Machine Learning in Healthcare: Key Uses and Benefits
- BLOG
- Artificial Intelligence
- December 27, 2025
Machine learning in healthcare is transforming how medical teams interpret clinical data, predict risks, and deliver timely treatment. As the volume of medical information grows, these systems help uncover patterns that support earlier diagnosis, personalised care, and more accurate decision-making. The result is faster insights, reduced variability, and improved patient outcomes across diverse clinical settings. This guide outlines how the technology is applied effectively, the benefits it delivers, and the practical steps required for safe and scalable implementation. Machine learning in healthcare works through healthcare machine learning algorithms that study large patient datasets and produce clinical insights. These systems learn patterns that support diagnosis, risk prediction, and daily decision making across hospitals.
Machine learning in healthcare works through healthcare machine learning algorithms that study large patient datasets and produce clinical insights. These systems learn patterns that support diagnosis, risk prediction, and daily decision making across hospitals. Machine learning supports diagnosis, prediction, and clinical decision-making across many areas of healthcare. It helps teams handle complex patterns, large datasets, and real-time signals that humans cannot process alone.
Machine learning supports diagnosis, prediction, and clinical decision-making across many areas of healthcare. It helps teams handle complex patterns, large datasets, and real-time signals that humans cannot process alone.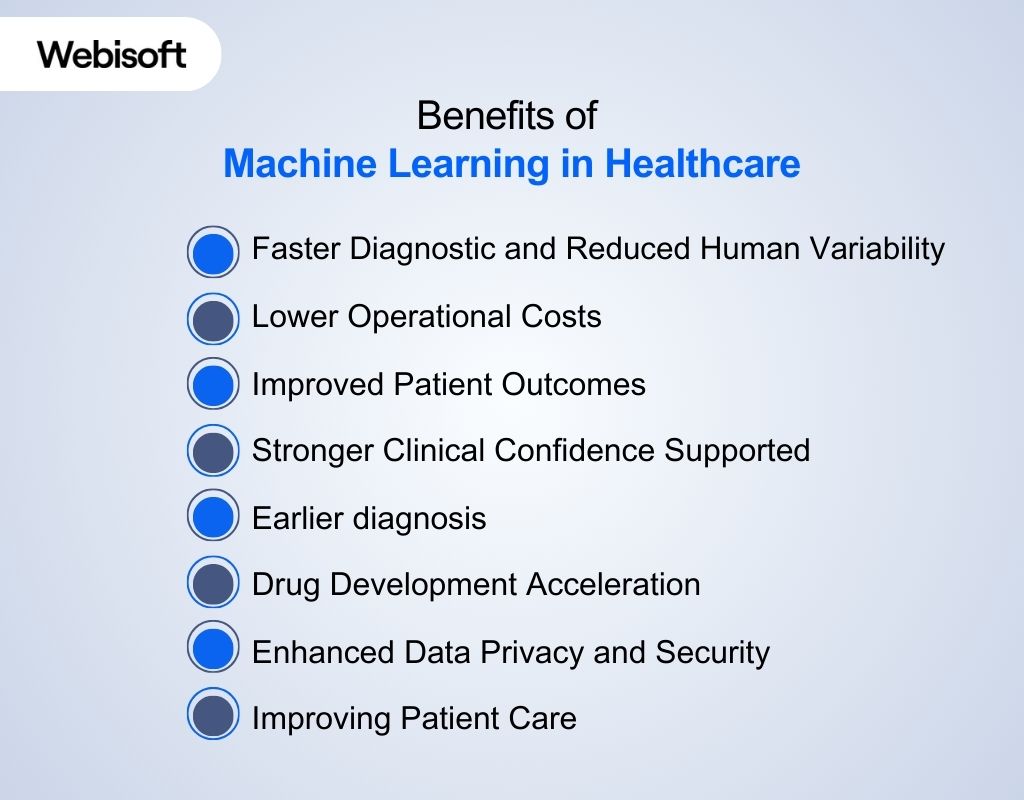 Machine learning strengthens clinical performance, operations, and research. It offers measurable gains in accuracy, consistency, and decision speed. These improvements highlight the growing influence of machine learning benefits in healthcare:
