot mainnet. Ensure you have validators ready to validate transactions on your parachain.
Maintain Your Parachain
After launching, you’ll need to maintain your parachain. This includes regular updates, dealing with potential issues or bugs, and possibly ongoing participation in slot auctions to maintain your parachain slot.
How to Rent a Parachain: A Guide to the Process
There’s a bit of competition when it comes to securing a spot for your blockchain in the Polkadot ecosystem, mainly because these so-called parachain slots are limited in number. So, how does one go about renting a parachain?

The Auction: Bidding for a Slot
As it stands, the process involves an auction. Interested parties place bids using DOT, the native token of the Polkadot network. Winning the auction doesn’t come without its conditions though. The amount of DOT bid by the winning party is held as a deposit throughout the lease period.
The Minimum Bid: Setting the Stage
Be prepared. The bar is set fairly high for these auctions, with the minimum bid starting at around 10,000 DOT. At the time of writing, this translates to roughly 400,000 USD. A serious investment indeed.
Crowdloans: Boosting the Bid
Given the considerable financial commitment, bidders often turn to their supporters for help. They request them to contribute their own DOT to bolster the bid. This practice is known as a Polkadot crowdloan.
The Payoff: Tokens in Return
What’s in it for the supporters, you may ask? Well, in exchange for their contribution, the crowdloan participants receive tokens issued by the Parachain company during the rental period. If the company thrives, these supporters, or ‘crowdloaners’, stand to make a considerable return on their investment.
Exploring Parachain Projects: Examples and Use Cases
One of the most exciting aspects of the parachain universe is its inherent specialization. It’s not about being a jack of all trades, but rather mastering one. Let’s dive into some examples of these super-powered projects, either in progress or currently bidding for a parachain slot.

Efinity: Pioneering the NFT and Metaverse Realms
Efinity takes the lead in the realm of cross-chain Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and the expansive metaverse. This parachain project specializes in these next-gen digital phenomena, paving the way for new interactions and transactions.
KILT: Simplifying Verification Processes
KILT has a very different focus. Its goal? To make verification of credentials easier and more straightforward for individuals and businesses alike. It’s all about streamlining and enhancing the trust within the digital world.
Bifrost: Optimizing Investments for Crowdloan Providers
Bifrost takes a financial route, concentrating on making it possible for crowdloan providers to reinvest their DOT deposits. This project focuses on optimizing the investment landscape within the Polkadot ecosystem.
Phala: Prioritizing User Privacy
Phala aims to tackle a persisting issue in the world of public blockchains: user privacy. This parachain project is designed to ensure that user privacy is maintained, safeguarding sensitive information within the transparent blockchain environment.
Subsocial: Powering Decentralized Social Networks
Lastly, we have Subsocial, a project dedicated to empowering users to create their own decentralized social networks. This project encapsulates the essence of decentralization, allowing users to have their autonomous digital social platforms.
These diverse parachain projects showcase the potential and versatility of the Polkadot ecosystem. Each parachain, with its distinct focus, contributes to creating a rich and diverse blockchain environment.
What about Parathreads?
Lastly, let’s talk about another cool feature of the Polkadot system – parathreads.

They’re somewhat like parachains, but from an economic viewpoint, they’re quite different. Parathreads connect to Polkadot via a pay-per-block model. They’re perfect for projects that only need temporary connectivity to the Polkadot system or can’t get their hands on a full parachain slot.
Even though parathreads have slower block times than parachains, they still enjoy the same level of security and interoperability features. And depending on their needs and availability of slots on the Relay Chain, any blockchain can switch between being a parachain or a parathread. That’s flexibility for you!
Acala Network: Stepping into Polkadot’s Parachain Ecosystem
Acala Network’s triumphant claim of the first parachain slot on the Rococo Testnet marked a significant step towards Polkadot’s vision for a sharded parachain ecosystem. The so-called “DeFi hub” for Polkadot, Acala Network, took to the stage on March 26th, 2021 to share the exciting news.

Not long before, in February, Acala launched an Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) based on Polkadot’s Substrate framework. This move aimed to bridge interoperability with assets native to Ethereum.
But the ambitions don’t stop there. Acala has set its sights on cross-chain interoperability on the flourishing Polkadot Network. Plus, it intends to introduce a dollar-pegged stablecoin, specially crafted for cross-chain applications, to be a part of any Polkadot-based project.
Rococo came into existence in August 2020 as a parachain testnet launched by Polkadot. Its mission? To put cross-shard communication protocols to the test for Polkadot and to allow projects to unfurl as parachains on Polkadot’s sibling chain, the Kusama Network.
Kusama Parachain Auctions: The Adventure Begins
Not one to be left behind, Polkadot’s ‘canary network’ Kusama also embarked on the journey of implementing parachain slot auctions. It’s on the hunt for the crème de la crème of projects to join its Network as parachains. The adventure began with the launch of Kusama Chain Candidate 1 in August 2019.
The first to break the ice was Statemine, essentially Kusama’s iteration of Polkadot’s Statemint. This Polkadot-based, generic asset parachain was conceived by Parity Technologies. Its mission is to offer users a platform for deploying assets ranging from CBDCs, stablecoins, to other fungible tokens, and even NFTs.
In Kusama’s landscape, Statemine serves as a common goods parachain, acquiring its slot through governance rather than an auction system. It offers a platform for deploying an array of digital currencies, including CBDCs, NFTs, and other fungible tokens.
Although Statemine’s standalone utility adds significant value to the KSM ecosystem, its true potential will come to the fore when the community of interoperable parachain networks sprouts on the Kusama architecture.
The grand opening of Kusama’s first parachain slot auction took place on June 15th, 2021. Karura Network emerged victorious, locking up a bid of 500,000 KSM, which translated to more than $100 million at the time.

