Machine Learning in Recruitment: Hiring Decisions Explained
- BLOG
- Artificial Intelligence
- February 15, 2026
Machine learning in recruitment is no longer an experimental add-on to hiring software. 87 percent of companies use AI-driven systems to screen resumes, rank candidates, and manage growing applicant volumes as hiring moves firmly into data-led territory.
Still, this shift is not about replacing recruiters with algorithms. It is about handling volume, speed, and consistency without burning out hiring teams or turning recruitment into keyword roulette.
To understand what that support actually looks like, this article breaks down how ML in recruitment is applied and where it fits in the hiring process. It also explains what it improves, what can go wrong, and how teams can use it responsibly in real hiring scenarios.
Contents
- 1 What Is Machine Learning in Recruitment?
- 2 Why Recruitment Needs Machine Learning Today
- 3 Design recruitment machine learning systems for real hiring.
- 4 Where Machine Learning Fits in the Recruitment Lifecycle
- 4.1 Talent Sourcing and Market Mapping
- 4.2 Resume Parsing and Initial Screening
- 4.3 Candidate Ranking and Shortlisting
- 4.4 Recruiter Decision Support
- 4.5 Job Description Analysis and Role Calibration
- 4.6 Candidate Rediscovery and Talent Pool Reuse
- 4.7 Post Interview Signal Consolidation
- 4.8 Retention and Post Hire Outcome Analysis
- 4.9 Workforce Demand Forecasting
- 5 How Machine Learning for Recruitment Systems Actually Work
- 5.1 Step 1: Collect Hiring Data Inputs
- 5.2 Step 2: Convert Unstructured Text Into Structured Fields
- 5.3 Step 3: Extract Useful Signals From Candidate and Role Data
- 5.4 Step 4: Run the Model to Generate Rankings or Fit Scores
- 5.5 Step 5: Present Recommendations Inside the Recruiter Workflow
- 5.6 Step 6: Capture Recruiter Feedback and Hiring Outcomes
- 5.7 Step 7: Update and Monitor the System Over Time
- 6 Machine Learning Models Used in Recruitment
- 6.1 Supervised learning for candidate screening and ranking
- 6.2 Unsupervised learning for organizing large talent pools
- 6.3 Natural language processing for resume and job description analysis
- 6.4 Similarity and matching models for candidate shortlisting
- 6.5 Predictive models for recruitment pipeline support
- 7 Benefits of Machine Learning in Recruitment Process
- 7.1 Better Candidate Prioritization at Early Stages
- 7.2 More Consistent Screening Across Hiring Teams
- 7.3 Reduced Manual Effort in High Volume Hiring
- 7.4 Improved Visibility Into Hiring Pipelines
- 7.5 Scalable Hiring Without Loss of Structure
- 7.6 Support for Fairer and More Accountable Review
- 7.7 Data Driven Fairness Monitoring
- 8 Limitations and Risks of Machine Learning in Hiring
- 9 Implementing Machine Learning in Recruitment the Right Way
- 10 Future Trends of Machine Learning in Recruiting
- 11 Machine Learning Recruitment Solutions Built by Webisoft
- 11.1 Recruitment Use Case Strategy and Data Readiness
- 11.2 Custom Models Built Around Your Hiring Rules
- 11.3 Production Deployment That Holds Up Under Real Load
- 11.4 Monitoring, Drift Detection, and Controlled Retraining
- 11.5 System Integration That Fits Your Existing Stack
- 11.6 Flexible Delivery Options for Your Team Structure
- 12 Design recruitment machine learning systems for real hiring.
- 13 Conclusion
- 14 Frequently Asked Question
What Is Machine Learning in Recruitment?
Machine learning in recruitment refers to the use of data driven algorithms to support hiring decisions across sourcing, screening, and candidate evaluation. These systems analyze patterns from resumes, job descriptions, recruiter feedback, and hiring outcomes to generate predictions rather than relying on fixed rules.
