Healthcare compliance plays a crucial role in ensuring the delivery of safe and high-quality care while adhering to legal and ethical standards. It encompasses a wide range of regulations, guidelines, and best practices designed to protect patients, healthcare providers, and the healthcare system as a whole.
Understanding and navigating the complex landscape of healthcare compliance is vital for healthcare professionals and organizations.
In today’s ever-evolving regulatory environment, staying compliant with the multitude of laws and regulations can be challenging. From privacy and security regulations like HIPAA to fraud and abuse laws, healthcare compliance covers various aspects of operations, data management, billing, and patient safety.
Compliance failures can result in severe penalties, legal consequences, reputational damage, and compromised patient care.
This pocket guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of healthcare compliances, helping healthcare professionals, administrators, and organizations navigate the regulatory landscape effectively. It will delve into key regulatory bodies, frameworks, and laws, while also addressing emerging trends and best practices.
By following this guide, readers will gain the necessary knowledge and tools to establish and maintain compliance, safeguard patient information, and promote a culture of ethical and legal healthcare practices.
So, without further ado, let’s get into a compact handbook on healthcare compliances.
Contents
- 1 What does Healthcare Regulation Compliance Refer to?
- 2 What Is The Purpose Of Compliance In Health Care?
- 3 What is the Significance of Healthcare Compliance?
- 4 What are the Potential Consequences of Compliance Issues?
- 5 Key Regulatory Bodies and Frameworks
- 6 Regulatory Landscape and Compliance in the US Healthcare System
- 7 Enhanced Oversight for Digital Health Solutions
- 8 Other Healthcare-Related Regulatory Requirements
- 9 Conclusion
What does Healthcare Regulation Compliance Refer to?
Healthcare regulation compliance refers to adherence and conformity to the laws, regulations, guidelines, and standards that govern the healthcare industry. It encompasses a set of rules and requirements designed to ensure the delivery of safe, effective, and ethical healthcare services.
Compliance is essential for healthcare providers, organizations, and professionals to protect patients’ rights, maintain data privacy and security, prevent fraud and abuse, and meet quality and safety standards.
In a complex and highly regulated industry, healthcare regulation compliance covers various aspects, including patient privacy (e.g., HIPAA), billing and coding accuracy, medical device regulations, and quality assurance. Compliance failures can have severe consequences, including legal penalties, reputational damage, and compromised patient care.
Maintaining healthcare regulatory compliance requires a comprehensive understanding of the regulatory landscape, ongoing monitoring and assessment, robust policies and procedures, and employee training. It ensures that healthcare entities operate within legal and ethical boundaries, promoting patient trust, transparency, and the delivery of high-quality care.
What Is The Purpose Of Compliance In Health Care?
The purpose of compliance in healthcare is to ensure that healthcare providers, organizations, and professionals operate within legal and ethical boundaries, promoting patient safety, privacy, and the delivery of high-quality care. Compliance encompasses adherence to laws, regulations, guidelines, and industry standards specific to healthcare.
By maintaining compliance, healthcare entities demonstrate their commitment to ethical practices, protect patient rights, and prevent fraud and abuse. Compliance efforts aim to safeguard sensitive patient information, maintain data privacy and security, and ensure accurate billing and coding practices.
It also helps in meeting quality and safety standards, reducing medical errors, and improving patient outcomes.
Furthermore, compliance plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the healthcare system by preventing illegal activities, such as kickbacks or fraudulent billing. It fosters trust and transparency between healthcare providers and patients, as well as regulatory bodies.
Ultimately, the purpose of compliance in healthcare is to create an environment that prioritizes patient well-being, upholds legal and ethical standards, and safeguards the integrity of the healthcare industry.
What is the Significance of Healthcare Compliance?
Healthcare compliance is of utmost importance for several reasons.
Firstly, it ensures the delivery of safe and high-quality care to patients, protecting their well-being and rights. Compliance helps prevent medical errors, ensures accurate billing and coding, and promotes adherence to evidence-based practices.
