Machine Learning in Crypto: Benefits, Risks, and Use Cases
- BLOG
- Artificial Intelligence
- February 16, 2026
Machine learning in crypto refers to using data-driven models to analyze blockchain activity, market behavior, and trading signals in real time. Instead of relying on static rules, these systems learn from historical and live data to support forecasting, automation, and risk detection in highly volatile markets. In practice, many crypto machine learning systems fail after deployment. Models that perform well in backtests often collapse during sudden liquidity shocks, regulatory news, or coordinated market moves.
Trading desks and DeFi teams repeatedly face model drift, unreliable data feeds, and execution delays that turn accurate predictions into losses. In this blog, we will discuss where machine learning is used in crypto today, the benefits it can realistically provide, and the technical challenges that limit its effectiveness. We will also explain who should use machine learning in crypto and who should not.
Contents
- 1 What Machine Learning Means in Crypto Systems
- 2 Where Machine Learning Is Used in Crypto Today
- 3 Data Foundations for Machine Learning in Crypto
- 4 Common Machine Learning Models Used in Crypto
- 4.1 LSTM and GRU for Time-Based Market Forecasting
- 4.2 XGBoost and Gradient Boosting for Structured Signals
- 4.3 Random Forest for Classification and Signal Filtering
- 4.4 Transformer Models for Complex Market Relationships
- 4.5 Reinforcement Learning for Strategy Optimization
- 4.6 CNN Models for Short-Term Pattern Detection
- 5 Machine Learning in DeFi and Protocol Risk
- 6 How a Crypto Machine Learning Pipeline Works
- 7 Why Most Machine Learning Fails in Crypto
- 8 Build machine learning systems that survive real crypto markets.
- 9 Benefits of Using Machine Learning in Crypto
- 10 Who Should Use Machine Learning in Crypto and Who Should Not
- 11 Challenges of Using Machine Learning in Crypto
- 12 How Webisoft Helps Teams Apply Machine Learning in Crypto
- 12.1 Strategic Planning and Problem Definition
- 12.2 Custom ML Model Architecture Designed for Crypto Data
- 12.3 Data Engineering and Feature Development
- 12.4 Integration With Existing Systems and Software
- 12.5 Enterprise-Grade Architecture and Scalability
- 12.6 MLOps and Long-Term Model Maintenance
- 12.7 Security, Governance, and Compliance Built In
- 12.8 Human-Centered Support and Ongoing Collaboration
- 12.9 Cross-Disciplinary Expertise Across Tech Stacks
- 12.10 Measurable Impact on Business KPIs
- 13 Build machine learning systems that survive real crypto markets.
- 14 Conclusion
- 15 FAQs
- 15.1 Can machine learning predict crypto prices accurately?
- 15.2 How much data is needed to use machine learning in crypto?
- 15.3 Is machine learning better than technical analysis in crypto?
- 15.4 Can small teams or startups use machine learning in crypto?
- 15.5 Does machine learning work for all cryptocurrencies?
What Machine Learning Means in Crypto Systems
Machine learning in crypto systems means using data-driven models to spot patterns in blockchain and market data instead of relying on fixed rules. These models learn from examples and adjust their behavior over time, so they can handle the vast and noisy data in crypto systems.
For example, models trained on millions of Ethereum transactions can spot unusual patterns that might indicate fraud or abuse. In the real world, research confirms machine learning’s value in security tasks. Supervised ML approaches, such as XGBoost and federated learning models, reached up to about 95% accuracy in detecting blockchain-based fraud when trained on labeled datasets of transaction activity.
Because these models learn directly from real data, such as transaction histories, price movements, and order flow, they can generate signals that human analysts and static rules often miss. This makes ML a practical tool for crypto analytics, not just theory.
Where Machine Learning Is Used in Crypto Today
 Machine learning in crypto is used where systems must react fast, process large data volumes, and reduce human bias. Teams apply it across trading, analytics, security, and protocol operations. Each use case connects data signals to direct system actions.
Machine learning in crypto is used where systems must react fast, process large data volumes, and reduce human bias. Teams apply it across trading, analytics, security, and protocol operations. Each use case connects data signals to direct system actions.
Algorithmic and Automated Trading
Machine learning crypto trading focuses on automated systems that analyze price, volume, and order flow in real time. These systems rely on crypto price prediction using machine learning to estimate short-term direction during volatile conditions.
Most platforms use machine learning crypto models trained on historical and live market data to guide execution. Price swings also require volatility awareness. machine learning models for crypto volatility help systems adjust position size and timing when markets move fast. This reduces exposure during unstable periods without manual input.
Market Sentiment Analysis
AI in cryptocurrency markets is commonly used to interpret public sentiment. NLP systems scan social posts, comments, and headlines to detect fear or optimism around assets. This helps platforms react to crowd behavior that often drives short-term moves.