Machine learning strengthens clinical performance, operations, and research. It offers measurable gains in accuracy, consistency, and decision speed. These improvements highlight the growing influence of machine learning benefits in healthcare:  Machine learning offers major clinical advantages, but it also brings significant barriers that limit safe adoption. These issues influence reliability, trust, fairness, and long term performance. Together, they outline the core machine learning challenges in healthcare, which are:
Machine learning offers major clinical advantages, but it also brings significant barriers that limit safe adoption. These issues influence reliability, trust, fairness, and long term performance. Together, they outline the core machine learning challenges in healthcare, which are: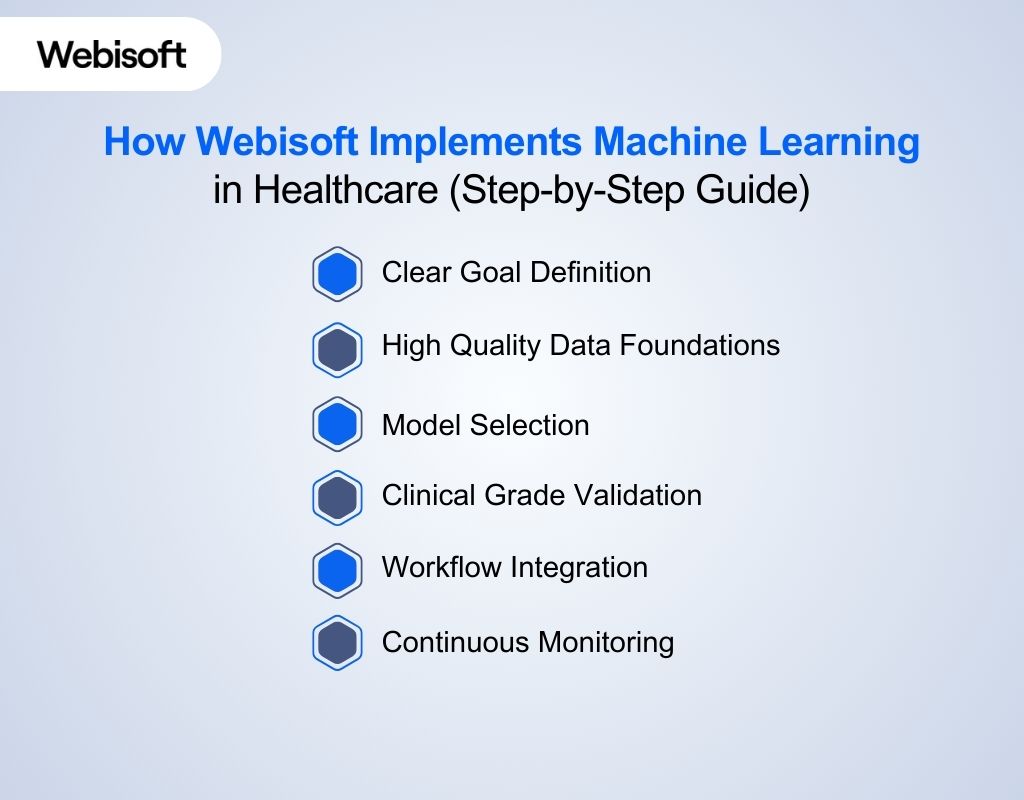 Machine learning in healthcare succeeds only when strategy, data integrity, workflow design, and clinical relevance move together. At Webisoft, we apply machine learning through a disciplined, engineering-driven process. The process is shaped by our experience in AI, IoT, EMR development, workflow automation, and remote patient monitoring. Each stage focuses on improving outcomes and lowering operational strain:
Machine learning in healthcare succeeds only when strategy, data integrity, workflow design, and clinical relevance move together. At Webisoft, we apply machine learning through a disciplined, engineering-driven process. The process is shaped by our experience in AI, IoT, EMR development, workflow automation, and remote patient monitoring. Each stage focuses on improving outcomes and lowering operational strain:
Contents
- 1 Understanding Machine Learning in Healthcare
- 2 How Machine Learning Works in Healthcare Settings
- 3 Key Applications of Machine Learning in Healthcare Today
- 3.1 ML for Diagnostic Imaging
- 3.2 Disease Prediction Models
- 3.3 Pattern-Based Decision Support
- 3.4 ML in Research
- 3.5 ML in Diagnosis and Risk Assessment
- 3.6 ML in Personalised Treatment
- 3.7 ML in Drug Discovery
- 3.8 ML in Predictive Analytics
- 3.9 ML for Operational Efficiency
- 3.10 ML in Real Clinical Practice
- 4 Benefits of Machine Learning in Healthcare
- 5 Challenges and Limitations of Healthcare Machine Learning
- 6 How Webisoft Implements Machine Learning in Healthcare (Step-by-Step Guide)
- 7 Ready to bring advanced AI into your healthcare systems!
