HR Portal Development: Key Steps to Build a Seamless System
- BLOG
- Software Development
- October 19, 2025
Many assume an HR portal is just a digital version of routine HR tasks or a glorified employee dashboard. But that’s a shallow view. A well-built HR portal redefines how organizations manage people—it’s not just automation, it’s a rethinking of the entire HR workflow.
Developers new to HR portals often treat them like just another software project. But HR portals come with unique architectural and design challenges that set them apart. It’s not just about building features—it’s about structuring systems around complex workflows, compliance, and user roles.
A Modern HR portal development process will include –
- Employee Self-Service Layer
- Complex Role & Permission Hierarchies
- Regulatory Compliance Handling
- Full Employee Lifecycle Coverage
- Sensitive Data Handling
- Legal Document Management
- Benefits & Payroll Integrations
- Localization & Globalization
- Internal Communication Integration
- Real-Time Compliance Alerts & Workflows
Read this guide to get details on how to develop a high-performing HR portal that meets today’s business needs.
Contents
- 1 What is The HR Portal?
- 2 Key Features of a Modern HR Portal
- 3 How To Develop an HR Portal? Stepwise Guide
- 3.1 Step 1: Auditing HR Processes and Identifying Functional Requirements
- 3.2 Step 2: Defining User Roles and Access Levels
- 3.3 Step 3: Designing for the Employee Lifecycle
- 3.4 Step 4: UX/UI with Self‑Service in Mind
- 3.5 Step 5: Building Secure and Compliant Architecture
- 3.6 Step 6: Developing Core Modules
- 3.7 Step 7: Testing, Security Hardening & Quality Assurance
- 3.8 Step 8: Launch, Train, and Iterate Launch, Train, and Iterate
- 3.9 Step 9: Post-Launch Support and Optimization
- 4 Best Practices for an Effective HR Portal Development
- 5 Integrating AI Trechnogies in HR Portal
- 6 Advantages of a Modern HR Portal
- 7 HR Portals for Small & Medium‑Sized Businesses (SMBs)
- 8 How to Choose an HR Portal Service
- 9 The Future of HR Portals: Growing Trends & Innovations
- 10 Common Challenges in HR Portal Implementation & How to Overcome Them
- 11 In Closing
- 12 FAQs
- 12.1 How long does it take to develop and implement an HR portal?
- 12.2 How does role-based access control work in an HR portal?
- 12.3 What security measures should be implemented to protect sensitive employee data?
- 12.4 How do HR portals support remote and hybrid workforces?
- 12.5 Can an HR portal help with employee retention?
What is The HR Portal?
An HR portal is a centralized digital platform that optimizes human resource management.
It serves as a secure, self-service hub. Employees and HR teams access essential HR functions, documents, and communication tools.
Modern HR portals integrate employee data management, payroll processing, benefits administration, and compliance tracking within a unified system.
They enhance operational efficiency by reducing manual HR tasks and improving accessibility.
A well-designed HR portal supports automated workflows. You can ensure smoother onboarding, leave requests, and performance evaluations.
Key Features of a Modern HR Portal
A modern HR portal is more than just an employee database.
Below are key features that define a high-performing HR software development:
- Employee Self-Service (ESS): Employees can update personal details, access payroll data, and track benefits without HR intervention. It reduces administrative workload and enhances efficiency.
- Centralized Document Management: Policies, contracts, handbooks, and compliance documents are stored in an easily accessible repository. The employees and HR teams of your company can retrieve updated files anytime.
- Automated Workflows: The time has gone for manual approvals. By automating leave requests, expense reimbursements, you’ll save time and ensure the accuracy of your HR processes.
- Role-Based Access Control: With role-based access control, you can ensure that each person only sees what they need to. It protects your data while giving employees and managers access to relevant information.
- Performance and Feedback System: Track, set goals, and give real-time feedback—all in one place. This system helps you align employee performance with company objectives.