Sentiment signals rarely stand alone. Systems combine them with price and volume data to reduce false reactions. This makes sentiment analysis a support layer rather than a single trigger.
Risk Management and Portfolio Control
Risk systems depend on on-chain data machine learning to track real asset flows. Models read transaction histories to detect sudden changes in network activity. These insights help platforms adjust exposure before losses expand.
Advanced platforms rely on blockchain data analytics using ML to rebalance portfolios automatically. This allows continuous risk control without fixed thresholds. The result is faster response during sharp market shifts.
Security and Fraud Detection
Security teams use wallet clustering machine learning to group related addresses by behavior. This helps identify coordinated activity across multiple wallets. Such patterns often signal scams or laundering attempts.
Detection systems also rely on fraud detection in crypto using ML to flag abnormal transactions. Models learn what normal behavior looks like and surface deviations early. This reduces reaction time when attacks begin.
DeFi and Protocol-Level Monitoring
Protocols apply machine learning in DeFi to track liquidity and exposure across pools. Models watch how users move funds between contracts. This helps teams understand stress points before failures occur.
Risk tools use DeFi risk analysis machine learning to monitor abnormal contract interactions. Some systems also apply MEV detection machine learning to identify extraction patterns that affect user outcomes. These insights support protocol-level decisions.
System Design and Model Stability
Production systems depend on a clear crypto machine learning pipeline from data intake to decision output. Engineers rely on feature engineering for crypto markets to convert raw data into usable signals. Poor inputs usually lead to unstable results.
Over time, models face ML model drift in crypto markets as behavior changes. This creates challenges for ML in cryptocurrency systems that rely on static assumptions. These issues define the real limitations of machine learning in crypto today.
Data Foundations for Machine Learning in Crypto
 Machine learning in crypto works only as well as the data behind it. Crypto systems produce large, fast, and messy data streams. Models fail quickly when this data lacks structure or context.
Machine learning in crypto works only as well as the data behind it. Crypto systems produce large, fast, and messy data streams. Models fail quickly when this data lacks structure or context.
On-Chain Transaction and Network Data
On-chain data shows how value moves across a blockchain in real time. This data includes transactions, fees, timestamps, and wallet activity. Ethereum processes over one million transactions per day, which gives ML systems a constant view of real user behavior. Teams rely on this data for pattern detection. Models use it to understand normal network activity. Sudden changes often signal risk or manipulation.
Wallet Behavior and Network Patterns
Wallet activity helps models understand user intent. With wallet clustering machine learning, the systems group addresses based on behavior instead of identity. This helps platforms detect coordinated actions that look normal when viewed one transaction at a time. These patterns matter in fraud cases. Coordinated wallet movement often appears before scams or draining events. ML systems surface these signals early.
Market and Exchange Data
Market data explains how prices react to behavior. This includes price, volume, and order book depth from exchanges. Spot crypto markets process billions in daily volume, which gives models dense and fast-moving inputs. Source: This data feeds the broader crypto machine learning pipeline. Models learn short-term shifts in liquidity and volatility. Without clean market data, predictions drift fast.
Sentiment and Off-Chain Signals
Sentiment data captures how people respond to news and events. This layer supports AI in cryptocurrency markets by adding context charts cannot show. Spikes in social activity often appear before sharp price moves. Raw text needs structure. Through feature engineering for crypto markets, systems convert posts and headlines into usable signals. These signals strengthen short-term models.
Smart Contract and DeFi Activity
Smart contract data shows how users interact with protocols. This data supports machine learning in DeFi by tracking swaps, staking, borrowing, and liquidations. DeFi platforms lock tens of billions in value, which creates dense interaction patterns. Models use this data for risk tracking.
DeFi risk analysis machine learning helps teams spot liquidity stress early. Some systems also flag extraction behavior through MEV detection machine learning.