- 8 Conclusion
- 9 FAQs
Understanding Machine Learning in Healthcare
Machine learning in healthcare refers to the use of algorithms that learn from medical data and improve their predictions over time. When people talk about machine learning in medicine, they mean systems that study patterns in patient records, images, labs, or sensor data to support clinical judgment. These models recognise trends that are difficult for humans to track at scale. They help identify risks, suggest possible diagnoses, and forecast likely outcomes. ML works only when devices, EHRs, and clinical systems share information, since the volume of patient data is too large to analyze manually. Clinicians interact with ML through tools inside existing workflows, such as image scoring software, risk alerts, or documentation aids. Administrators use ML to predict demand, manage resources, and monitor performance. In short, machine learning provides data-driven support that strengthens decision-making across the healthcare system.How Machine Learning Works in Healthcare Settings
 Machine learning in healthcare works through healthcare machine learning algorithms that study large patient datasets and produce clinical insights. These systems learn patterns that support diagnosis, risk prediction, and daily decision making across hospitals.
Machine learning in healthcare works through healthcare machine learning algorithms that study large patient datasets and produce clinical insights. These systems learn patterns that support diagnosis, risk prediction, and daily decision making across hospitals.Data for Training
ML models rely on clean, diverse medical data. Each dataset becomes part of the model’s experience, much like clinical training shapes a young physician. Hospitals generate imaging files, lab values, sensor readings, and written notes. No human can examine this volume in real time. ML systems can. High-quality data improves accuracy and reduces harmful errors. Poor data introduces bias and weakens model reliability. Data also arrives in many forms, which means natural language tools often convert notes into structured inputs that models can learn from.From Data to Insight
ML systems follow a clear process. Data arrives from EHRs, devices, or imaging systems. It is cleaned and standardised so the model sees consistent information. The model is trained on this prepared dataset and tested on information it has never seen before. If performance holds, the system is added to clinical software. The insight then appears inside tools clinicians already use, such as risk dashboards or imaging viewers. After deployment, the model is monitored for drift, since medical data changes over time.Validated Models
Validation focuses on safety. Models must perform well on internal tests and independent external datasets. Clinicians rely on sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values instead of broad accuracy scores. These metrics show how the model behaves across different risk levels. Some systems undergo clinical trials to prove benefits during real patient care. Regulators expect clear evidence that the model improves outcomes and stays reliable under changing conditions.Safety and Trust
ML tools support decisions but do not replace clinical judgment. Human oversight remains essential because clinicians understand the context that models cannot capture. Bias remains a known risk, which is why diverse datasets and routine audits matter. Privacy and security also play a central role. Health data must remain protected through encryption and strict access controls. Trust grows when clinicians can see how the model reached its conclusion and understand its limits.Key Applications of Machine Learning in Healthcare Today
 Machine learning supports diagnosis, prediction, and clinical decision-making across many areas of healthcare. It helps teams handle complex patterns, large datasets, and real-time signals that humans cannot process alone.
