How Does Blockchain Prevent Hacking and Keeps Data Safe
- BLOG
- Blockchain
- October 17, 2025
Blockchain helps stop hacking by using many computers to share data, strong secret codes, and open records that everyone can check. It started as the base for cryptocurrencies but now protects all kinds of digital information.
What makes blockchain hard to hack? How does blockchain prevent hacking attacks that trouble regular systems every day?
This article will explain the main ideas behind blockchain’s security. It will show why its design makes hacking very tough.
After reading, you will understand how blockchain’s shared and open system builds strong defenses. You’ll also see why it is becoming a key part of trust in our digital world.
Contents
- 1 What is blockchain security?
- 2 Why Blockchain Is More Secure Than Traditional Systems
- 3 Keep Hackers Away with Webisoft’s Blockchain Solutions!
- 4 Distinction Between Private and Public Blockchain Security
- 5 So How Does Blockchain Stop Hacking?
- 6 Type: Flowchart or layered diagram
- 7 Limitations and Challenges in Blockchain Security
- 8 How Fraudsters Attack Blockchain Technology
- 9 Blockchain Security Tips and Best Practices
- 10 How Webisoft Protects You from Hacks with Blockchain
- 11 Keep Hackers Away with Webisoft’s Blockchain Solutions!
- 12 Conclusion
- 13 Frequently Asked Questions
What is blockchain security?
Blockchain security means protecting blockchain systems, networks, and data from hackers and wrong changes. It keeps the information true, safe, and impossible to change by using strong codes, shared control, and clear data structures.
Unlike usual systems that depend on one boss or server, blockchain spreads control across many independent users. This makes it very hard for any one person to change or damage the data.
It also protects the programs on the blockchain, like smart contracts, to stop bugs or weak spots that hackers could use. In the end, blockchain security builds trust. It lets people check, store, and share digital transactions safely without needing middlemen or a central boss. This makes the whole system open and safe for everyone.
Why Blockchain Is More Secure Than Traditional Systems
Blockchain is safer than old-style systems because it works in a very different way. In normal systems, one server or one boss controls all the data. If that server is hacked or fails, everything can break.
In contrast, blockchain spreads the control across many computers. This makes it much harder for attackers to break the system or change the data without being noticed.
To understand this better, let’s compare the key security differences between blockchain and traditional systems:
| Feature | Traditional Systems | Blockchain Systems |
| Data Storage | Centralized – stored on one or few servers | Decentralized – stored across many nodes |
| Single Point of Failure | Yes – if the central server fails, all fails | No – system continues even if one node fails |
| Data Integrity | Easier to modify or corrupt data | Nearly impossible to alter data without consensus |
| Transparency | Limited – depends on the organization | High – all participants can see transactions |
| Tamper Resistance | Low – data can be changed by administrators | High – cryptographic hashes prevent tampering |
| Auditability | Manual or limited automation | Built-in – every transaction is recorded immutably |
| User Trust | Based on institution or authority | Based on code and network consensus |
| Security in Attack Scenarios | Vulnerable to targeted attacks | Resistant due to distributed nature |
Keep Hackers Away with Webisoft’s Blockchain Solutions!
Call us or schedule a free meeting to learn how it works.
Distinction Between Private and Public Blockchain Security
Public blockchains are open networks where anyone can join, take part, and verify transactions. Their security depends on decentralization, strong encryption, and consensus methods like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake.
Private blockchains on the other hand only allow certain authorized people to join. Their security is based on controlling who can access the network, permissioned nodes, and rules set by the organization managing it.
In summary:
| Aspect | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain |
| Access | Open to anyone | Restricted to authorized participants |
| Decentralization | Highly decentralized | Partially decentralized or centralized |
| Security Reliance | Cryptography, consensus, and network size | Access control, permissions, internal policies |
| Vulnerability | 51% attacks possible but costly | Insider threats and weak permissions risk |
| Transparency | High (public ledger) | Limited to participants |
Both types have strong security models but apply them differently based on their design and use cases.