Mirroring its sibling, Acala Network, Karura Network aspires to deliver a similar DeFi hub but on Kusama’s stage. While the two are engineered to operate concurrently and employ the same code, they differ in their financial derivatives. The expectation is for them to achieve full interoperability once the cross-chain bridge between Polkadot and Kusama is up and running.
The Growing Buzz Around Parachains: What’s Ahead?
There’s no doubt that parachains are stirring up excitement across the blockchain landscape. They’ve grabbed the attention of users, investors, and developers alike.
The proof? Over $200 million has already been raised through slot auctions, and various campaigns have been initiated in the competitive race to secure a parachain slot.

At present, the secured parachain slots on the Kusama Network are held by Karura Network, Statemine, and Moonriver. But if we take a closer look at the PolkadotJS App, it’s clear there are more to come.
Polkadot’s Upcoming Parachains
Parachains specifically for Polkadot are slated to be launched later this year, but the exact timeline remains uncertain. To provide some clarity, Polkadot’s founder Gavin Wood explained:
“The launch of Polkadot’s parachains will kick-off when two milestones are reached: first, an exhaustive external audit of all new logic must be finished; and second, Kusama’s canary network should prove the functionality of the new logic by successfully conducting at least one auction that includes crowdloans and hosting at least one working parachain. Once Kusama’s first auctions conclude successfully, we can expect Polkadot’s auctions to follow shortly after.”
— Gavin Wood – Polkadot Medium
What are the Fees and Costs of Running a Parachain?
Running a parachain on Polkadot incurs certain fees and costs. Let’s explore the different aspects involved:

Slot Auction Costs
Acquiring a parachain slot through the slot auction requires bidding with DOT tokens, the native cryptocurrency of the Polkadot network.
The costs associated with winning a slot auction can vary depending on the demand for slots and the competitiveness of the auction. Higher demand and competition can drive up the costs of acquiring a slot.
Development and Infrastructure Costs
Developing and deploying a parachain involves costs associated with development resources and infrastructure. The development process requires skilled developers who are familiar with blockchain technology and the Substrate framework.
Additionally, infrastructure costs include hosting, server maintenance, and ongoing technical support.
Operational Costs
Running a parachain requires validators to stake and lock up DOT tokens as collateral. Validators play a crucial role in securing the network and validating transactions.
As a validator, there may be costs associated with acquiring and staking the required number of DOT tokens. Validators also need to maintain their infrastructure, such as servers and network connectivity, which incurs operational expenses.
Governance Costs
Participating in governance processes can involve costs. In order to vote or make proposals, token holders may need to lock up their tokens or pay transaction fees. These costs contribute to the governance mechanism’s overall functioning and ensure the active involvement of token holders in decision-making processes.
Conclusion
Think of parachains as the building blocks that fuel the cross-chain interaction and flexibility within Polkadot and Kusama Networks. They pave the way for an adaptable and highly dynamic structure.
Essentially, with the incorporation of parachains, Polkadot splits its foundation into several simultaneous Layer-1 blockchains. This enables it to process transactions more efficiently and decentralize the movement of assets across the network.
Aligning with the vision of future blockchains, Polkadot’s parachain model supports the notion that these blockchains should offer a wide range of specialized functionalities.
Given their inherent adaptability, scalability, and ability to work in tandem, parachains may well provide the key to overcoming the most critical challenges plaguing the blockchain technology today. They could potentially resolve the intricate hurdles that have so far hindered blockchain from becoming mainstream and finding extensive use.
Now that we’ve unpacked the potential of parachains, it’s clear how pivotal they could be for the future of blockchain technology. Are you interested in exploring more about blockchain solutions and how they can benefit your business?
At Webisoft, we’re at the forefront of the latest blockchain developments and ready to assist. Let’s connect today and discover the right blockchain solutions for your needs!
FAQs
How does Polkadot connect blockchains?
Polkadot connects blockchains via its relay chain, which serves as the central hub. Parachains (parallel chains) and Parathreads (pay-as-you-go chains) connect to the relay chain, allowing them to interoperate and share security.
What problems do Parachains solve?
Parachains address the issue of blockchain scalability by processing transactions concurrently rather than sequentially. They also solve interoperability challenges, allowing diverse blockchains to communicate and interact. Lastly, they mitigate the security issue by sharing the security of the Polkadot relay chain.