- Mobile Accessibility for Flexibility: With mobile optimization, employees can access pay slips, request leave, and complete tasks from anywhere. They have the flexibility to stay connected anytime, anywhere.
How To Develop an HR Portal? Stepwise Guide
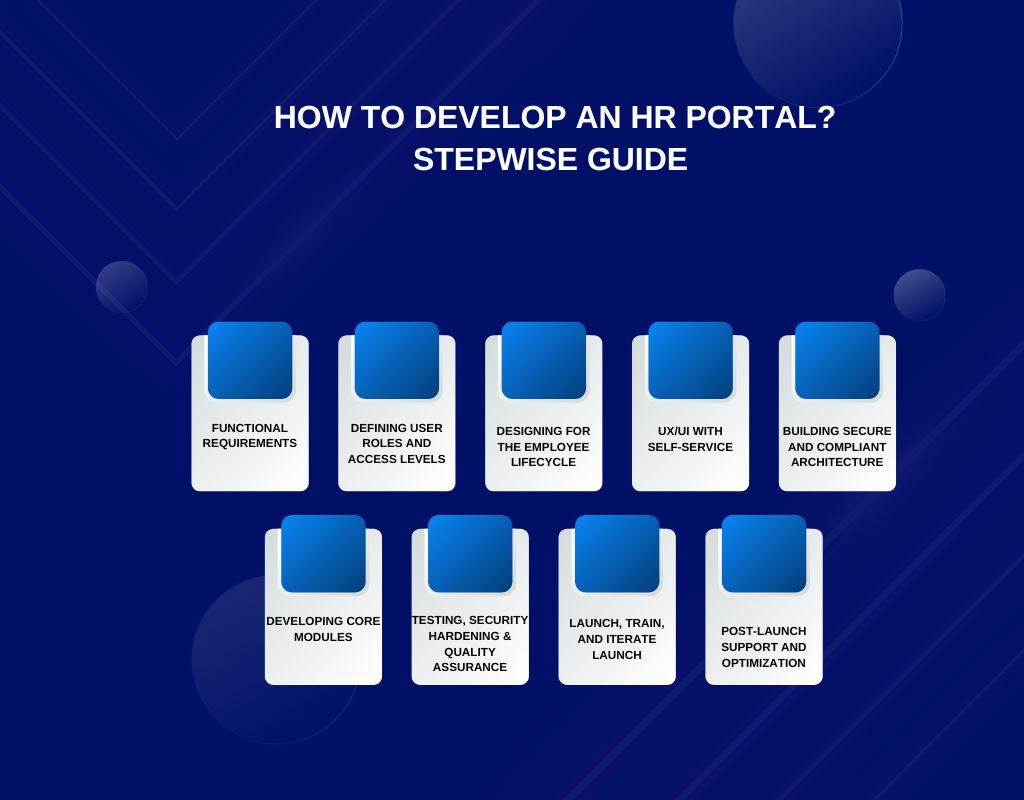
Building an HR portal means translating real‑world HR workflows and data into a secure, self‑service platform anyone can use. This roadmap walks you from initial process audit to launch and ongoing optimization—minus the technical jargon.
Step 1: Auditing HR Processes and Identifying Functional Requirements
Before development begins, we conduct a deep‑dive audit of the organization’s existing HR processes. This involves sitting with HR personnel, finance, and IT to understand how tasks are currently handled, where bottlenecks exist, and which manual steps they want automated or improved. We ask:
We probe how the hire‑to‑exit journey works today, what unique policies or approval loops exist, which time‑savers HR craves, where compliance or security gaps lie, and which legacy tools or spreadsheets hold data we’ll need to migrate.
This quick audit keeps the portal aligned with real HR operations—not generic software.
Step 2: Defining User Roles and Access Levels
An HR portal typically serves multiple user types—employees, HR admins, team managers, finance teams, etc. We define:
- What each role can view, edit, or approve
- Which actions trigger notifications or workflows
- How data privacy is maintained across departments
This is the backbone of the platform’s permission architecture.