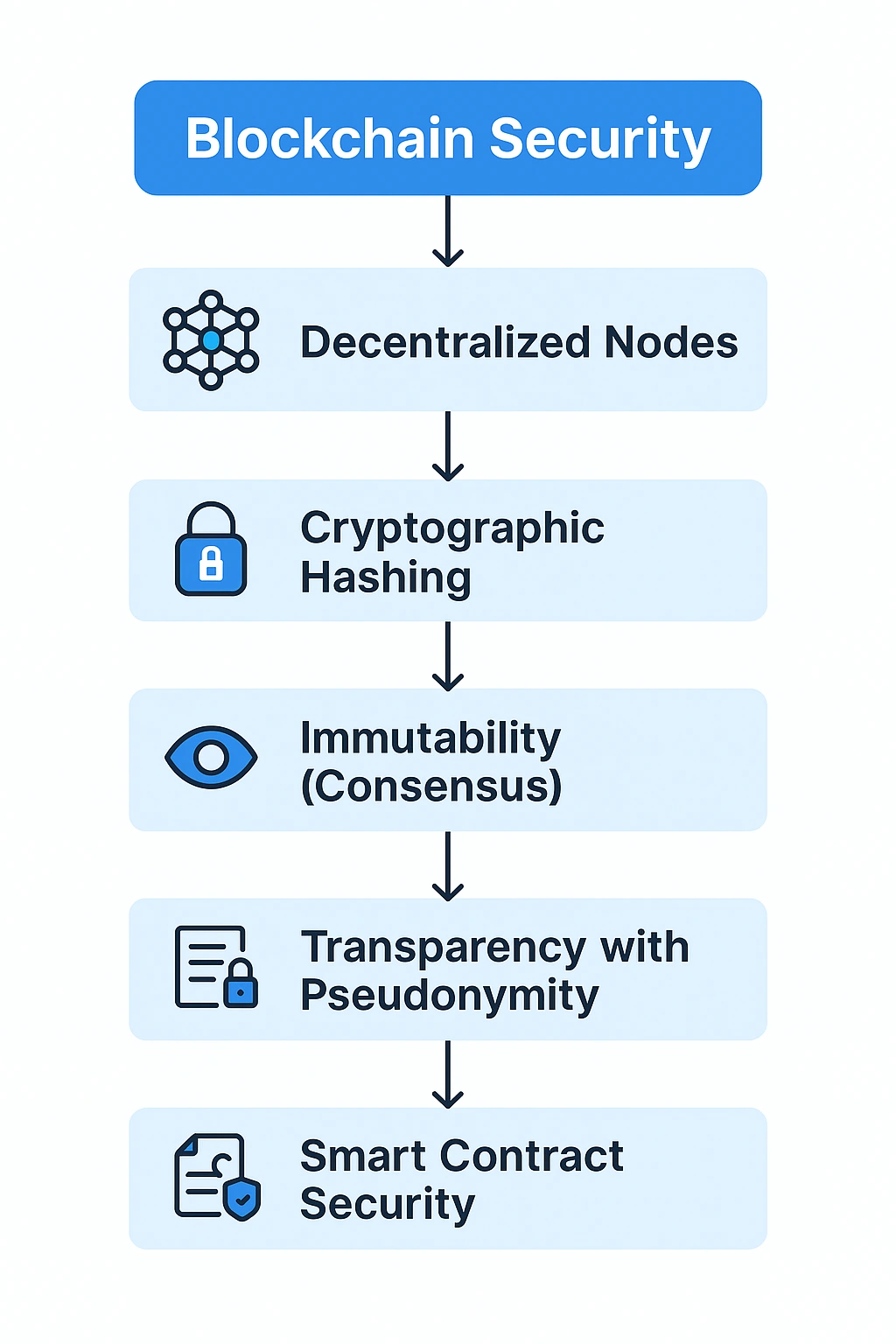
So How Does Blockchain Stop Hacking?