Machine learning supports diagnosis, prediction, and clinical decision-making across many areas of healthcare. It helps teams handle complex patterns, large datasets, and real-time signals that humans cannot process alone.ML for Diagnostic Imaging
Models built for medical imaging machine learning examine X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans with high precision. They highlight subtle abnormalities that may escape human review, especially in high-volume environments. Radiologists then use these insights to confirm or question early impressions.Disease Prediction Models
Tools built for machine learning for disease prediction review patient histories, genetics, lifestyle factors, and real-time health signals. They estimate who may develop a condition, how fast it may progress, and when intervention should begin. This supports earlier care and stronger long-term outcomes.Pattern-Based Decision Support
Systems powered by deep learning in medical diagnosis recognise patterns across images, labs, and clinical notes. They support diagnosis, triage, and case review during busy clinical hours. These models help reduce variation in care and improve decision accuracy.ML in Research
In a lab environment, machine learning helps researchers study disease behaviour and refine hypotheses. Algorithms simulate progression and treatment response, which helps teams understand how conditions evolve. This is valuable in oncology, where predicting drug response guides personalised strategies. Researchers adjust and refine models as data grows, improving accuracy and supporting faster collaboration.ML in Diagnosis and Risk Assessment
Machine learning transforms diagnostic workflows by reviewing large datasets faster than humans can. Radiology tools detect lesions, tumours, and structural changes that signal early disease. These models support early stage cancer and cardiac screening, where detection speed affects survival. ML also predicts the likelihood of disease onset and progression, which helps clinicians plan personalised prevention.ML in Personalised Treatment
ML reviews each patient’s history, genetics, and ongoing response data. It helps clinicians choose treatments with higher success rates and fewer side effects. This is important in oncology, where responses vary widely across patients. As new data arrives, the model updates its guidance. This improves dosing, medication selection, and long term care planning. ML systems also predict medication adherence and guide reminders that keep patients on track.ML in Drug Discovery
Machine learning supports drug discovery by analysing genetic data, protein structures, and chemical properties. Models predict how compounds interact with targets and estimate safety risks early. They also analyse past trials to identify promising patient groups and dosing strategies. These tools reveal repurposing opportunities for known compounds and help teams refine trial design.ML in Predictive Analytics
Predictive models study EHR data, genomic information, and wearable signals to forecast disease progression and complication risk. They support early action by identifying patients who may decline soon. These tools guide chronic disease planning, oncology treatment selection, and post-surgical monitoring. They also help teams manage medication choices based on genetic traits.ML for Operational Efficiency
Machine learning improves hospital operations without lowering care quality. It helps teams plan staffing, predict admissions, and manage beds. ML automates scheduling, billing, and paperwork tasks. This reduces errors and frees time for clinicians. Supply chain models predict demand and reduce waste. Patient flow tools analyse admission patterns and treatment times to reduce bottlenecks.ML in Real Clinical Practice
Hospitals use ML to detect sepsis early by analysing vitals, labs, and clinical notes. Screening tools grade retinal images and highlight cases that need specialist review. Radiology triage tools reorder worklists when urgent findings appear. Predictive models estimate readmission risk and guide follow up planning. Trial screening tools review patient records to speed recruitment and support smoother study execution.Benefits of Machine Learning in Healthcare
 Machine learning strengthens clinical performance, operations, and research. It offers measurable gains in accuracy, consistency, and decision speed. These improvements highlight the growing influence of machine learning benefits in healthcare:
Machine learning strengthens clinical performance, operations, and research. It offers measurable gains in accuracy, consistency, and decision speed. These improvements highlight the growing influence of machine learning benefits in healthcare: Faster Diagnostics and Reduced Human Variability
Machine learning speeds up the diagnostic process by analysing large volumes of clinical data in seconds. It reviews imaging, lab results, and clinical documentation at a scale no team can match manually. Studies show that ML models can match or surpass radiologists in more than ten diagnostic imaging tasks, improving detection speed and consistency. ML also reduces diagnostic variability. Human interpretation changes with fatigue, workload, and experience. Machines maintain stable performance under all conditions. This helps clinicians confirm findings and avoid missed details, especially during high-volume periods.Lower Operational Costs
Machine learning improves how hospitals manage staff, equipment, and time. Models predict patient arrivals, procedure durations, and discharge patterns. These predictions help reduce overcrowding by guiding staffing decisions and resource planning. ML also automates repetitive tasks. It sorts documentation, prioritises tasks, and improves scheduling accuracy. This lowers overtime costs and frees clinical teams from burdensome administrative tasks.Improved Patient Outcomes