Step 3: Designing for the Employee Lifecycle
We structure the portal around every phase of an employee’s journey:
- Recruitment: Job posting, application tracking
- Onboarding: Digital forms, task checklists, policy sign-offs
- Active Employment: Leave requests, timesheets, payslips, performance goals
- Offboarding: Exit forms, asset handover, final pay reports
This modular structure allows HR to manage every stage from a single dashboard.
Step 4: UX/UI with Self‑Service in Mind
Most users of the portal aren’t tech‑savvy, so every interaction is streamlined: we minimize clicks, use clear labels like “Request Leave” instead of vague buttons, embed contextual tooltips, and ensure the experience is fully responsive across mobile and desktop. Accessibility and simplicity remain the guiding principles.
Step 5: Building Secure and Compliant Architecture
Given the sensitivity of HR data, security is woven into every layer of development: we enforce role‑based access control to confine data to the right eyes, store every record with AES‑256 encryption, strengthen logins with optional two‑factor authentication, and maintain detailed audit logs that satisfy GDPR and regional labor‑law requirements.
Step 6: Developing Core Modules
Each feature is developed as a module that can work independently and integrate seamlessly:
- Data Migration & Legacy Integration – scripts and ETL pipelines to import historical employee records, timesheets, and payroll data from spreadsheets or third‑party systems
- User Management
- Leave & Attendance
- Payroll Integration
- Document Center
- Performance Review Engine
- User Management
- Leave & Attendance
- Payroll Integration
- Document Center
- Performance Review Engine
- Notifications & Alerts System
APIs are built to connect with third-party tools like payroll systems, calendars, and internal communication platforms.
Step 7: Testing, Security Hardening & Quality Assurance
We combine functional QA with rigorous security checks to ensure the portal is reliable and resilient:
- Functional walkthroughs of core HR flows (hire → onboard → pay → exit)
- Cross‑browser and mobile responsiveness testing
- Automated unit and integration tests for critical logic (leave accrual, payroll rules)
- Penetration testing and vulnerability scans to uncover SQL‑injection, XSS, CSRF, and authentication flaws
- Verification of encryption in transit (TLS) and at rest (database, file store)
- Role‑based access validation—ensuring no privilege escalation
- Performance and load testing under peak payroll cycles
These layers catch both usability hiccups and security gaps before production.
Step 8: Launch, Train, and Iterate Launch, Train, and Iterate
We deploy the portal in phases:
- Internal HR team beta
- Manager rollout
- Company-wide release
Alongside this, we provide:
- Admin training
- In‑app guidance for employees
- A final go‑live security checklist (SSL certificates, secure headers, WAF rules)
- Feedback loops to continuously refine usability
Step 9: Post-Launch Support and Optimization
HR policies change, and so does legislation. We ensure the system evolves with:
- Regular updates
- Compliance patching
- New feature integrations (like chatbot assistants or performance analytics dashboards)
The portal is treated as a living product—not a one-time build.
Best Practices for an Effective HR Portal Development
Developing a high-performing HR portal requires a strategic approach.
Follow these HR portal best practices to minimize operational risks and ensure long-term value.
1. User-Centric Approach: An HR portal must cater to employees, HR teams, managers, executives, and external partners. You need to ensure that each user group can efficiently perform its tasks. For example, the employee management system should provide payroll access, while HR teams have robust administrative controls
2. Self-Service for HR Processes: A modern custom HR portal must have self-service capabilities. It enhances efficiency and reduces administrative burdens. For instance, employees should access HR tasks independently, while managers track performance and approve requests. HR teams automate onboarding, compliance, and policy updates for real-time accuracy.
3. Efficient Onboarding Process: A well-structured HR portal streamlines onboarding and ensures the new hires integrate smoothly into the organization. You need to implement automated workflows to reduce paperwork and administrative delays.
4. Two-Way Communication: An HR portal should facilitate open communication between employees and management. Employees should provide feedback easily, and managers should share performance feedback. It helps build a collaborative work environment.