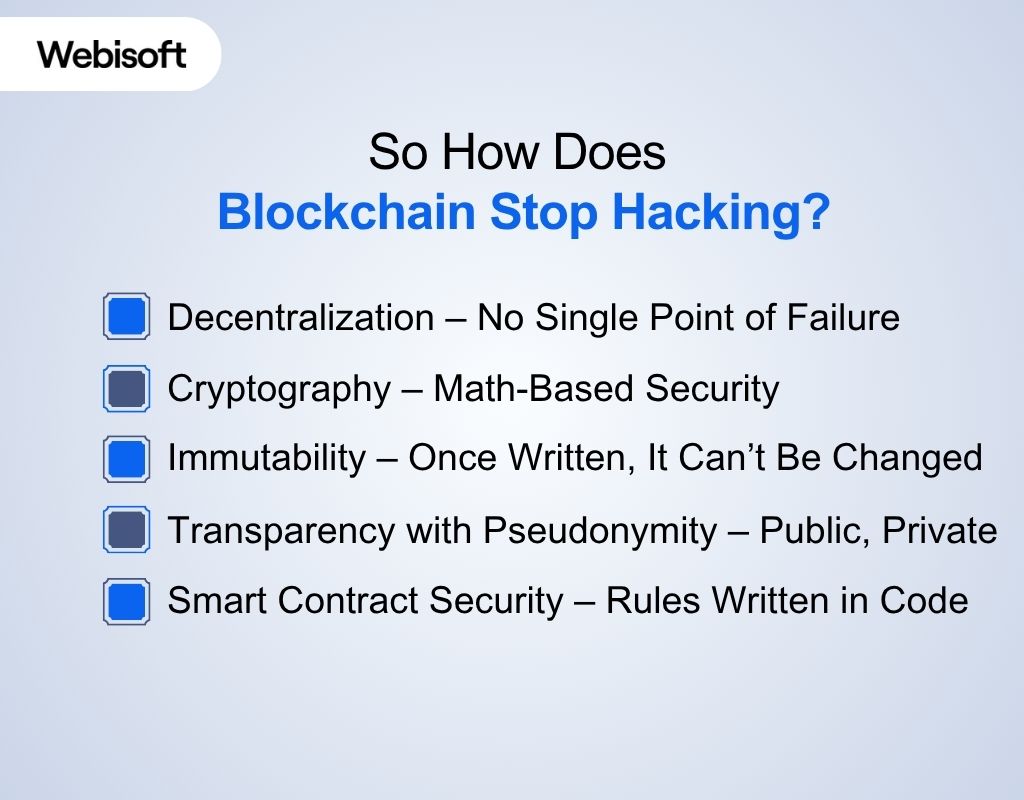
Blockchain keeps your data safe in a way that feels almost like magic—but it’s a really smart design. This technology uses strong codes, shared records, and careful checks to make hacking very hard. Here, you’ll learn how does blockchain prevent hacking and why it’s one of the safest systems out there.
Decentralization – No Single Point of Failure
In normal systems, all the data is stored in one main server. If hackers break into that one place, they can steal or change everything. But blockchain cybersecurity works differently—it uses a decentralized network made up of many computers called nodes.
Each node has a full copy of the entire blockchain. When a new transaction happens, all these nodes work coordinate to check if it’s valid and then record it.
Why this protects against hacking:
- To make any changes, a hacker would need to take control of more than 50% of all the computers (nodes) in the network at the same time. This is called a 51% attack.
- In huge blockchains like Bitcoin or Ethereum, that would mean hacking thousands of computers all over the world at once. That’s almost impossible and would cost a lot of money and resources.
Because the system is spread out across so many computers, there’s no single weak spot. This makes blockchain very strong against central hacking attacks.
Cryptography – Math-Based Security
Blockchain uses a special kind of math called cryptographic hashing to protect data. A hash is like a digital fingerprint of some information. If you change even one small part of the data, the hash will completely change.
Each block in the blockchain includes:
- A list of transactions,
- A unique hash (like a fingerprint),
- And the hash of the block before it.
This setup connects all the blocks like links in a chain. If someone tries to change even a small detail in one transaction:
- The hash of that block becomes different,
- The next block won’t match the old hash anymore,
- And the rest of the chain becomes broken and invalid.
To get around this, a hacker would need to recalculate the hash for every block that comes after the one they changed. Doing this would take an enormous amount of computer power and time.
In the real world, this is nearly impossible to pull off—so it protects the blockchain from being tampered with.
Immutability – Once Written, It Can’t Be Changed
In a blockchain, once a block is added to the chain and confirmed, it becomes unchangeable. This means no one can edit or delete it later. This rule is enforced by two key systems:
- The hash linking system – Each block is connected to the next using a special code (called a hash). If someone tries to change even a tiny part of a block, the link breaks, and the chain no longer fits properly.
- The consensus mechanism – All computers (called nodes) in the network must agree on new blocks. If one node tries to change something, the others will reject it.
Why this makes the system secure:
- The entire transaction history is permanent,
- No one can secretly change or erase records,
- This builds automatic trust, because the data always stays the same.