Unlike traditional recruitment software that follows predefined filters, machine learning models adapt based on historical hiring data and ongoing inputs.
The goal is to assist recruiters by identifying relevant candidates, ranking profiles, and highlighting signals that may not be visible through manual review alone.
Why Recruitment Needs Machine Learning Today
 Recruitment has shifted from low volume decision making to large scale filtering under time pressure. Manual reviews and rule based systems struggle to keep up with this change.
Recruitment has shifted from low volume decision making to large scale filtering under time pressure. Manual reviews and rule based systems struggle to keep up with this change.
Machine learning helps hiring teams manage volume, consistency, and accountability without removing human judgment.
Application Volume Has Outpaced Manual Screening
Many roles attract hundreds or thousands of applications within days. Recruiters cannot review each profile with the same level of attention, which leads to delays, inconsistent screening, and missed candidates. Machine learning supports early prioritization so human review focuses on the most relevant profiles.
Keyword Filters Fail to Reflect Real Hiring Needs
Keyword based screening treats resumes as text matches rather than experience histories. Candidates with relevant skills expressed differently, or gained across varied roles, are often excluded.
Machine learning analyzes patterns and relationships in data, allowing screening to move beyond rigid keyword logic.
Hiring Decisions Lack Consistency at Scale
As hiring teams grow, decisions vary by recruiter, region, or workload. This inconsistency affects candidate quality and hiring outcomes.
Machine learning introduces shared evaluation signals based on historical hiring data, which helps standardize shortlisting without forcing uniform decisions.
Fair Hiring Requires Measurable Oversight
Hiring processes are increasingly reviewed for bias and unequal outcomes. Manual processes offer limited visibility into decision patterns.
Machine learning systems make it easier to analyze trends across hiring stages and identify where adjustments are needed.
Speed Expectations Conflict With Hiring Quality
Organizations are under pressure to reduce time to hire while maintaining candidate standards. Faster manual screening often lowers review quality.
Machine learning supports quicker prioritization and ranking, allowing recruiters to move faster without relying on rushed judgments.
Design recruitment machine learning systems for real hiring.
Discuss hiring data readiness, workflows, and deployment with Webisoft experts!
Where Machine Learning Fits in the Recruitment Lifecycle
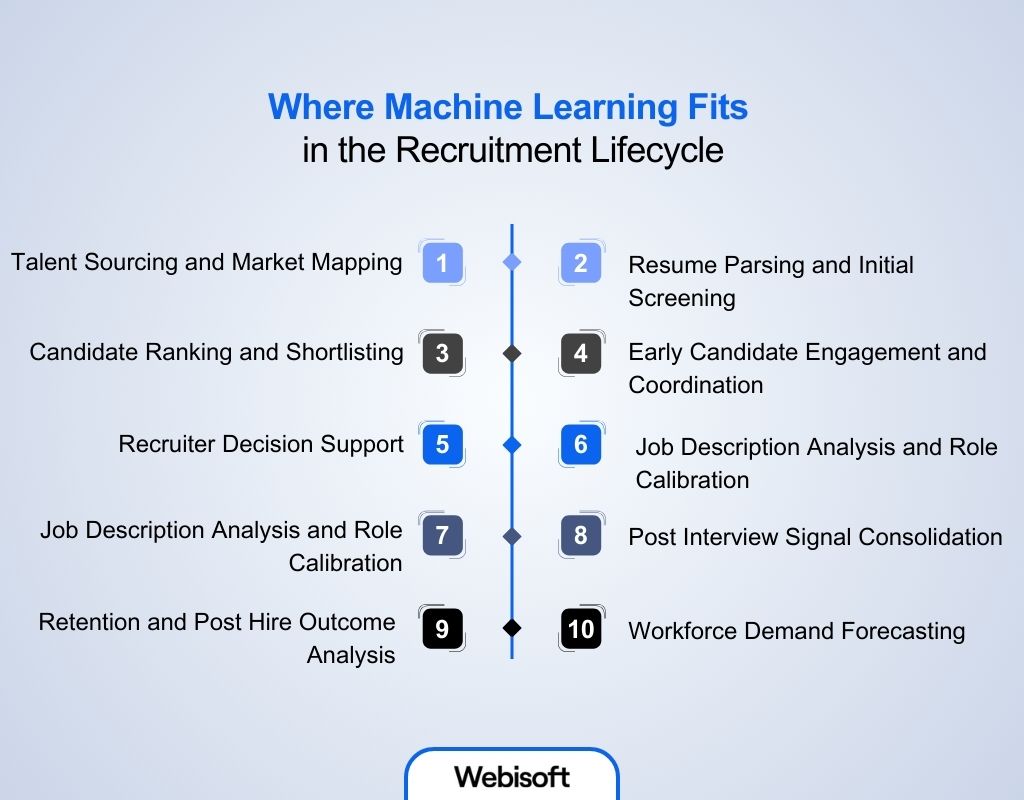 Machine learning supports recruitment at specific stages where volume, repetition, and pattern recognition affect outcomes.