5. Security Audits and Updates: With employee data breaches rising by 41% in 2023, it is now essential to perform regular security audits. It helps to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with GDPR and HIPAA.
Research says that non-compliant businesses face an average of $14 million in penalties and remediation costs.
6. Launch the Portal with Training: To have a successful HR portal, you need to launch a structured training program to ensure user adoption and efficiency.
Studies indicate that 92% of employees feel more engaged when provided with comprehensive training.
Integrating AI Trechnogies in HR Portal
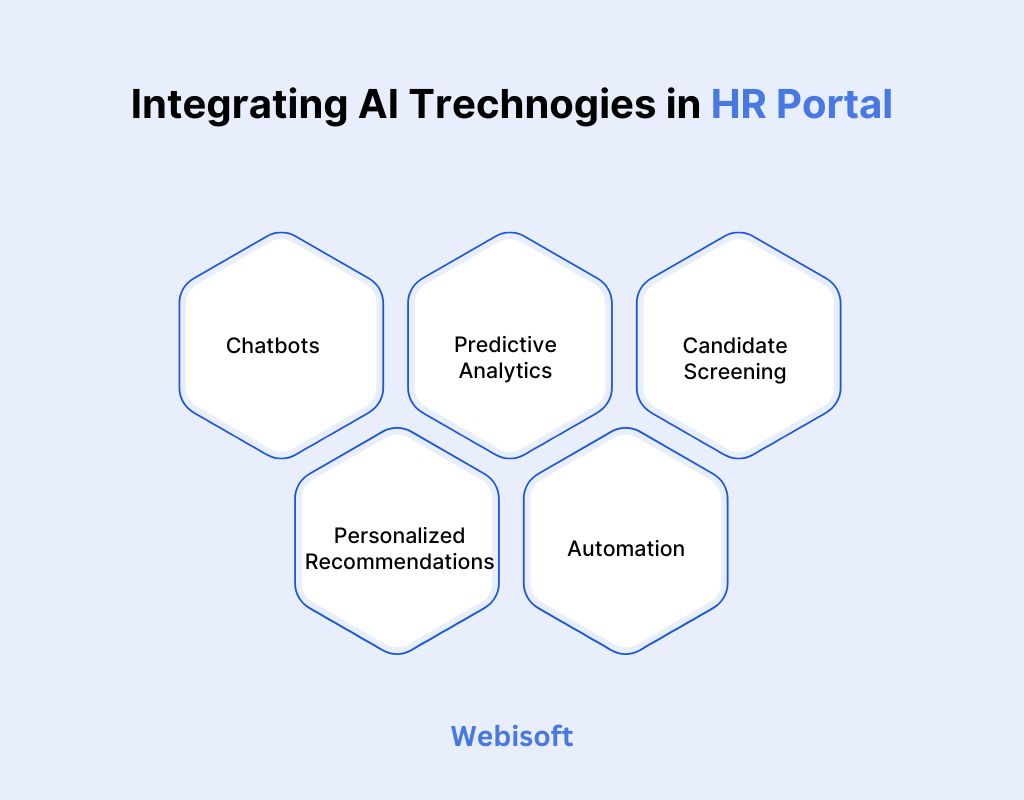
AI is transforming HR portals by automating tasks, improving decision-making, and enhancing user experiences.
Have a quick glimpse of key AI technologies that are transforming HR portals.
1. Chatbots – Automating Employee Assistance
Chatbots are AI-driven virtual assistants that handle HR inquiries in real-time. They replace traditional helpdesk functions, offering quick, automated responses.
In HR portals, AI-powered chatbots assist employees with leave requests, payroll queries, and benefits information. They guide new hires through onboarding and answer common policy-related questions.
It reduces HR workload, improves response time, and ensures 24/7 availability.
2. Predictive Analytics – Data-Driven Workforce Planning
Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast HR trends and help you predict challenges before they arise.
With AI-driven models, you can analyze performance records, absenteeism, and engagement levels. It detects patterns that signal attrition risk, productivity shifts, and future hiring needs.