Even if a hacker gets control of one computer in the network, they can’t change the past. They’d need to convince all the other computers to accept that change—which is nearly impossible.
Transparency with Pseudonymity – Public, Yet Private
Most blockchains (like Bitcoin and Ethereum) are open to everyone. This means anyone can see all the transactions happening on the blockchain.
But instead of showing real names, the system shows user addresses—a long string of letters and numbers. This is called pseudonymity, which means people are hidden behind fake names.
So, you can see what each address is doing—like sending or receiving tokens—but you don’t always know who owns that address.
Security benefits:
- Because the data is open to all, it becomes easier to notice if something looks strange or suspicious.
- If someone tries to cheat or change something, the entire network can see it.
- This openness helps protect the system. Hackers know that if they try to do anything wrong, it won’t stay hidden—so they are less likely to try.
Smart Contract Security – Rules Written in Code
Smart contracts are small computer programs that are saved on the blockchain. They work on their own when certain conditions are met. For example, smart contracts can:
- Automatically send money after a product is delivered,
- Control or manage loans and property,
- Handle deals or agreements without needing a middleman like a lawyer or company.
Once a smart contract is added to the blockchain, it usually can’t be changed—unless it was designed from the start to allow updates. If the smart contract development is done carefully and audited, it’s very hard for hackers to break it.
How this helps stop hacking:
- No manual process = fewer chances for human mistakes or cheating,
- The code is open for everyone to see, so anyone can check how it works. If the contract is written carefully and checked (audited) by experts, it’s very hard for hackers to break it.
But if the contract has mistakes in the code or is written badly, hackers can still find a way to attack it. That’s why it’s very important to check the smart contract code with a security audit before using it.
Type: Flowchart or layered diagram
Limitations and Challenges in Blockchain Security
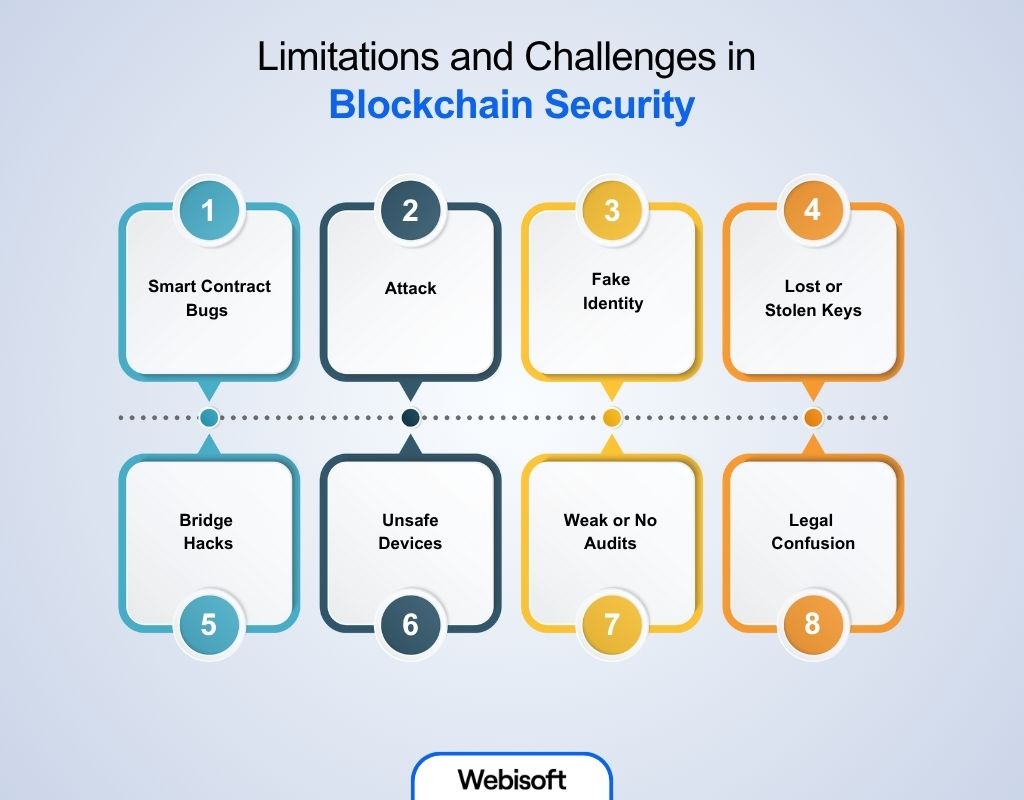
Despite its promise of decentralization and immutability, blockchain is not inherently immune to vulnerabilities. The following are the major blockchain security issues and challenges that developers, organizations, and users must consider:
Smart Contract Bugs
Smart contracts are auto-running programs. But if the code is weak, hackers can break it.