Common Machine Learning Models Used in Crypto
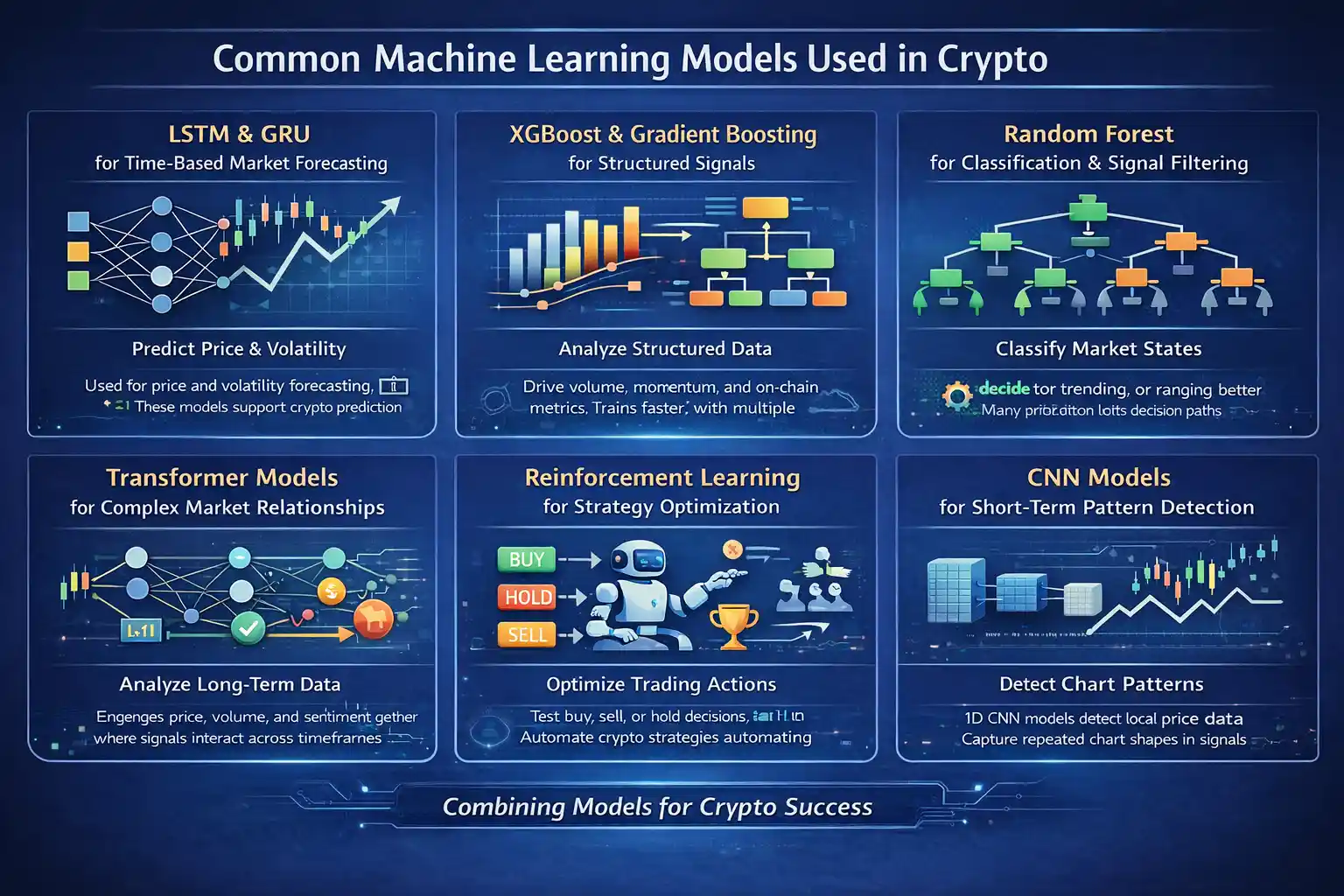 Machine learning in crypto relies on models that can handle fast markets, noisy data, and constant change. Each model serves a different role depending on whether the task involves prediction, classification, or decision-making. Teams often combine models instead of relying on a single approach.
Machine learning in crypto relies on models that can handle fast markets, noisy data, and constant change. Each model serves a different role depending on whether the task involves prediction, classification, or decision-making. Teams often combine models instead of relying on a single approach.
LSTM and GRU for Time-Based Market Forecasting
LSTM and GRU models are commonly used for price and volatility forecasting. They work well because crypto prices depend heavily on past movement patterns. These models support crypto price prediction using machine learning by learning how trends form over time rather than reacting to single data points.
XGBoost and Gradient Boosting for Structured Signals
XGBoost is widely used when inputs come from structured indicators like volume, momentum, and on-chain metrics. It trains faster than deep learning models and handles noisy data better. Many platforms rely on boosting models as stable machine learning crypto models for short-term signals. (Source: MDPI)
Random Forest for Classification and Signal Filtering
Random Forest models help classify market states such as trending or ranging. They reduce overfitting by averaging multiple decision paths. This makes them useful in machine learning crypto trading systems that need reliable confirmation before executing trades.
Transformer Models for Complex Market Relationships
Transformer models handle long-term and multi-input relationships better than older neural networks. They analyze price, volume, and sentiment together instead of sequentially. This ability makes them useful in AI in cryptocurrency markets where signals interact across timeframes.
Reinforcement Learning for Strategy Optimization
Reinforcement learning models focus on learning actions instead of predictions. These systems test decisions like buy, sell, or hold and improve based on outcomes. This approach helps automate strategy adjustment in fast-moving crypto environments.
CNN Models for Short-Term Pattern Detection
1D CNN models detect local patterns in price data. They work well for short-term setups where repeated shapes appear on charts. Some systems combine CNNs with sequence models to strengthen intraday forecasts.
Machine Learning in DeFi and Protocol Risk
 Machine learning in crypto plays a direct role in DeFi because protocols run without pauses or intermediaries. Risk appears fast when liquidity shifts, contracts fail, or attackers exploit timing gaps. ML helps protocols react early instead of after losses occur.