3. Candidate Screening – Smarter Recruitment Decisions
AI-powered screening automates resume help you automate filtering and applicant evaluation. You can ensure faster and data-driven hiring decisions.
In HR portals, AI scans resumes, highlights relevant skills, and ranks candidates based on job requirements. Machine learning continuously refines the selection criteria to improve accuracy.
With bias-free algorithms, you ensure fair evaluations that save you time and reduce hiring costs.
4. Personalized Recommendations – Employee Growth & Engagement
AI-driven personalization tailors training, career paths, and internal job opportunities to individual employees.
In HR portals, AI analyzes employee performance, skills, and career goals. It recommends training programs, mentorship opportunities, and internal job postings.
Employees gain relevant skills, feel more engaged, and progress within the company.
5. Automation – Efficiency in HR Operations
HR automation helps you automate manual and repetitive processes. It reduces errors and saves time. In HR portals, automated workflows handle payroll processing, compliance tracking, leave approvals, and document verification.
It improves accuracy, reduces administrative burden, and ensures compliance.
Advantages of a Modern HR Portal
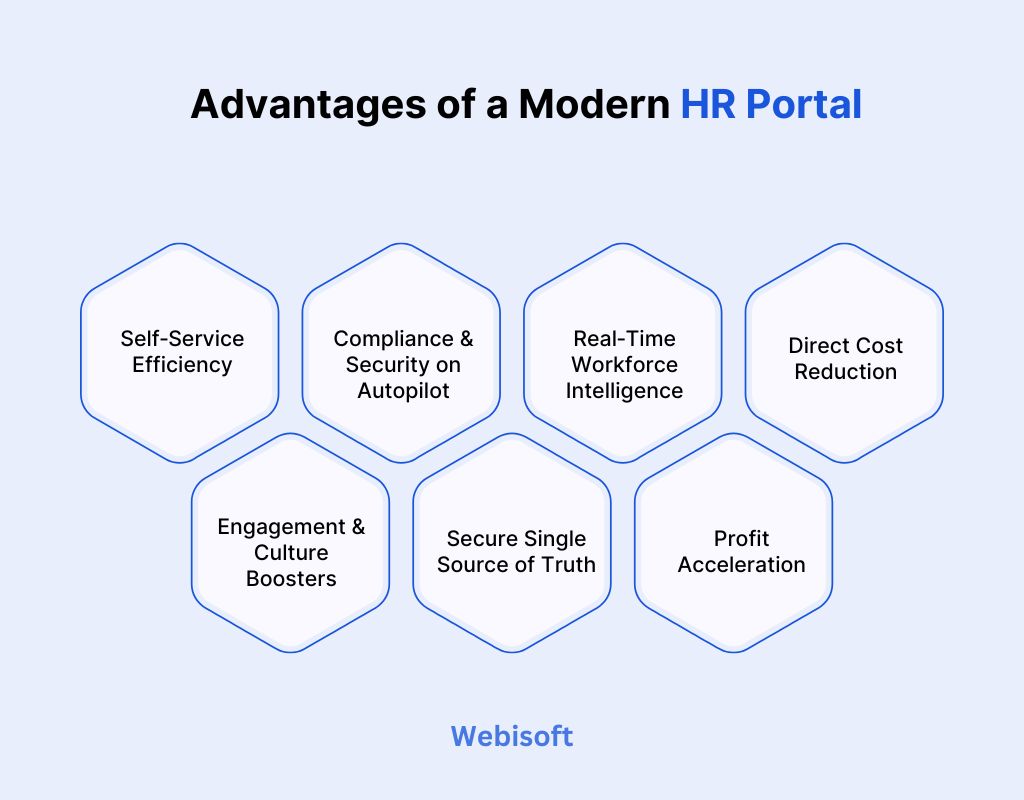
A well‑built HR portal is more than a convenience app—it’s a profit booster, risk reducer, and engagement engine rolled into one. Here’s how a modern platform turns everyday HR tasks into strategic wins:
1. Self‑Service Efficiency (Time Saving)
Employees complete onboarding, leave requests, and profile updates without emails or paper forms—releasing HR staff to focus on strategy and cutting turnaround time from days to minutes.