Machine learning supports recruitment at specific stages where volume, repetition, and pattern recognition affect outcomes.
Instead of replacing recruiters, it operates alongside existing workflows, helping teams manage scale, prioritize effort, and maintain consistency across the hiring lifecycle.
Talent Sourcing and Market Mapping
Machine learning is used to analyze large talent datasets to identify potential candidates beyond active applicants. It helps surface passive profiles, map skill availability, and highlight candidate pools aligned with role requirements and hiring demand.
Resume Parsing and Initial Screening
At the application stage, machine learning structures resume data into standardized formats. This allows hiring teams to review candidates based on experience, skills, and relevance rather than raw document layout or keyword presence.
Candidate Ranking and Shortlisting
Machine learning supports shortlisting by ranking candidates based on multiple signals instead of binary filters. Recruiters receive prioritized lists that reflect role alignment while retaining control over final selection decisions.
Early Candidate Engagement and Coordination Some recruitment workflows use machine learning to assist with interview scheduling and early communication. These systems help manage response timing, availability matching, and candidate follow ups during high volume hiring periods.
Recruiter Decision Support
During final review stages, machine learning provides contextual insights such as profile comparisons or historical hiring patterns. These signals support recruiter judgment without automating hiring decisions or removing human accountability.
Job Description Analysis and Role Calibration
Machine learning can analyze job descriptions to identify unclear requirements, skill inflation, or misaligned expectations. This helps teams refine roles before sourcing begins and improves downstream candidate relevance.
Candidate Rediscovery and Talent Pool Reuse
Machine learning helps revisit past applicants and internal talent pools by re-evaluating profiles against new roles. This reduces repeated sourcing effort and improves the value of existing candidate data.
Post Interview Signal Consolidation
After interviews, machine learning can help organize interviewer feedback by identifying common themes and inconsistencies. This supports structured review without scoring or overriding recruiter judgment.
Retention and Post Hire Outcome Analysis
Machine learning in recruitment does not end at offer acceptance. In some environments, hiring data connects with post hire signals such as tenure and early attrition. This helps teams evaluate whether screening and shortlisting decisions align with long term role stability and informs future hiring adjustments.
Workforce Demand Forecasting
Machine learning also supports recruitment before roles are opened. By analyzing historical hiring volume, seasonal shifts, and business growth signals, models can anticipate workforce demand. This helps teams prepare sourcing strategies earlier and reduce reactive hiring driven by urgent staffing gaps.
How Machine Learning for Recruitment Systems Actually Work
 AI and Machine learning in recruitment systems follow a repeatable workflow that turns hiring inputs into ranked recommendations. The system does not make final hiring decisions. It generates structured signals that recruiters can review, validate, and act on.