Machine learning in crypto plays a direct role in DeFi because protocols run without pauses or intermediaries. Risk appears fast when liquidity shifts, contracts fail, or attackers exploit timing gaps. ML helps protocols react early instead of after losses occur.
Real-Time Threat and Anomaly Detection
Machine learning helps DeFi platforms detect abnormal activity in real time. Models monitor transaction flows to flag patterns linked to flash loan attacks or sudden fund drains. Plus, automated detection systems now surface most high-risk DeFi incidents within minutes, not hours.
Protocol Risk Monitoring and Stress Signals
DeFi protocols use ML to monitor health metrics like collateral ratios and liquidation pressure. These signals help systems predict liquidity stress before pools collapse. Platforms tracking lending risk rely on DeFi risk analysis machine learning to adjust parameters early.
Automated Parameter Adjustment
Machine learning supports real-time governance in DeFi systems. Models adjust interest rates, collateral limits, or incentives as market conditions change. This reduces the need for slow manual votes during fast-moving market events.
Wallet-Based Credit Assessment
Machine learning helps assess borrower behavior without identity checks. Models analyze wallet history to estimate repayment risk based on past actions. This supports trustless lending without centralized credit scores.
Liquidity and Yield Optimization
Machine learning guides liquidity placement across pools and strategies. Systems track yield, risk, and pool usage to reduce losses from poor allocation. Protocols like Yearn rely on automated strategies shaped by market behavior.
MEV and Market Manipulation Detection
Machine learning helps surface extraction patterns that harm users. Models analyze transaction ordering and timing to identify MEV detection machine learning signals. This insight helps protocols adjust incentives and protect execution fairness.
How a Crypto Machine Learning Pipeline Works
 A modern crypto machine learning pipeline connects live market data, streaming systems, and predictive models into one continuous flow. Unlike batch-based systems, a real-time crypto data pipeline processes events the moment they arrive.
A modern crypto machine learning pipeline connects live market data, streaming systems, and predictive models into one continuous flow. Unlike batch-based systems, a real-time crypto data pipeline processes events the moment they arrive.
Each stage prepares data for the next, from ingestion to streaming, storage, machine learning inference, and visualization. The result is a production-grade crypto analytics system that delivers timely insights instead of stale reports.
Data Ingestion and Streaming Foundation
A crypto machine learning pipeline starts with real-time market data ingestion from exchanges like Binance. WebSocket feeds stream prices, volumes, trades, and order book updates multiple times per second for liquid pairs such as BTCUSDT and ETHUSDT, which removes ingestion latency.
Unlike batch systems, this real-time crypto data pipeline processes events the moment they arrive, ensuring no market movement is missed. Crypto markets generate sharp traffic spikes during liquidations or major news events.
Apache Kafka absorbs these bursts by buffering millions of events per second while maintaining message order and durability. This capability makes Kafka a core component of streaming crypto analytics systems used in production environments.
Change Data Capture and Data Quality Control
Change data capture keeps databases and streams aligned in real time. Debezium monitors PostgreSQL transaction logs and streams row-level changes into Kafka with minimal delay. Red Hat benchmarks show CDC pipelines often deliver events in under one second, which prevents lag across the pipeline.
Raw crypto market data arrives as nested JSON with inconsistent schemas. The pipeline flattens payloads, standardizes timestamps, removes duplicates, and validates fields before downstream processing. This step protects machine learning for crypto markets from corrupted or incomplete inputs.
Feature Engineering and Model Training
Machine learning models rely on structured signals, not raw prices. Feature engineering computes returns, rolling volatility, volume changes, and order book imbalance from live ticks. The CFA Institute reports that engineered features improve short-term crypto prediction accuracy by over 20 percent.
Crypto prices follow fast-changing temporal patterns that linear models fail to capture. Recurrent neural networks such as GRU learn these dependencies more effectively. A 2025 MDPI study showed GRU models consistently outperformed ARIMA and regression across ten major cryptocurrencies.
Real-Time Inference and Risk Detection
Predictions must run at streaming speed to remain useful in live markets. The crypto machine learning pipeline performs inference directly inside Kafka consumers as new events arrive. McKinsey reports this approach reduces reaction time from minutes to seconds in financial systems.
Real-time inference enables immediate detection of abnormal behavior. Models flag sharp price drops, volume spikes, and liquidity gaps as they occur. Deloitte notes that real-time analytics now power most crypto risk monitoring systems.
Storage, Visualization, and Production Readiness
Model training and analytics require reliable access to historical and live data. Apache Cassandra supports this need by handling heavy write workloads and fast time-series reads with predictable latency. This design supports always-on real-time crypto analytics without single points of failure.
Visualization turns model output into actionable insight. Grafana renders prices, indicators, and predictions with second-level refresh rates, while alerts trigger automated responses when conditions change. This architecture mirrors production-grade trading infrastructure used by exchanges and institutional trading desks, where scalability, observability, and fault tolerance define system reliability.