- Example: In 2016, hackers stole ~$60M from The DAO on Ethereum.
- Common problems: Repeating function calls (reentrancy), number errors (overflow), unfair advantages (front-running), and missing input checks.
51% Attack
If one group controls over half of a network’s mining power, they can cheat the system.
- What they can do: Change past records, block other people’s transactions, or spend coins twice.
- Smaller blockchains face this risk more than big ones like Bitcoin.
Fake Identity (Sybil Attack)
One person can pretend to be many users by creating fake accounts.
- Why it’s bad: It can trick the network and mess up how decisions are made.
Lost or Stolen Keys
Your private key is like your secret password. Lose it, and your crypto is gone forever.
- There’s no “forgot password” option. You are the only one who can protect it.
Bridge Hacks
Bridges let tokens move between blockchains. But they are often weak spots.
- Big losses: Hackers stole $600M from Ronin and $320M from Wormhole.
- Why? These bridges often rely on a small group of validators. That makes them easy targets.
Unsafe Devices
Even if the blockchain is safe, your phone, browser, or wallet might not be.
- Risks include: Viruses, fake websites, bad browser extensions, and apps that steal your data.
Weak or No Audits
Smart contracts should be checked before going live. But there’s no one global rule for doing this right.
- Some audits miss bugs. Projects may look safe but are not.
Legal Confusion
Blockchains work across the world. But laws don’t.
- That means a blockchain may be legal in one country, but not in another.
- This can cause trouble for businesses and users, and it’s one of the often overlooked disadvantages of blockchain.
Together, these examples highlight both how does blockchain prevent hacking and the areas where its security must still be strengthened.
How Fraudsters Attack Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is made to be very safe. But bad people still try to find ways to trick or hack it. They may attack the system or go after the users. To understand how does blockchain prevent hacking, it’s also important to learn how these attacks happen:
- 51% Attack: When someone controls more than half the network to change records or spend coins twice.
- Smart Contract Bugs: Using mistakes in the code to steal money or cause problems.
- Phishing: Tricking people to give away passwords or secret keys.
- Fake Accounts (Sybil Attack): Making many fake users to confuse the system.
- Bridge Attacks: Attacking places where tokens move between blockchains.
- Lost or Stolen Keys: If your secret key is lost or stolen, you lose your money.
- Bad Software or Fake Wallets: Apps or programs that steal your data or money.
By learning how these attacks work, and how does blockchain prevent hacking, you can better protect yourself and your assets.
Blockchain Security Tips and Best Practices
Keeping blockchain safe is not just about technology. Users must also be careful. Following good habits helps protect your money and data from hackers.
- Use Strong Passwords: Make passwords hard to guess.
- Turn On Two-Factor Authentication: Add extra protection to your accounts.
- Update Your Software: Always use the latest version of apps and wallets.
- Check Smart Contracts: Have experts look at smart contracts before you use them.
- Keep Backup of Keys: Save your secret keys safely and offline.
- Be Careful with Links and Emails: Don’t click on suspicious links or emails.
- Use Trusted Services: Use well-known wallets, exchanges, and bridges.
- Learn About New Risks: Stay updated on the latest security tips and threats.