2. Compliance & Security on Autopilot
Role‑based access, encryption, automatic policy updates, and audit‑ready logs guard sensitive data and satisfy regulators—far beyond what spreadsheets or generic workflow tools can provide.
3. Real‑Time Workforce Intelligence (Better Decisions)
Dashboards track turnover, absentee trends, and skill gaps in real time, giving leaders hard data to fine‑tune hiring plans, retention tactics, and compensation models.
4. Direct Cost Reduction
Automated payroll, digital document flows, and error‑free calculations slash admin hours, prevent costly fines, and shrink paperwork, stretching every HR dollar further.
5. Engagement & Culture Boosters
Recognition badges, pulse surveys, and onboarding checklists live inside the same workspace employees already use, making culture programs friction‑free and measurable.
6. Secure Single Source of Truth
Encrypted, role‑based storage replaces scattered spreadsheets, reducing breach risk and the hidden costs of data clean‑up during audits.
7. Profit Acceleration
Quicker onboarding and higher retention get revenue‑generating staff productive sooner, while lower admin overhead drops straight to the bottom line.
HR Portals for Small & Medium‑Sized Businesses (SMBs)
Smaller companies often run lean HR teams—or no dedicated HR staff at all—so every minute lost to paperwork hurts. A modern portal levels the playing field by delivering enterprise‑grade tools at subscription prices SMBs can afford.
When Is It Worth Having an Employee Portal?
Data shows the tipping point arrives sooner than many founders expect. Once headcount crosses 40–50 employees, manual onboarding, payroll prep, and leave tracking start eating more than one full work‑day per week of admin time. In fact, SMBs that adopt cloud HR software save up to 800 admin hours a year, worth roughly $25 K in payroll (Folks HR ROI study, 2023).
No‑Code & Low‑Code Options
If you’re not ready for a full‑scale SaaS suite—or you need something ultra‑custom—no‑code builders like Softr, Glide, or Microsoft Power Apps let you assemble a branded employee portal with drag‑and‑drop components. You connect spreadsheets or Airtable bases, add secure login, and launch in days instead of months. Nocode portals can handle basics like document libraries, onboarding checklists, and PTO forms, then scale up later by plugging into payroll APIs or single sign‑on.
Tip for SMBs: Start with a no‑code MVP to prove the concept, gather employee feedback, and build the business case for a larger platform once usage (and headcount) grows.
How to Choose an HR Portal Service
- Match Features to Pain Points List the three HR chores that burn the most time—e.g., timesheets, compliance paperwork, or recruiting—and verify the vendor automates those first.
- Check SMB Pricing Tiers Look for per‑employee pricing with no minimums and free support. Hidden implementation fees can wipe out year‑one ROI.
- Evaluate Data Migration Tools A good provider offers CSV import wizards or white‑glove migration from spreadsheets and legacy payroll systems.
- Demand Security Proof Ask for SOC 2 or ISO 27001 certifications, data‑at‑rest encryption, and MFA. SMBs are targets too.
- Review Integration Ecosystem See whether the portal connects natively to your accounting, Slack/Teams, or biometric devices. Zapier or native API access is a must for future automation.
- Test the Employee Experience Run a demo with a non‑technical staffer. If they can request leave and find their payslip in under 60 seconds, adoption will be easy.
- Scalability & Exit Options Make sure you can upgrade tiers, add modules, or export data cleanly if you outgrow the service.
Choosing the right portal is less about chasing features and more about eliminating today’s biggest administrative drains while laying a foundation you won’t outgrow tomorrow.
The Future of HR Portals: Growing Trends & Innovations
The evolution of Human Resource (HR) portals is being shaped by several emerging trends and innovations.