Secondly, compliance plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and sustainability of the healthcare system. It helps prevent fraud, abuse, and unethical practices that can undermine the trust and confidence patients have in the healthcare system. Compliance efforts also help in controlling healthcare costs, reducing waste, and improving overall efficiency.
Additionally, compliance is essential for legal and regulatory reasons. Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties, legal actions, and reputational damage. Adhering to healthcare regulations and guidelines helps healthcare providers and organizations avoid legal liabilities and ensure they meet the standards set by regulatory bodies.
Ultimately, healthcare compliance is vital for building trust between patients, providers, and regulatory authorities. It fosters a culture of accountability, ethical conduct, and patient-centered care, ensuring the well-being of individuals and the integrity of the healthcare industry as a whole.
What are the Potential Consequences of Compliance Issues?
High-risk compliance issues refer to areas within healthcare operations that have a greater likelihood of non-compliance with regulatory requirements, guidelines, or ethical standards. These issues pose a higher risk of legal and financial consequences, reputational damage, compromised patient care, and potential harm to the organization and individuals involved.
Examples of high-risk compliance issues include:
1. Patient privacy and data security:
Failure to adequately protect patient information, maintain data privacy, and implement appropriate security measures can lead to breaches, unauthorized access, and violations of privacy regulations like HIPAA.
2. Fraud and abuse:
Engaging in fraudulent billing practices, improper coding, kickbacks, or other forms of healthcare fraud can result in significant financial penalties, legal actions, and reputational harm.
3. Drug and medication compliance:
Non-compliance with regulations related to prescribing, dispensing, and documenting controlled substances can lead to legal consequences, regulatory scrutiny, and patient safety concerns.
4. Medical device regulations:
Failing to comply with regulatory requirements for the development, manufacturing, and use of medical devices can result in product recalls, regulatory actions, and patient harm.
Identifying and addressing high-risk compliance issues is crucial for healthcare organizations. Implementing robust compliance programs, conducting regular risk assessments, providing comprehensive staff training, and maintaining ongoing monitoring and auditing practices are essential in mitigating these risks and ensuring compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Frameworks
Regulatory bodies and frameworks play a vital role in healthcare compliance. Government agencies are responsible for establishing and enforcing regulations to ensure the safety, quality, and integrity of healthcare services. Some key regulatory bodies include the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS), and the Office for Civil Rights (OCR).
The FDA oversees the regulation of drugs, medical devices, and digital health technologies. It sets standards for product approval, labeling, and post-market surveillance to protect patient safety.
CMS administers programs like Medicare and Medicaid, setting reimbursement rules and guidelines for healthcare providers. Compliance with CMS regulations is crucial for billing and coding accuracy, preventing fraud, and ensuring program integrity.
Regulatory frameworks such as the Stark Law and Anti-Kickback Statute address potential fraud and abuse in healthcare. The Stark Law prohibits physician self-referrals for certain services, while the Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits offering or receiving remuneration for referrals. Understanding and complying with these frameworks is crucial to avoid legal penalties and maintaining ethical practices.
Compliance with these regulatory bodies and frameworks is essential for healthcare providers and organizations to maintain legal and ethical operations, protect patient welfare, and promote transparency and trust in the healthcare system.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance in the US Healthcare System
Healthcare regulations and compliance in the US form a complex framework of laws and standards that govern the industry. These regulations encompass areas such as patient privacy, billing and coding, fraud prevention, and quality care.
Compliance with these regulations is crucial for healthcare providers to ensure ethical practices, protect patient rights, and avoid penalties. Staying updated with evolving regulations and implementing robust compliance programs are essential to navigating this intricate landscape and maintaining the highest standards of care.
1. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Imagine a guardian of privacy and security standing tall in the realm of healthcare. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) plays a vital role as a federal law in the United States. Its mission is to safeguard the sanctity of individuals’ health information.