Why Most Machine Learning Fails in Crypto
 Machine learning in crypto fails because the market behaves in unstable and unpredictable ways. Models struggle when price patterns shift quickly and data quality varies. Most failures come from mismatched assumptions, not weak algorithms.
Machine learning in crypto fails because the market behaves in unstable and unpredictable ways. Models struggle when price patterns shift quickly and data quality varies. Most failures come from mismatched assumptions, not weak algorithms.
Market Instability
Crypto markets change structure often, which breaks learned patterns. A model trained during a bull market usually fails during a bear market. This constant shift causes ML model drift in crypto markets, where predictions lose accuracy over time.
Limited and Noisy Data
Crypto assets have short and fragmented histories. This makes crypto price prediction using machine learning unreliable because models learn random spikes instead of real signals. Backtests look strong, but live results often collapse.
Unreliable Data Sources
Many exchanges report inflated volume and distorted order books. These inputs weaken machine learning crypto models that rely on market feeds. When training data does not reflect real trading, predictions fail in execution.
Misleading Backtests
Many models fail because testing methods hide real risk. Look-ahead bias and survivor bias inflate results in machine learning crypto trading experiments. Live markets quickly expose these hidden flaws.
Execution and Cost Limits
Correct predictions still fail when fees and slippage erase gains. High volatility increases execution risk for machine learning models for crypto volatility. Small predicted edges disappear once real costs apply.
System Constraints
Many teams ignore practical system limits. Weak feature engineering for crypto markets causes models to misread price action. These gaps reveal the true limitations of machine learning in crypto and the ongoing challenges of ML in cryptocurrency systems.
At Webisoft, our engineers design ML systems around real crypto constraints, not ideal datasets. Instead of chasing prediction accuracy alone, we focus on data quality, regime awareness, execution limits, and long-term model reliability.
That approach helps teams avoid the common failure patterns outlined above. If you are exploring machine learning in crypto and want to pressure-test feasibility before committing resources, our team can help you assess that realistically.
Build machine learning systems that survive real crypto markets.
Apply machine learning in crypto with proper data controls, execution awareness, and production readiness.
Benefits of Using Machine Learning in Crypto
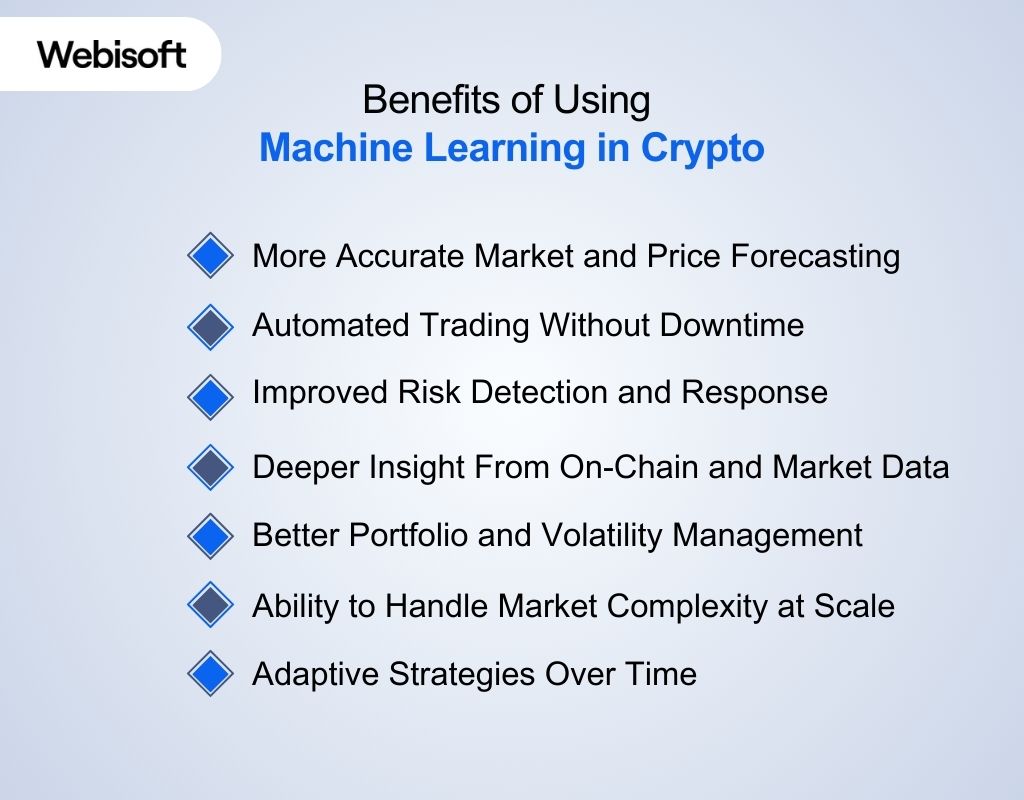 Machine learning in crypto helps systems operate in fast, complex, and always-on markets. It replaces guesswork with data-backed decisions. These benefits show most clearly in trading, risk control, and large-scale analysis.