AI and Machine learning in recruitment systems follow a repeatable workflow that turns hiring inputs into ranked recommendations. The system does not make final hiring decisions. It generates structured signals that recruiters can review, validate, and act on.
Step 1: Collect Hiring Data Inputs
The system pulls data from resumes, job descriptions, application forms, recruiter actions, interview notes, and past hiring outcomes. These inputs define what the role needs and what each candidate offers.
Step 2: Convert Unstructured Text Into Structured Fields
Resumes and job descriptions are processed so the content becomes searchable, comparable data. Skills, titles, years of experience, education, certifications, and role history are mapped into consistent fields.
Step 3: Extract Useful Signals From Candidate and Role Data
From those structured fields, the system derives signals such as skill overlap, role similarity, seniority alignment, keyword context, job stability patterns, and relevant experience depth.
Step 4: Run the Model to Generate Rankings or Fit Scores
Machine learning models analyze the extracted signals and produce a score or rank for each candidate. This output represents relative relevance for that role, not a final pass or fail decision.
Step 5: Present Recommendations Inside the Recruiter Workflow
Results appear in the hiring workflow as ranked lists, suggested shortlists, or flagged profiles. Recruiters can review the evidence, compare candidates, and decide what moves forward.
Step 6: Capture Recruiter Feedback and Hiring Outcomes
Recruiter actions, interview outcomes, and final hiring decisions are recorded as feedback. This feedback becomes training signals that help the system adjust future recommendations, a practice aligned with workforce data governance principles.
Step 7: Update and Monitor the System Over Time
The system is periodically updated to reflect role changes, new skill demands, and shifting candidate markets. Monitoring is necessary to prevent performance drop, drift, or repeated patterns that harm hiring quality.
Understanding how recruitment ML systems work is one thing. Building them correctly is another. Webisoft helps teams design and implement recruitment machine learning systems that align with real hiring data, recruiter workflows, and operational constraints.
Machine Learning Models Used in Recruitment
 Recruitment platforms rely on specific machine learning model types, each applied to a defined hiring task. These models are selected based on how recruiters screen, compare, and manage candidates across the hiring process, not on abstract machine learning theory.
Recruitment platforms rely on specific machine learning model types, each applied to a defined hiring task. These models are selected based on how recruiters screen, compare, and manage candidates across the hiring process, not on abstract machine learning theory.
Supervised learning for candidate screening and ranking
Supervised learning is used in recruitment when historical hiring outcomes are available, such as shortlisted candidates, interview selections, or past hires.
In this context, the goal is not automation, but learning patterns that reflect how recruiters have evaluated candidates for similar roles. Supervised models are commonly used in recruitment to:
- Rank applicants during resume screening based on relevance to the role
- Reflect role specific hiring patterns from past recruiter decisions
- Support consistent shortlist creation for recurring hiring needs
Unsupervised learning for organizing large talent pools
Many recruitment datasets do not include explicit labels, especially at early application stages. Unsupervised learning allows hiring teams to organize candidate data without predefined outcomes, helping recruiters make sense of large applicant volumes. These models are applied in recruitment to:
- Group candidates with similar experience or skill profiles after intake
- Structure high volume applicant pools for easier review
- Support rediscovery of past candidates for new or evolving roles
Natural language processing for resume and job description analysis
Recruitment relies heavily on unstructured text, including resumes and job descriptions. Natural language processing models are used to interpret this text in a way that reflects meaning rather than surface level keyword matches. In recruitment workflows, NLP models help:
- Extract skills, responsibilities, and experience from resumes
- Interpret job requirements expressed in different formats
- Enable structured comparison between candidate profiles and role needs
Similarity and matching models for candidate shortlisting
Similarity models are used when recruiters need to compare candidates against job requirements or existing employee profiles. Especially when experience does not align perfectly with job titles or exact skill lists. These models support recruitment by:
- Comparing candidate profiles with role requirements beyond keywords
- Identifying transferable or adjacent skills across industries
- Assisting shortlisting for roles with flexible experience criteria
Predictive models for recruitment pipeline support
Predictive models in recruitment focus on understanding how candidates move through hiring stages based on past patterns. These models are not used to decide who should be hired, but to support pipeline awareness and planning. They are applied to recruitment tasks such as:
- Anticipating candidate progression through interview stages
- Identifying points where candidate drop off commonly occurs
- Supporting recruiter workload and hiring timeline planning
Benefits of Machine Learning in Recruitment Process
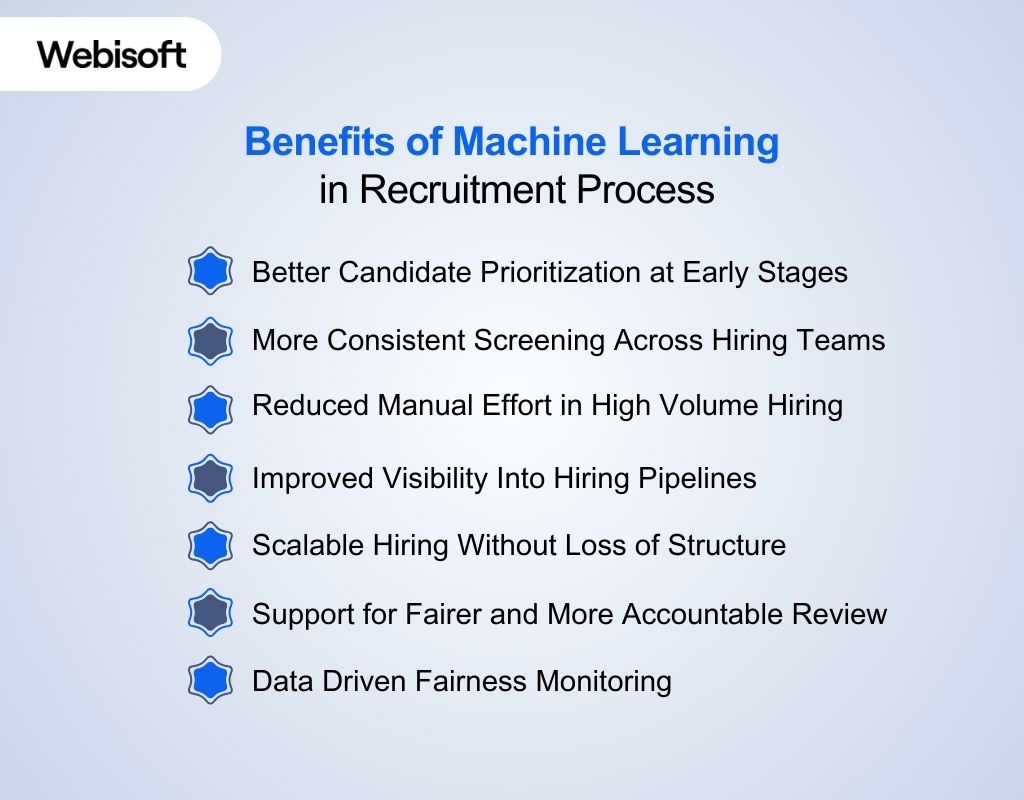 Machine learning supports recruitment by improving how candidates are reviewed and prioritized at scale. Its value is most visible in high volume hiring, where time limits and repetition affect decision consistency. Below are the key benefits of using machine learning in recruitment:
Machine learning supports recruitment by improving how candidates are reviewed and prioritized at scale. Its value is most visible in high volume hiring, where time limits and repetition affect decision consistency. Below are the key benefits of using machine learning in recruitment:
Better Candidate Prioritization at Early Stages
Machine learning helps recruiters handle large application volumes by ranking and organizing profiles based on relevance signals.
This allows early attention to focus on candidates who align more closely with role requirements, instead of relying on random or first come review order.