HIPAA extends its protective embrace to various entities, such as healthcare providers, health plans, healthcare clearinghouses, and their trusted business associates. By enforcing strict regulations, HIPAA shields sensitive data, preserving patient privacy and instilling a sense of confidence in the healthcare ecosystem.
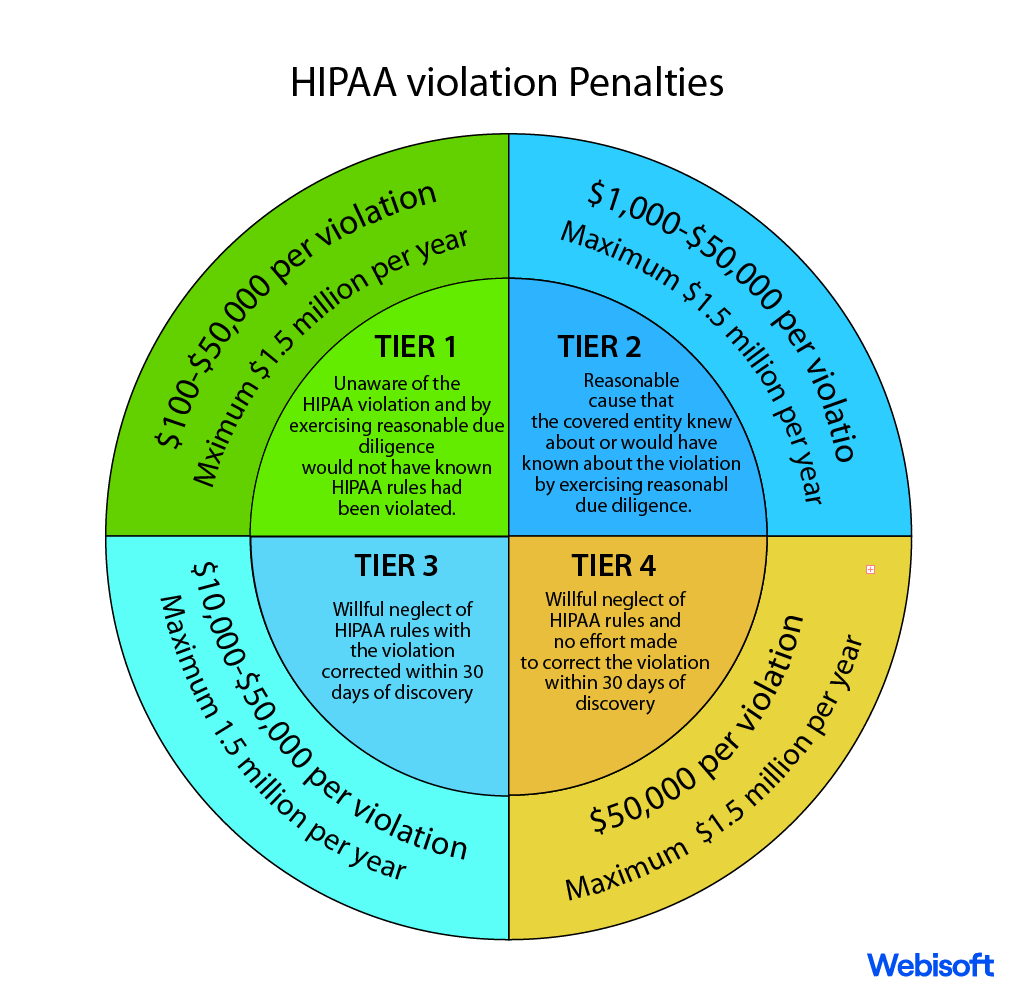
With HIPAA as a steadfast sentinel, the sacred bond of trust between individuals and their healthcare providers remains unyielding and unbroken.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a critical federal law in the United States that protects the privacy and security of individuals’ health information. HIPAA applies to covered entities, including healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses, as well as their business associates.