Machine learning in crypto helps systems operate in fast, complex, and always-on markets. It replaces guesswork with data-backed decisions. These benefits show most clearly in trading, risk control, and large-scale analysis.
More Accurate Market and Price Forecasting
Machine learning improves forecasting by learning from patterns that repeat across cycles. Models support crypto price prediction using machine learning by combining price action with network activity. This helps systems anticipate volatility shifts instead of reacting late.
Automated Trading Without Downtime
Machine learning enables continuous execution in markets that never close. This makes machine learning crypto trading effective for reacting to overnight or weekend moves. Automated systems reduce missed opportunities caused by human limits.
Improved Risk Detection and Response
Machine learning strengthens risk control by spotting abnormal behavior early. Systems use fraud detection in crypto using ML to flag suspicious flows and coordinated activity. This reduces damage before issues spread across platforms.
Deeper Insight From On-Chain and Market Data
Machine learning connects raw blockchain activity to decision-making. Through on-chain data machine learning, models track wallet flows, exchange balances, and network stress signals. This gives traders and platforms clearer insight into market behavior.
Better Portfolio and Volatility Management
Machine learning helps systems adjust exposure as conditions change. Models apply machine learning models for crypto volatility to scale risk during unstable periods. This supports steadier performance during sharp market swings.
Ability to Handle Market Complexity at Scale
Machine learning processes data beyond human capacity. Through blockchain data analytics using ML, systems combine price, sentiment, and transaction data at once. This scale improves consistency and reduces emotional bias.
Adaptive Strategies Over Time
Machine learning systems improve as they retrain on new data. This helps manage challenges of ML in cryptocurrency environments where behavior shifts often. Adaptation matters more than static accuracy in crypto markets.
Who Should Use Machine Learning in Crypto and Who Should Not
Machine learning in crypto works best when users understand both data and market structure. It supports scale, speed, and automation, but it also adds cost and complexity. The gap between success and failure depends on who uses it and why.
Who Should Use Machine Learning in Crypto
Quantitative traders and funds benefit most from machine learning crypto trading because they process large volumes of market and on-chain data. These teams already manage infrastructure, monitoring, and risk controls.
Glassnode reports that institutional and algorithmic activity now dominates volume during high-volatility periods, where automation matters most. Security teams and DeFi platforms also gain value from ML. They use models for anomaly detection, protocol monitoring, and fraud prevention. This makes ML practical beyond price prediction.
Who Should Not Use Machine Learning in Crypto
Beginners often struggle with crypto price prediction using machine learning because models need deep setup and constant care. Without data skills and market context, users misread outputs and take false confidence from backtests.
This leads to losses instead of insight. Low-capital and hands-off traders should also avoid ML systems. Infrastructure costs, data access, and execution risks quickly outweigh gains. These users face the real limitations of machine learning in crypto without the support needed to manage them.
Challenges of Using Machine Learning in Crypto
 Machine learning in crypto faces structural problems that do not exist in traditional markets. Crypto trades nonstop, reacts to sentiment fast, and lacks long historical stability. These conditions create limits that models must fight from day one.
Machine learning in crypto faces structural problems that do not exist in traditional markets. Crypto trades nonstop, reacts to sentiment fast, and lacks long historical stability. These conditions create limits that models must fight from day one.
Unstable and Non-Stationary Markets
Crypto markets change behavior often, sometimes within weeks. A model trained during a bull phase usually fails when volatility spikes or liquidity dries up. Glassnode data shows that crypto market regimes shift more frequently than equity markets, which shortens the usable life of trained models. Price structure also changes when new participants enter or exit the market. Institutional flows, ETF news, or regulatory action can alter behavior overnight.
This constant change makes long-term prediction unreliable. Frequent retraining sounds like a solution, but it creates new problems. Retraining too often increases overfitting risk. Waiting too long makes the model outdated.
Low Signal-to-Noise Ratio
Crypto price data contains more noise than structure. Sudden spikes often come from liquidations, social hype, or large holders rather than organic demand. These events confuse models that try to learn stable patterns.
Thin liquidity amplifies this problem. Smaller markets show exaggerated moves that disappear quickly. The Block reports that short-term price changes in crypto often reflect reaction rather than trend. Noise forces models to guess more than learn. When guessing dominates, accuracy drops in live conditions. This is why many models perform no better than random during real trading.
Poor and Fragmented Data Quality
Crypto data lacks consistent standards. Prices, volume, and liquidity differ widely across exchanges. Many platforms still report inflated volume or incomplete order book data. Chainalysis highlights data inconsistency as a major barrier to reliable crypto analytics. Models trained on distorted inputs learn distorted behavior. Fragmentation also hurts historical accuracy. When an exchange delists a token or shuts down, data disappears.