More Consistent Screening Across Hiring Teams
Recruitment decisions often differ between recruiters, teams, or regions. Machine learning introduces shared reference signals based on past hiring data, which supports more consistent screening without forcing uniform decisions.
Reduced Manual Effort in High Volume Hiring
Screening large numbers of applications manually requires significant time and effort. Machine learning reduces repetitive review tasks, allowing recruiters to spend more time on evaluation, interviews, and candidate communication.
Improved Visibility Into Hiring Pipelines
Machine learning makes it easier to observe how candidates move through different stages of recruitment. This visibility helps teams identify delays, bottlenecks, or uneven drop off points within the hiring process.
Scalable Hiring Without Loss of Structure
As organizations grow, hiring processes often become fragmented. Machine learning supports structured screening and prioritization across multiple roles and locations, helping teams scale recruitment more reliably.
Support for Fairer and More Accountable Review
By analyzing hiring patterns over time, machine learning helps teams recognize inconsistencies in screening and shortlisting. This awareness supports process improvements that encourage more balanced candidate evaluation.
Data Driven Fairness Monitoring
Machine learning enables teams to review structured hiring outcomes across screening and shortlisting stages. Instead of relying on assumptions, organizations can identify inconsistencies across roles or candidate groups, supporting more transparent and accountable recruitment decisions without removing recruiter judgment.
Limitations and Risks of Machine Learning in Hiring
Machine learning adds structure to recruitment, but it also introduces constraints that hiring teams must manage carefully.
These limitations appear when models interact with real hiring data, human judgment, and organizational practices. Understanding these risks is necessary before relying on machine learning for hiring decisions.
- Historical Bias Propagation: Models learn from past hiring data. If previous decisions favored certain profiles or backgrounds, the system may repeat those patterns instead of correcting them.
- Incomplete or Low Quality Hiring Data: Recruitment data is often inconsistent, missing, or subjective. Poor input data can lead to unreliable rankings and misleading candidate signals.
- Loss of Context in Candidate Evaluation: Machine learning focuses on patterns, not personal nuance. Career breaks, unconventional paths, or soft skills may be undervalued if not captured clearly in data.
- Overdependence on Automated Rankings: Recruiters may rely too heavily on model output, even when rankings conflict with human judgment or role specific context.
- Limited Transparency in Decision Signals: Some models produce scores without clear explanations. This makes it harder for recruiters to justify decisions to candidates or internal stakeholders.
- Model Drift Over Time: Hiring needs change as roles, skills, and markets evolve. Models trained on outdated data may lose relevance if not reviewed and updated regularly.
- Legal and Accountability Exposure: Automated decision support in hiring increases compliance responsibility. Organizations remain accountable for outcomes, even when decisions are influenced by machine learning systems.
- Fairness Metrics and Model Evaluation Challenges: Fair hiring depends on measurable criteria, yet defining fairness metrics in recruitment is complex, especially when historical data reflects imbalance. Without monitoring selection rates and proxy variables, models may reinforce bias and increase legal or reputational risk.
Implementing Machine Learning in Recruitment the Right Way
The limitations and risks of machine learning in hiring highlight why implementation matters as much as the technology itself.
Applying these systems correctly depends on how recruitment teams define boundaries, involve human judgment, and manage data across real hiring workflows.
- Clear Problem Definition: Recruitment teams must identify where machine learning adds value, such as screening volume or shortlist prioritization. Instead of applying it broadly without a defined hiring objective.
- Quality and Relevance of Hiring Data: Machine learning depends on accurate resumes, job descriptions, and recruiter feedback. Inconsistent or outdated data weakens model reliability and reduces trust in system outputs.
- Human Oversight and Decision Control: Machine learning should support recruiters, not replace them. Recruiters must remain responsible for final decisions, with clear checkpoints where human judgment overrides automated signals.
- Gradual Rollout and Pilot Testing: Introducing machine learning through limited pilots helps teams validate results, compare outcomes, and adjust workflows before full scale deployment.