I. The nature of the entity that uses the application:
HIPAA applies to various entities within the healthcare ecosystem, including hospitals, clinics, doctors’ offices, health insurance companies, and pharmacy benefit managers. These entities handle sensitive patient health information, and HIPAA sets strict guidelines for their handling and safeguarding.
II. The nature of data the application produces, preserves, and shares further:
Applications used within the healthcare industry, such as electronic health record systems or health apps, generate, store, and transmit protected health information (PHI). PHI includes individually identifiable health information, such as medical records, treatment history, and payment details.
HIPAA mandates that these applications comply with privacy and security rules to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of PHI.
III. The underlying software that powers the application:
The software supporting healthcare applications must adhere to HIPAA regulations. It should include features like access controls, encryption, audit trails, and secure data transmission protocols.
Additionally, the software should undergo regular vulnerability assessments and patch management to address potential security risks and maintain compliance with HIPAA requirements.
By following HIPAA guidelines, healthcare entities, and their associated applications can protect patient privacy, mitigate security risks, and promote trust within the healthcare ecosystem. Compliance with HIPAA helps safeguard sensitive health information, ensuring its confidentiality while supporting seamless healthcare delivery.
2. Federal Trade Commission Act (FTC Act)
The Federal Trade Commission Act (FTC Act) is a pivotal piece of legislation that empowers the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) to safeguard consumer rights and promote fair competition.
Enacted in 1914, the FTC Act prohibits unfair methods of competition and deceptive practices in commerce. It grants the FTC the authority to investigate and take enforcement actions against businesses engaging in anti-competitive behaviors or deceptive marketing.
With its broad scope, the FTC Act plays a crucial role in protecting consumers from fraud, false advertising, and monopolistic practices. By ensuring a level playing field and fostering a competitive marketplace, the FTC Act promotes innovation, consumer trust, and economic growth.
3. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act)
The Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act) is a landmark legislation that safeguards public health by regulating food, drugs, and cosmetics in the United States. Enacted in 1938, the FD&C Act empowers the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ensure the safety, efficacy, and proper labeling of these products.
It sets standards for manufacturing, labeling, and marketing practices, aiming to protect consumers from unsafe or misbranded products. The FD&C Act also grants the FDA authority to oversee clinical trials, monitor product recalls, and enforce compliance with regulations.
By upholding stringent standards, the FD&C Act promotes consumer confidence, drives innovation, and safeguards the well-being of individuals nationwide.
4. Fraud and Abuse Laws
Fraud and abuse laws form a crucial framework in healthcare, deterring illicit practices and preserving the integrity of the system. Key statutes include the False Claims Act, targeting false billing and deceptive practices, and the Stark Law, addressing improper physician referrals.
Violations of these laws carry severe penalties, including fines, exclusion from federal programs, and even criminal charges. To prevent fraud and abuse, healthcare organizations must implement robust compliance strategies.
These include conducting regular audits, implementing effective internal controls, providing comprehensive staff training, and fostering a culture of ethics and accountability. By embracing these practices, healthcare providers fortify their defenses, ensuring a system built on trust, transparency, and quality care.
5. Billing and Coding Compliance
Accurate billing and coding are essential in healthcare, ensuring proper reimbursement, streamlined operations, and compliance with regulations. Coding systems like CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) and ICD-10 (International Classification of Diseases, 10th Edition) provide standardized codes for medical procedures and diagnoses, respectively.
Precise documentation is crucial to support accurate billing and coding, requiring detailed and specific information. Compliance challenges may arise from coding errors, upcoding, or inadequate documentation.
To mitigate risks, best practices include conducting regular coding audits, providing ongoing staff training, implementing coding compliance policies, and fostering a culture of accuracy and accountability. By prioritizing billing and coding compliance, healthcare providers uphold transparency, reduce financial risks, and ensure fair and ethical practices.