This breaks continuity and weakens long-term learning. Off-chain data adds another challenge. Social sentiment data often includes spam, bots, and coordinated manipulation. Models must filter aggressively or risk learning false signals.
Model Overfitting and Weak Generalization
Machine learning models often look strong in backtests. This strength usually comes from memorizing historical noise. When market conditions change, the model collapses. Short crypto histories make this problem worse. Bitcoin has data since 2009, but most tokens have only a few years of activity. That is not enough for complex models to generalize well. Even now, overfitting remains a top risk in crypto trading models.
Models that fail to generalize lose money quickly once deployed. Generalization requires careful feature selection. Many teams skip this step. They feed raw prices into complex models and expect stability.
High Costs and Execution Constraints
Machine learning systems cost money to build and maintain. Data feeds, computing resources, and monitoring tools add up quickly. These costs often outweigh gains for smaller operators. Execution introduces another layer of risk. Fees, slippage, and API delays reduce expected returns. Execution costs play a larger role in crypto than in traditional markets. Even correct predictions can fail in practice.
A delayed trade or partial fill can flip a profitable signal into a loss. This reality limits how aggressive models can be. Infrastructure reliability also matters. Exchange outages and latency spikes happen often. Models that assume perfect execution break under real conditions.
Lack of Transparency and Trust
Many machine learning models act as black boxes. They produce signals without explaining why. This creates trust issues for traders, teams, and regulators. Complex models make debugging harder. When performance drops, teams struggle to identify the cause.
This slows response and increases losses. Regulatory pressure adds another layer. Financial systems increasingly require explainability. Models that cannot justify decisions face adoption limits in institutional settings.
How Webisoft Helps Teams Apply Machine Learning in Crypto
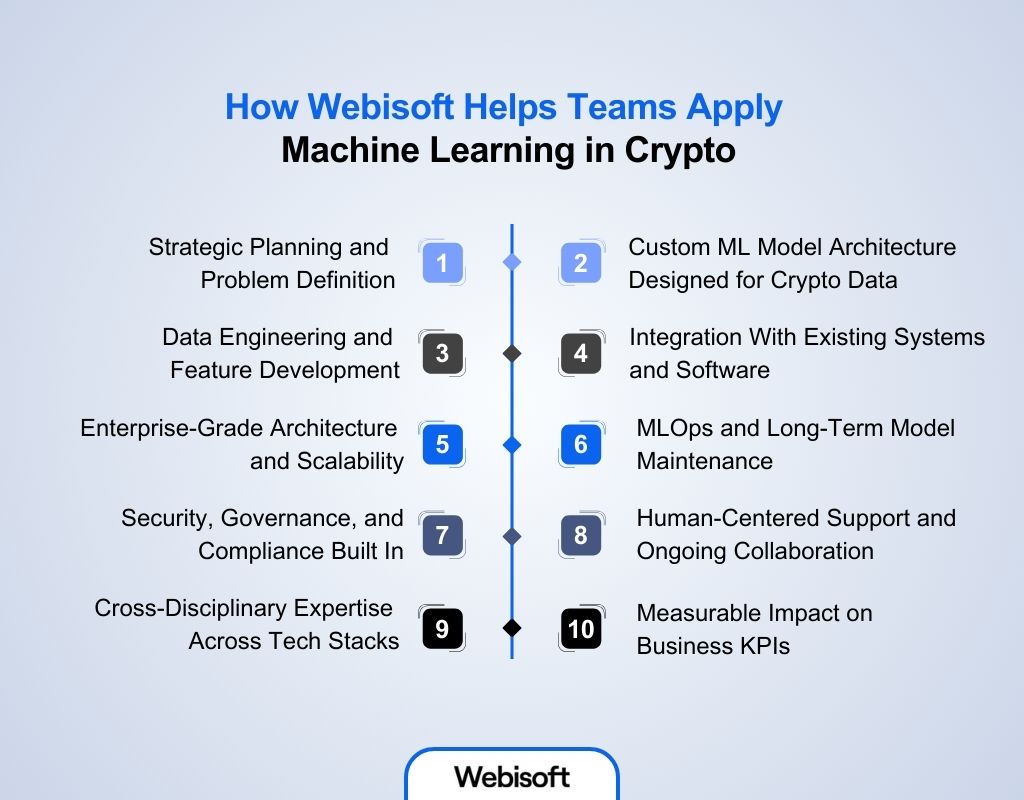 Webisoft helps teams transform machine learning in crypto into real, working systems for crypto and blockchain use cases. Our engineers bring deep technical experience across AI, data engineering, and enterprise software to solve real production challenges. Instead of experiments that never scale, we deliver intelligent systems that integrate with your business goals and existing workflows:
Webisoft helps teams transform machine learning in crypto into real, working systems for crypto and blockchain use cases. Our engineers bring deep technical experience across AI, data engineering, and enterprise software to solve real production challenges. Instead of experiments that never scale, we deliver intelligent systems that integrate with your business goals and existing workflows:
Strategic Planning and Problem Definition
Webisoft starts every engagement by defining what success looks like and whether a machine learning initiative is viable. We assess your goals, data readiness, and crypto context so teams don’t waste time on models that fail in real use. This strategic beginning ensures your machine learning efforts align with measurable business outcomes, not guesswork.