Predictive models flag risk before symptoms escalate. They analyse vitals, test results, medications, and clinical patterns that often appear before deterioration. This gives clinicians valuable time to intervene. ML supports chronic disease management through continuous monitoring. It tracks small changes in blood glucose, heart rhythm, oxygen levels, or behavioural patterns. Early alerts prevent complications and reduce avoidable admissions.Stronger Clinical Confidence Supported
Because clinicians spend over 49% of their day on documentation and admin tasks, ML-driven automation significantly reduces workload burdens. Clinicians gain confidence when complex information becomes structured and understandable. Machine learning models organise thousands of data points into clear patterns and meaningful predictions. This helps physicians confirm their reasoning and reduce uncertainty in high-pressure situations. ML systems highlight the evidence that supports each recommendation. This transparency helps clinicians explain decisions to patients and align care plans with real-world data.Earlier diagnosis
ML-based risk models improve early disease identification by up to 30 percent versus standard clinical risk scores. Machine learning identifies early disease signals that may not be visible to the human eye. It studies imaging scans, subtle biomarker trends, and patient history data. Early findings lead to faster treatment planning and higher survival rates. This approach improves detection in cancer, cardiovascular disease, neurological conditions, and infectious disease. Earlier diagnosis reduces treatment costs and improves patient comfort during recovery.Drug Development Acceleration
ML speeds drug discovery by analysing molecular structures and historical trial outcomes. Models identify promising compounds and highlight potential safety issues before laboratory testing begins. This reduces research waste and shortens development timelines. Pharmaceutical teams use ML to design smarter trials. They predict which patients will respond, which endpoints matter most, and which risks require closer monitoring. This improves trial efficiency and strengthens regulatory readiness.Enhanced Data Privacy and Security
Machine learning protects sensitive data by detecting unusual behaviour and potential threats in real time. Algorithms study access logs, device patterns, and network activity. Suspicious activity receives immediate attention. ML also supports anonymisation of clinical records. This protects patient identity while allowing researchers to work with valuable datasets. Stronger security helps organisations maintain trust as digital adoption grows.Improving Patient Care
Machine learning supports personalised treatment by analysing each patient’s unique data profile. It guides medication choices, monitoring plans, and early intervention strategies. This improves care quality and reduces unnecessary side effects. ML systems monitor patients continuously and send alerts when conditions shift. These models help hospitals manage chronic diseases, surgical recovery, and acute deterioration with greater accuracy.Challenges and Limitations of Healthcare Machine Learning
 Machine learning offers major clinical advantages, but it also brings significant barriers that limit safe adoption. These issues influence reliability, trust, fairness, and long term performance. Together, they outline the core machine learning challenges in healthcare, which are:
Machine learning offers major clinical advantages, but it also brings significant barriers that limit safe adoption. These issues influence reliability, trust, fairness, and long term performance. Together, they outline the core machine learning challenges in healthcare, which are:Data Fragmentation and Model Accuracy Risk
Healthcare data is scattered across EHR systems, labs, imaging platforms, and older databases. Each system stores information differently, which breaks continuity and weakens model learning. Incomplete and inconsistent data also introduce errors that directly reduce predictive accuracy. Models struggle when training data does not reflect real clinical complexity. They may perform well in controlled environments but fail when deployed in hospitals with different populations or equipment. This generalization gap limits trust and increases risk. Bias also forms in fragmented datasets. If a model learns mostly from one demographic group, it may misclassify or overlook patterns in others. This raises fairness concerns and requires careful evaluation before deployment.Ethical and Regulatory Considerations for AI Adoption
Machine learning introduces complex ethical issues in healthcare AI that influence safety, responsibility, and trust. Patients must understand how their data is used, yet consent rules vary widely. Many institutions still rely on outdated forms, creating legal vulnerabilities. Privacy is another major challenge. Medical data is sensitive, valuable, and frequently targeted. Any breach harms patients and erodes institutional credibility. Strict controls are required for storage, access, and transmission. Regulatory frameworks continue to evolve. Agencies expect clear documentation, audit logs, transparent risk assessments, and human oversight. Approval slows when models appear opaque or when developers cannot explain their decisions. Regulators also expect proven clinical value, not just statistical performance.Bias, Fairness, and Population Diversity Concerns