6. Quality and Patient Safety Compliance
Quality and patient safety are paramount in healthcare compliance, driving efforts to deliver exceptional care. Accreditation organizations like The Joint Commission set rigorous standards, ensuring healthcare facilities adhere to best practices and protocols. Monitoring and reporting adverse events are crucial for identifying and addressing potential risks and improving patient safety.
Developing a culture of compliance fosters a commitment to continuous improvement, where staff actively engage in quality initiatives, training, and reporting concerns. By prioritizing quality and patient safety compliance, healthcare providers build trust, enhance outcomes, and safeguard the well-being of every individual. Together, they create a resilient healthcare environment where excellence and patient safety thrive.
Enhanced Oversight for Digital Health Solutions
In addition to the specific acts and regulations mentioned earlier that directly target healthcare applications, there are other state-backed norms that have been adapted to encompass the realm of digital health. In this section, we will provide an overview of these regulations that entrepreneurs in the mHealth industry must comply with.
1. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
Digital health technologies undergo critical regulation by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to safeguard their safety, effectiveness, and quality. The FDA assumes a pivotal role in overseeing the compliance of these technologies to ensure their adherence to rigorous standards.
The FDA’s oversight extends to various aspects of digital health, including Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), wireless medical devices, telemedicine, health IT, medical device data systems (MDDS), medical device interoperability (MDI), device software functions, cybersecurity, and artificial intelligence/machine learning.
I. Software as a Medical Device (SaMD):
SaMD, as per the FDA’s definition, encompasses software designed for medical purposes that functions independently from hardware medical devices. This distinction highlights the FDA’s recognition of the significance of standalone software in the healthcare landscape.
SaMD may include mobile apps, clinical decision support systems, and remote monitoring software. The FDA assesses SaMD based on its risk level and functionality to determine appropriate regulatory oversight.
II. Wireless Medical Devices:
Wireless medical devices, such as wearable health trackers or remote monitoring systems, fall under FDA regulations. The FDA ensures these devices are safe, and reliable, and provide accurate data. It evaluates factors like wireless connectivity, battery life, data security, and interoperability.
III. Telemedicine:
Telemedicine utilizes technological means to deliver healthcare services remotely. It harnesses the power of technology to bridge the gap between healthcare providers and patients, enabling the provision of medical care from a distance.
The FDA regulates certain aspects, such as telemedicine platforms that incorporate medical devices or involve the transmission of medical data. Compliance with FDA regulations ensures patient safety and quality of care.
IV. Health IT:
Health IT encompasses a wide range of technologies, including electronic health records (EHRs), clinical decision support systems, and health information exchange platforms. The FDA provides guidance on the development, implementation, and use of health IT systems to ensure patient safety and data integrity.
V. Medical Device Data Systems (MDDS):
MDDS refers to software or hardware that transfers, stores, or displays medical device data. The FDA has issued guidance stating that MDDS, under certain conditions, will not be subject to the agency’s regulations, thus allowing flexibility for data management systems.
VI. Medical Device Interoperability (MDI):
MDI centers around ensuring the secure and efficient exchange and utilization of information among medical devices. Its primary focus is to establish a seamless and reliable flow of data, enabling medical devices to communicate and collaborate effectively while upholding patient safety.
The FDA encourages interoperability to facilitate seamless data exchange and improve patient care. It provides guidance to manufacturers to ensure device compatibility, data security, and patient safety.
VII. Device Software Functions:
The FDA regulates the software functions embedded in medical devices, such as infusion pumps, imaging systems, and diagnostic devices. It ensures that software functions operate reliably, accurately, and safely, without compromising patient well-being.
VIII. Cybersecurity:
Given the increasing reliance on digital health technologies, cybersecurity is a crucial aspect of FDA regulations. The agency emphasizes the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect patient data, prevent unauthorized access, and mitigate cybersecurity risks.