- Integration With Existing Recruitment Systems: Machine learning works best when aligned with ATS and HR workflows. Poor integration increases friction and reduces adoption by hiring teams.
- Ongoing Review and Adjustment: Hiring needs evolve over time. Models require regular review to remain aligned with changing roles, skills, and recruitment priorities.
Future Trends of Machine Learning in Recruiting
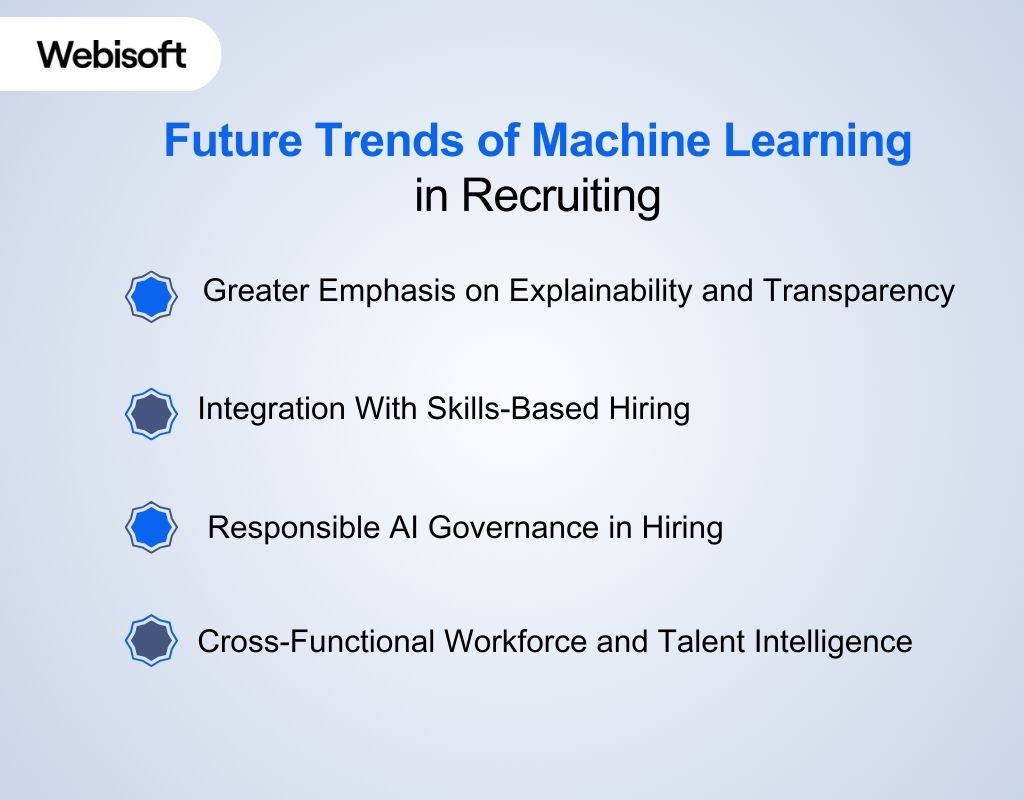 Machine learning in recruitment is moving from operational support to strategic workforce infrastructure. The focus is shifting toward transparency, skills intelligence, regulatory compliance, and long-term workforce alignment rather than simple automation gains.
Machine learning in recruitment is moving from operational support to strategic workforce infrastructure. The focus is shifting toward transparency, skills intelligence, regulatory compliance, and long-term workforce alignment rather than simple automation gains.
Greater Emphasis on Explainability and Transparency
As adoption increases, explainability is becoming a requirement rather than a feature. LinkedIn’s Future of Recruiting report shows 62% of talent professionals remain optimistic about AI in recruiting, though transparency concerns grow as adoption expands.
Organizations are now prioritizing interpretable ranking logic, audit trails, and human review checkpoints to ensure hiring decisions can be explained to candidates and regulators.