These innovations are transforming HR portals into comprehensive platforms:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI is changing HR portals by automating tasks such as employee onboarding. It saves HR departments significant time and reduces delays.
For instance, companies like Hitachi have implemented AI digital assistants to streamline onboarding processes. It results in reduced HR involvement and faster integration of new hires.
2. Growing Focus on Upskilling and Reskilling: With the rapid advancement of technology, there is a growing need for employees to continuously update their skills.
Notably, 83% of HR leaders believe upskilling is essential for workers to remain competitive in a job market shaped by AI.
Modern HR portals now include learning management systems to support ongoing employee growth and help the workforce keep up with changing industry needs.
3. Blockchain for Secure Data Management: Blockchain technology is being integrated into HR portals. It enhances the security and reliability of data management.
By encrypting and verifying employee information, blockchain enables HR managers to protect sensitive data. It confirms the authenticity of applicants’ credentials.
Common Challenges in HR Portal Implementation & How to Overcome Them
Implementing an HR portal can be complex, often leading to operational disruptions if not handled strategically.
These are the key challenges that organizations often face:
1. Employee Resistance to Change
Employees often feel hurdles to new systems due to a lack of familiarity, fear of complexity, or concerns about increased workload.
Solution: Conduct pre-launch awareness programs. Offer step-by-step role-based training with real-time assistance.
Assign HR ambassadors to provide continuous support, collect feedback, and address concerns to encourage long-term engagement.
2. Integration with Existing Systems
HR portals often struggle to integrate with payroll, compliance, and performance management systems due to compatibility issues.
Solution: Choose an HR portal with strong API capabilities and ensure compatibility with existing software before deployment. Conduct thorough system testing before launch to identify and fix integration gaps, ensuring seamless data flow.
3. Data Security and Compliance Risks
HR portals store sensitive employee information, which is vulnerable to cyber threats and non-compliance penalties.
Solution: Implement multi-factor authentication, encryption, and strict access controls to safeguard employee data. Conduct regular security audits and ensure compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific regulations to mitigate risks.
4. Poor User Experience and Accessibility Issues
A complex, non-intuitive design reduces usability and leads to low adoption rates among employees.
Solution: Design the HR portal with a mobile-friendly, user-centric interface featuring easy navigation and personalized dashboards. Gather user feedback post-launch and continuously refine the interface to enhance accessibility and engagement.
5. Lack of Continuous Improvement
Many organizations implement HR portals but fail to update them, causing inefficiencies over time.
Solution: Establish a feedback-driven improvement cycle, analyzing portal usage and addressing gaps. Schedule regular system updates, introduce new features, and ensure HR teams consistently optimize workflows.
In Closing
An effective HR portal development is more than a tool. It’s a strategic asset that enhances workforce management, improves compliance, and drives efficiency.
The right approach ensures seamless integration, security, and user adoption, making HR operations more agile and data-driven.
However, if you are planning to develop an HR portal that transforms your HR management and enhances overall business performance, Webisoft is the right choice. They have strong expertise in developing custom HR portals for clients.
FAQs
How long does it take to develop and implement an HR portal?
The timeline varies based on complexity, customization, and integration needs. On average, implementation takes 3 to 6 months, including testing and training.
How does role-based access control work in an HR portal?
Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that users only have access to the data they need. For example, employees can view their personal information, HR admins can access all data, and managers can view their team’s performance. This enhances security and confidentiality.
What security measures should be implemented to protect sensitive employee data?
Sensitive data should be protected using encryption (AES-256), two-factor authentication (2FA), secure login protocols, and role-based access controls. Regular security audits and compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, and other regulations should also be part of the security strategy.
How do HR portals support remote and hybrid workforces?
Cloud-based HR portals provide mobile accessibility, digital document management, remote onboarding, and virtual communication tools, ensuring seamless HR operations for distributed teams.
Can an HR portal help with employee retention?
Yes, features like real-time feedback, career development tracking, and personalized training recommendations enhance engagement and job satisfaction, reducing employee turnover.