IX. Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning:
With the rising prominence of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in the healthcare landscape, the FDA offers guidance on the regulation of medical devices and software that incorporate AI/ML. Recognizing the expanding influence of these technologies, the FDA ensures that AI/ML-based solutions in the medical field are subject to appropriate oversight and scrutiny. It focuses on algorithm transparency, performance validation, and real-world clinical evidence.
Ensuring adherence to FDA regulations in the realm of digital health is vital to safeguard patient well-being, uphold the integrity of data, and foster a climate of innovation. Healthcare technology developers and providers face the task of navigating the complex regulatory terrain, comprehending their responsibilities, and forging close collaboration with the FDA.
This collaboration is crucial to introduce digital health solutions that are both safe and effective, offering tangible benefits to patients while meeting the highest standards of regulatory compliance.
2. HL7 Standards
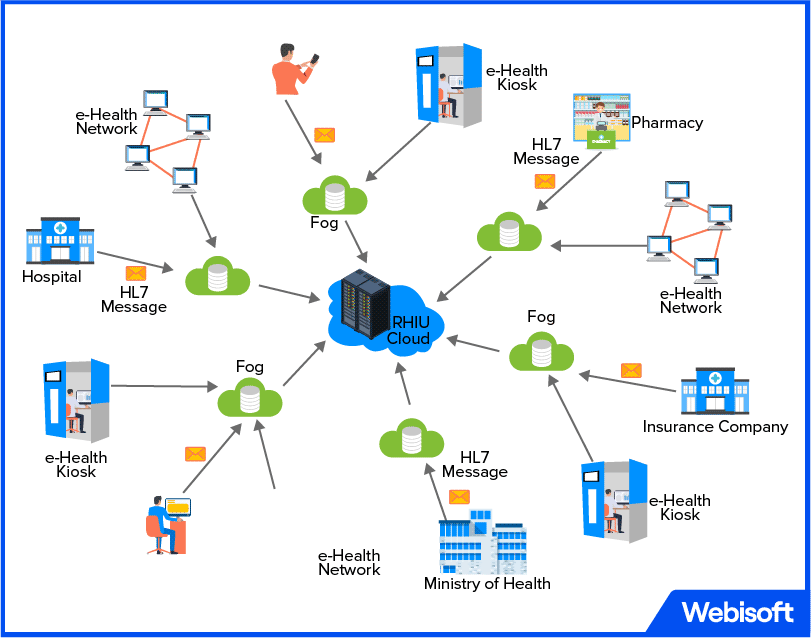
In the ever-evolving world of healthcare, HL7 standards emerge as a beacon of interoperability and seamless information exchange. HL7, short for Health Level 7, sets the groundwork for effective data sharing among healthcare systems, enabling the seamless transmission of patient information.
These standards ensure consistent formats and protocols, facilitating efficient communication between various healthcare applications and devices. By promoting interoperability, HL7 standards empower healthcare providers with a holistic view of patient data, leading to enhanced care coordination and informed decision-making.
With HL7 as the common language of healthcare information, the industry moves closer to a connected ecosystem where patient-centric care and collaboration flourish.
3. The HITECH Act
The HITECH (Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health) Act is a pivotal legislation that revolutionized healthcare technology in the United States. Enacted in 2009, it aims to promote the adoption and meaningful use of electronic health records (EHRs).
The HITECH Act introduced financial incentives for healthcare providers who implement certified EHR systems and demonstrate their effective use. It also reinforced privacy and security measures, imposing stricter penalties for data breaches.
With its focus on modernizing healthcare technology, the HITECH Act has paved the way for improved care coordination, enhanced patient engagement, and data-driven healthcare decision-making. By incentivizing the digital transformation of healthcare, it has catalyzed a new era of efficient, patient-centered, and technologically advanced healthcare delivery.