Custom ML Model Architecture Designed for Crypto Data
Our engineers design models that reflect the unique behavior of on-chain and off-chain crypto data. This includes building predictive forecasting engines, anomaly detectors, and risk models tailored to volatile markets, liquidity conditions, and protocol signals. By focusing on explainable, auditable architectures, we deliver systems that stakeholders trust and can maintain long term.
Data Engineering and Feature Development
Webisoft understands that good ML starts with good data. Our team prepares, cleans, and structures high-volume streaming and historical data so your models learn signal instead of noise. From feature engineering to validation, we create the foundations that improve accuracy and reduce false positives in live crypto environments.
Integration With Existing Systems and Software
Deploying a model is only half the job; integrating it into real systems is where value is realized. Webisoft embeds machine learning into your dashboards, trading engines, risk platforms, or backend services so teams can act on insights directly. This integration minimizes friction and accelerates adoption, turning data science outputs into operational workflows.
Enterprise-Grade Architecture and Scalability
Our engineers build infrastructure that scales with data growth and user demand across cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP. We design modular, secure data pipelines that power continuous model training, evaluation, and retraining. This enterprise readiness means your systems stay robust even as crypto volumes and complexity grow.
MLOps and Long-Term Model Maintenance
Webisoft doesn’t just deploy models; we ensure they stay accurate over time. Our MLOps practices include drift monitoring, retraining schedules, and performance alerts to prevent silent degradation as market behavior evolves. Teams receive automated monitoring dashboards and retraining pipelines so models remain reliable and efficient long after launch.
Security, Governance, and Compliance Built In
Security and transparency matter in crypto systems. We integrate governance frameworks, audit trails, and compliance measures into ML workflows so predictions and decisions can be validated and traced. This approach helps risk teams, auditors, and leadership teams trust the systems they depend on.
Human-Centered Support and Ongoing Collaboration
Webisoft provides ongoing support after launch, offering tuning, optimization, and performance reporting. Our engineers don’t just hand over code; we partner with your team, guiding adjustments as data patterns shift and requirements evolve. This long-term collaboration turns machine learning from a one-time project into a strategic asset.
Cross-Disciplinary Expertise Across Tech Stacks
Our team combines expertise in full-stack engineering and machine learning with deep blockchain and AI knowledge. This means problems are solved holistically, from backend data ingestion to frontend user insights. We pull from both Web2 and Web3 experience to make sure your crypto ML systems operate securely and efficiently.
Measurable Impact on Business KPIs
At Webisoft, success isn’t measured by lines of code but by real performance improvements. Teams can expect faster decision cycles, better risk detection, and reduced manual workload once machine learning systems are in place. Because every project begins with KPIs, results are clear, measurable, and tied back to your business goals.
Build machine learning systems that survive real crypto markets.
Apply machine learning in crypto with proper data controls, execution awareness, and production readiness.
Conclusion
Machine learning in crypto works when teams treat it as an engineering system, not a prediction shortcut. It helps analyze complex data, automate decisions, and manage risk, but it does not remove uncertainty or volatility.
Models fail when teams ignore data quality, market shifts, and execution constraints. Realistic expectations matter more than model choice or accuracy claims. When applied with proper data pipelines, monitoring, and human oversight, machine learning can support stronger crypto systems over time.
FAQs
Can machine learning predict crypto prices accurately?
Machine learning can identify patterns and probabilities, but it cannot predict prices with certainty. Crypto markets react to sudden events like regulation news, hacks, or liquidity shocks that models cannot foresee. Most systems focus on risk management and signal support, not exact price prediction.
How much data is needed to use machine learning in crypto?
There is no fixed amount, but more data does not always mean better results. Models need relevant, clean, and consistent data rather than long histories filled with noise. Many crypto projects fail because they collect data without validating its quality.
Is machine learning better than technical analysis in crypto?
Machine learning and technical analysis solve different problems. Technical indicators work well for simple rules and short-term signals, while machine learning handles complex relationships across multiple data sources. Many successful systems combine both instead of choosing one.
Can small teams or startups use machine learning in crypto?
Small teams can use machine learning if the scope is realistic. Lightweight models and focused use cases work better than large, complex systems. Without proper monitoring and maintenance, even simple models can become risky.
Does machine learning work for all cryptocurrencies?
Machine learning works better for high-liquidity assets with stable data availability. Thinly traded tokens and new projects produce unreliable signals due to sparse and noisy data. Asset selection matters as much as model choice.