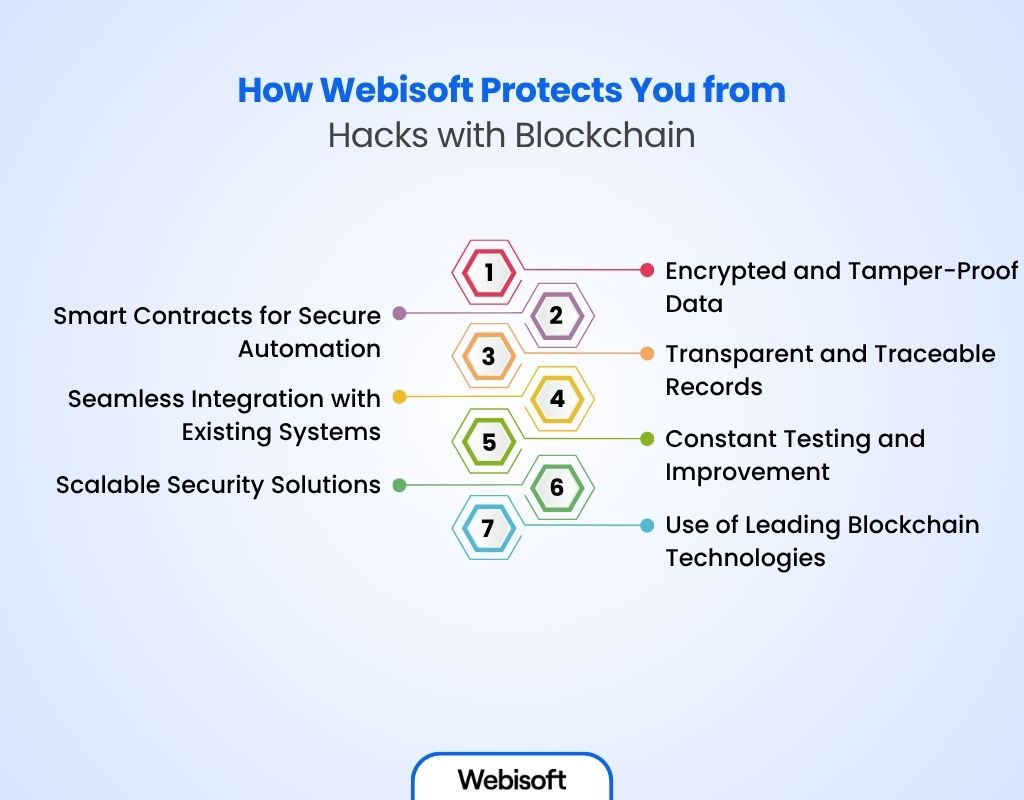
How Webisoft Protects You from Hacks with Blockchain
Cyber threats are everywhere today. Webisoft uses blockchain technology to keep your business safe with secure, unchangeable, and clear data. Their solutions protect you from hacks and data breaches, so you can grow without worry.
Many ask, “how does blockchain prevent hacking?” It spreads data across many computers, locks it with strong codes, and stops any secret changes. Webisoft uses these features to keep your systems secure.
Key Ways Webisoft Protects You:
- Encrypted and Tamper-Proof Data: Every transaction and piece of information is locked with secret codes and stored on the blockchain. This makes it almost impossible for hackers to change or steal your data.
- Smart Contracts for Secure Automation: Smart contracts work automatically and only act when all conditions are met. This lowers the chance of mistakes or fraud and builds trust in your business processes.
- Transparent and Traceable Records: Blockchain keeps a clear, unchangeable record of all activities. This helps find and stops fraud early before it can cause harm.
- Seamless Integration with Existing Systems: Webisoft makes sure blockchain fits well with your current technology without causing problems or risks.
- Constant Testing and Improvement: All parts of the system are regularly tested and improved to keep up with new cyber threats and maintain strong security.
- Scalable Security Solutions: As your business grows, Webisoft’s blockchain systems grow safely too, keeping your data protected even during busy times.
- Use of Leading Blockchain Technologies: Webisoft uses trusted platforms like Ethereum, Hyperledger, and Polkadot to provide strong security made just for your business needs.
Keep Hackers Away with Webisoft’s Blockchain Solutions!
Call us or schedule a free meeting to learn how it works.
Conclusion
So, how does blockchain prevent hacking? You’ve seen how blockchain stops hacking by its design using many computers, secret codes, and open records. These key ideas make it a breakthrough for digital safety.
Now, it’s time to decide how to use this strong technology to protect your data and build trust online.
With the right knowledge and help, you can move forward with confidence toward smarter, safer security.
If you want expert help to use blockchain in the best way for you, Webisoft is here to guide you at every step.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can someone edit or delete data from a blockchain?
No. Blockchain is immutable—once data is added to the chain, it cannot be changed or deleted without altering all subsequent blocks, which requires control over most of the network.
How does blockchain detect tampering?
Every block contains a hash of its data. If anyone alters a block, its hash changes—breaking the link to the next block. Nodes will reject this inconsistency instantly.
How do blockchain nodes help prevent hacks?
Each node has a full or partial copy of the blockchain. They continuously validate transactions and block updates. A single compromised node can’t change the global ledger.