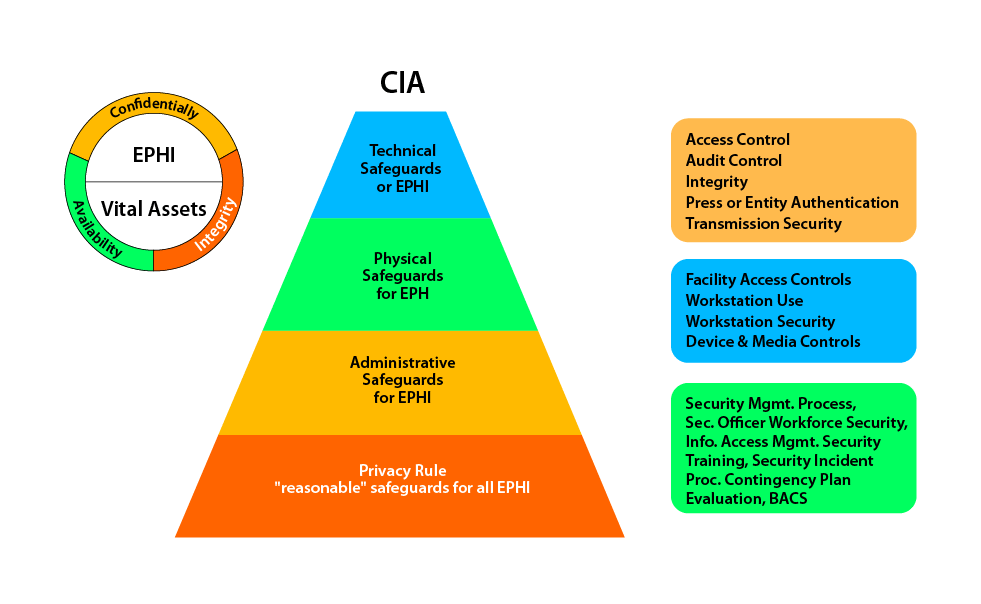
4. BYOD
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) in healthcare refers to the practice of employees using their personal smartphones, tablets, or laptops for work-related purposes. While BYOD offers flexibility and convenience, it poses unique challenges in the healthcare sector.
Confidential patient data can be at risk if devices are lost, stolen, or not properly secured. Healthcare organizations must implement robust policies and security measures to protect patient information while allowing BYOD. This includes encryption, remote wiping capabilities, strong authentication, and employee education on security best practices.
With proper safeguards in place, BYOD can enhance productivity and collaboration, but striking the right balance between convenience and security is vital in safeguarding patient privacy.
5. GDPR
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) is a landmark European Union law that governs data protection and privacy. It applies to healthcare organizations that process the personal data of EU residents.
GDPR empowers individuals with greater control over their data and imposes strict obligations on organizations, including healthcare providers, to ensure data protection. Compliance involves obtaining informed consent, implementing robust security measures, and providing transparent data handling practices. Non-compliance can result in significant fines.
By prioritizing GDPR compliance, healthcare organizations demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding patient privacy, fostering trust, and maintaining the highest standards of data protection. GDPR serves as a catalyst for a privacy-conscious healthcare environment, where individuals’ rights are respected and their data is treated with utmost care.

Other Healthcare-Related Regulatory Requirements
In addition to the well-known healthcare regulations and compliance standards, there exist several other compliances that are pertinent to the healthcare industry. These lesser-known compliances address specific areas such as data privacy, research ethics, waste management, and occupational safety, ensuring comprehensive adherence to legal and ethical requirements within the healthcare landscape.
By understanding and adhering to these lesser-known compliances, healthcare organizations can maintain a well-rounded approach to compliance, promoting patient safety, organizational integrity, and ethical practices across all facets of their operations.
1. Data Security and Privacy Compliance
In the digital age, safeguarding patient data and privacy is crucial in healthcare. Cybersecurity threats pose significant risks, such as data breaches and unauthorized access. Compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA is essential to ensure patient confidentiality.
To achieve data security and privacy compliance, healthcare organizations should adopt best practices. These include implementing robust encryption and access controls, regularly updating security measures, conducting employee training on data protection, and conducting thorough risk assessments.