Bias is one of the most difficult issues in healthcare AI. Models replicate patterns found in their training data. If that data excludes certain groups, the model may produce unequal outcomes. Fairness evaluation must become routine. Teams need to measure accuracy across age groups, ethnicities, languages, and socioeconomic backgrounds. Gaps must be fixed before deployment and monitored over time. Transparent reporting helps clinicians understand model limitations and implement safety checks.Integration Barriers Inside Hospital Systems
Many hospitals rely on legacy systems that do not communicate well with modern machine learning tools. Integrating AI into daily workflows is often harder than building the model itself. EHR platforms vary widely and rarely support smooth data exchange. Clinicians also lack time to adopt new tools that interrupt their workflow. If insights do not appear inside the EHR at the moment of care, adoption falters and trust declines. Model drift adds another layer of complexity. When patient behaviour or hospital processes change, model performance declines. Without monitoring tools, this drop remains hidden until errors appear in clinical decisions. Operational barriers also include financial constraints, staff training needs, and hardware limitations. Hospitals face heavy workloads, leaving little room for complex technology rollouts.How Webisoft Implements Machine Learning in Healthcare (Step-by-Step Guide)
 Machine learning in healthcare succeeds only when strategy, data integrity, workflow design, and clinical relevance move together. At Webisoft, we apply machine learning through a disciplined, engineering-driven process. The process is shaped by our experience in AI, IoT, EMR development, workflow automation, and remote patient monitoring. Each stage focuses on improving outcomes and lowering operational strain:
Machine learning in healthcare succeeds only when strategy, data integrity, workflow design, and clinical relevance move together. At Webisoft, we apply machine learning through a disciplined, engineering-driven process. The process is shaped by our experience in AI, IoT, EMR development, workflow automation, and remote patient monitoring. Each stage focuses on improving outcomes and lowering operational strain:Clear Goal Definition
We start by working with healthcare teams to define one specific outcome that machine learning must achieve. The goal may involve improving diagnostic accuracy, reducing delays across care pathways, increasing early detection rates, or strengthening clinical decision support. We establish a baseline, identify the data owner, and outline the expected result. This clarity ensures that every technical choice supports a real clinical or operational need rather than a theoretical model.High Quality Data Foundations
Once the objective is defined, we collect and structure the data needed to support the model. Healthcare data is fragmented and inconsistent, so we standardise medical codes, align measurement units, remove duplicates, and validate each dataset for completeness. Our team combines EHR data, imaging feeds, IoT sensor data, lab results, and other relevant information into a clean foundation. Privacy and compliance are central. We follow HIPAA, GDPR, and hospital-level requirements with strong audit trails and controlled access. Our experience with EMR and IoT integration helps us build pipelines that support accurate, secure, and scalable model performance.Model Selection
After preparing the data, we choose a model that matches the healthcare scenario. Different challenges require different approaches. Diagnostic tasks often rely on supervised learning. Patient clustering and risk grouping benefit from unsupervised learning. Adaptive treatment support may use reinforcement learning under strict clinical guidance. We also tailor the architecture to the data type. Imaging tasks use deep learning models. Medical text uses NLP tuned for healthcare language. Structured EHR tables use interpretable models that clinicians can review.Clinical Grade Validation
Training begins only when the data and model selection are complete. We validate performance using measurements that matter in healthcare, such as sensitivity, specificity, and calibrated confidence. Every result is reviewed for fairness across age, ethnicity, gender, and clinical settings. We document each experiment, dataset, and outcome so the process remains transparent and auditable. This step mirrors the discipline of clinical research and ensures the model performs reliably before it enters any live environment.Workflow Integration
Once validated, we embed the model into the software systems we develop for our partners. Our healthcare work often involves EMR platforms, remote monitoring tools, IoT systems, and workflow automation. We position the model where clinicians naturally work, so they receive insights without switching systems or changing routines. The interface remains simple, clear, and supportive. Predictions include meaningful context so users understand why the model produced a result. When confidence is low, the system follows established procedures and defers to clinical judgment. Integration focuses on reducing friction and supporting adoption.Continuous Monitoring
Healthcare environments change, so machine learning must adapt. We track live performance to detect drift or shifts in patient patterns. Our team updates models safely and releases improvements through a controlled process. Clinician feedback helps us refine features and ensure value stays aligned with real needs. Security and compliance checks follow each update to protect patient data. This continuous cycle keeps the system accurate, stable, and ready for long-term use.Ready to bring advanced AI into your healthcare systems!
Book your free consultation today and partner with Webisoft to build secure, scalable AI solutions that enhance care delivery, streamline workflows, and elevate clinical performance.