Integration With Skills-Based Hiring
Machine learning models are increasingly built around skill signals rather than rigid job titles. The World Economic Forum reports that 75% of companies plan to adopt
AI technologies by 2027, accelerating the shift toward structured skills intelligence across hiring systems. This shift supports skill adjacency mapping, internal mobility planning, and broader candidate pools beyond traditional title filters.
Responsible AI Governance in Hiring
Regulatory scrutiny around employment AI is increasing globally. Organizations are formalizing governance frameworks that include bias monitoring, documentation standards, and periodic model evaluation to manage legal and ethical risk in recruitment systems.
Governance is no longer optional; it is becoming embedded into procurement, deployment, and monitoring processes.
Cross-Functional Workforce and Talent Intelligence
Recruitment models are increasingly connected to retention data, performance indicators, and workforce planning systems.
This integration allows hiring decisions to be evaluated against long-term outcomes rather than short-term screening efficiency. Machine learning in recruitment is evolving from applicant filtering to workforce intelligence infrastructure.
Machine Learning Recruitment Solutions Built by Webisoft
 You have seen what machine learning can do in hiring and what can go wrong without control. At Webisoft, our job is to turn that into a production system recruiters can trust, with clear logic, stable performance, and real workflow fit.
You have seen what machine learning can do in hiring and what can go wrong without control. At Webisoft, our job is to turn that into a production system recruiters can trust, with clear logic, stable performance, and real workflow fit.
Recruitment Use Case Strategy and Data Readiness
We start by mapping your hiring goal to the data you already have, then close the gaps. Our team assesses data maturity and builds a practical roadmap before heavy build work begins.
Custom Models Built Around Your Hiring Rules
Generic templates fail when your roles and data are specific. We build custom ML models around your constraints and edge cases, so screening and matching reflect your hiring reality.
Production Deployment That Holds Up Under Real Load
A model that works in a notebook is not a hiring system. We deliver production ML with deployment design, safe rollouts, and infrastructure built for real traffic.
Monitoring, Drift Detection, and Controlled Retraining
Hiring data changes with skills, markets, and role shifts. We implement drift detection, monitoring, and retraining schedules, with rollback paths when performance drops.
System Integration That Fits Your Existing Stack
Recruitment systems depend on clean handoffs between tools. We build integration layers and data transformations so model outputs fit your current systems and formats.
Flexible Delivery Options for Your Team Structure
Some teams need a dedicated ML squad. Others need team extension or fixed scope delivery. We support multiple engagement models so you get the right pace and ownership level.
Hiring systems fail when recruitment data, workflows, and operational limits are not addressed before implementation. A conversation with Webisoft helps you assess whether machine learning fits your hiring structure and scale before moving into build, deployment, or long term operation.
Design recruitment machine learning systems for real hiring.
Discuss hiring data readiness, workflows, and deployment with Webisoft experts!
Conclusion
To bring it all together, machine learning in recruitment works best when it supports human decisions rather than replacing them. When applied with the right data, controls, and intent, it helps hiring teams manage scale, consistency, and accountability without losing judgment.
For teams ready to move from theory to execution, Webisoft helps turn recruitment goals into production-ready machine learning systems. Our focus stays on real hiring workflows, long-term reliability, and solutions recruiters can actually trust and use every day.
Frequently Asked Question
Can machine learning replace recruiters?
No. Machine learning supports recruiters by handling repetitive screening and data organization tasks. Human judgment remains necessary for interviews, contextual evaluation, stakeholder alignment, and relationship driven decisions that automated systems cannot perform.
Can machine learning predict candidate success?
Yes, but only to a limited extent. Machine learning can estimate progression likelihood using historical hiring data. These predictions are probabilistic, not definitive, and cannot account for future performance, team fit, or changing role expectations.
Does machine learning replace ATS systems?
No. Machine learning typically integrates with applicant tracking systems rather than replacing them. The ATS manages workflows and records, while machine learning adds intelligence through candidate ranking, analysis, and insight generation.