By prioritizing data security and privacy, healthcare providers can build trust with patients and protect sensitive information from potential threats.
2. Compliance Training and Education(regarding healthcare)
In the realm of healthcare compliance, training, and education serve as the mighty guardians, equipping the workforce with knowledge and fortitude. They unravel the enigmatic tapestry of regulations, policies, and ethical standards, weaving a shield against potential violations.
A comprehensive compliance training program becomes the cornerstone, an intricate mosaic that covers privacy, security, fraud, and abuse, ensuring no vulnerability remains unaddressed. Yet, the journey doesn’t end there.
Through ongoing education and awareness initiatives, employees embark on a perpetual quest to stay aligned with the ever-changing tides of compliance requirements. Together, training and education stand tall, the unwavering sentinels preserving the sanctity of healthcare practices.
Like a compass guiding a ship, regular assessments and evaluations serve as the North Star in measuring the impact of compliance training. They act as powerful tools that illuminate strengths, reveal gaps, and chart a course for improvement.
By placing training and education at the helm of their priorities, healthcare organizations equip their workforce with the navigational skills and expertise needed to steer a steady course toward compliance. This steadfast commitment fosters a culture of patient safety and trust, ensuring that the healthcare landscape remains a sanctuary where confidentiality is guarded, regulations are upheld, and the well-being of every individual is safeguarded.
3. Audits, Investigations, and Enforcement
In the realm of healthcare compliance, audits, and investigations serve as vigilant guardians, uncovering potential pitfalls and ensuring adherence to regulations. When faced with audits or investigations, healthcare organizations must respond promptly and diligently, cooperating with authorities and providing the requested information.
Understanding enforcement actions and penalties is crucial, as they can have significant consequences for non-compliance. To minimize compliance risks and address non-compliance, organizations should implement robust internal controls, conduct regular self-audits, and foster a culture of transparency and accountability.
By embracing these strategies, healthcare providers navigate the complex terrain of compliance, fortifying their integrity and protecting the well-being of patients.
4. Building an Effective Compliance Program
In the realm of healthcare, building an effective compliance program requires a strong foundation. Its components include clear policies, robust procedures, and risk assessments that navigate potential pitfalls.
Establishing a compliance governance structure provides the framework for accountability and oversight. To ensure adherence, monitoring, auditing, and reporting activities are crucial.
Like a well-tuned engine, this program keeps healthcare organizations running smoothly, safeguarding patient welfare and upholding ethical standards. By weaving these elements together, healthcare providers construct a fortress of integrity, nurturing a culture where compliance is ingrained, risks are mitigated, and the well-being of patients takes center stage.
5. Emerging Trends in Healthcare Compliance (regarding healthcare)
In the dynamic world of healthcare compliance, emerging trends shape the landscape. Technology and digital health innovations have profound impacts, requiring updated compliance requirements to protect patient data and privacy.
The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, with upcoming changes demanding vigilance and adaptability. Ethical and compliance challenges arise as new healthcare models emerge, necessitating proactive strategies to navigate uncharted territories.
Looking ahead, healthcare compliance professionals must anticipate the future, embrace emerging technologies, foster a culture of ethical behavior, and stay informed about evolving regulations. By embracing these trends, they become the guiding compass, ensuring the seamless integration of compliance in the ever-evolving healthcare ecosystem.
Conclusion
This compact handbook on healthcare compliance has provided a concise overview of healthcare compliance, covering key regulations, regulatory bodies, and frameworks. We have highlighted the importance of maintaining compliance in the healthcare industry to ensure patient safety, protect data privacy, and foster trust.
By adhering to regulations, healthcare providers and organizations can mitigate risks, avoid legal consequences, and uphold ethical standards. It is crucial to stay informed about evolving compliance requirements and seek further resources for in-depth knowledge. Remember, compliance is an ongoing commitment that supports the delivery of high-quality care and the integrity of the healthcare system.