Ethereum has emerged as a revolutionary technology in the digital world, aiming to transform the Internet’s workings entirely. If fully actualized, it is used to handle finances, store data, make contracts, and establish trust.
This comprehensive guide on Ethereum for beginners will cover its various aspects, use cases, and the prominent issues it faces. So, go through this complete review guide and learn about the ETH and smart contract.
Contents
Bitcoin – The Predecessor

The year 2008 marked the greatest milestone in the world of digital currency. Satoshi Nakamoto, a pseudonymous individual or group, introduced Bitcoin to the world. This was a groundbreaking moment.
It was the first instance where currency could be programmed. Bitcoin’s introduction meant that transactions could occur on a peer-to-peer network. This eliminated the need for intermediaries, whether trusted or not.
It was a radical shift in the way financial transactions were conducted. Bitcoin demonstrated that mathematics could take on the role of a “trusted intermediary.” Initially, the term “Bitcoin” denoted two distinct aspects.
First, it referred to the cryptocurrency itself. This was a piece of code that represented digital assets. Second, it referred to the Blockchain. This is the underlying framework that enables the functioning of the currency.
However, the Bitcoin blockchain has a limitation. It was confined only to financial transactions. This restriction curtailed the potential of blockchain technology. It could have been used in other applications, but the focus remained solely on financial transactions.
What Is Ether Or Ethereum For Beginners?

Ethereum is a unique, open-source platform with a global reach. It’s designed specifically for decentralized applications, also known as dApps. The beauty of Ether lies in its flexibility. You can write code on this platform that controls digital value.
This code operates as programmed without any possibility of downtime, censorship, fraud, or third-party interference. Ethereum’s functionality isn’t confined to a specific location. It’s accessible from anywhere worldwide, making it a truly global platform.
This accessibility is a significant advantage in today’s interconnected digital world. One of Ethereum’s key achievements is its ability to free blockchain technology from the financial constraints of Bitcoin.
While Bitcoin introduced the world to Blockchain, its application was limited to financial transactions. Ether took this technology and expanded its scope.
Ethereum demonstrated that blockchain technology could benefit many industries, not just finance. From supply chain management to gaming, the potential applications of Ethereum’s Blockchain are vast and varied.
In essence, Ether is a programmable blockchain like no other. It allows developers to build and deploy smart contracts and dApps to facilitate direct interactions between parties.
This eliminates the need for intermediaries, leading to more efficient, transparent, and secure systems. View details below:
What Is The Vision Of Ethereum Or ETH Vision?
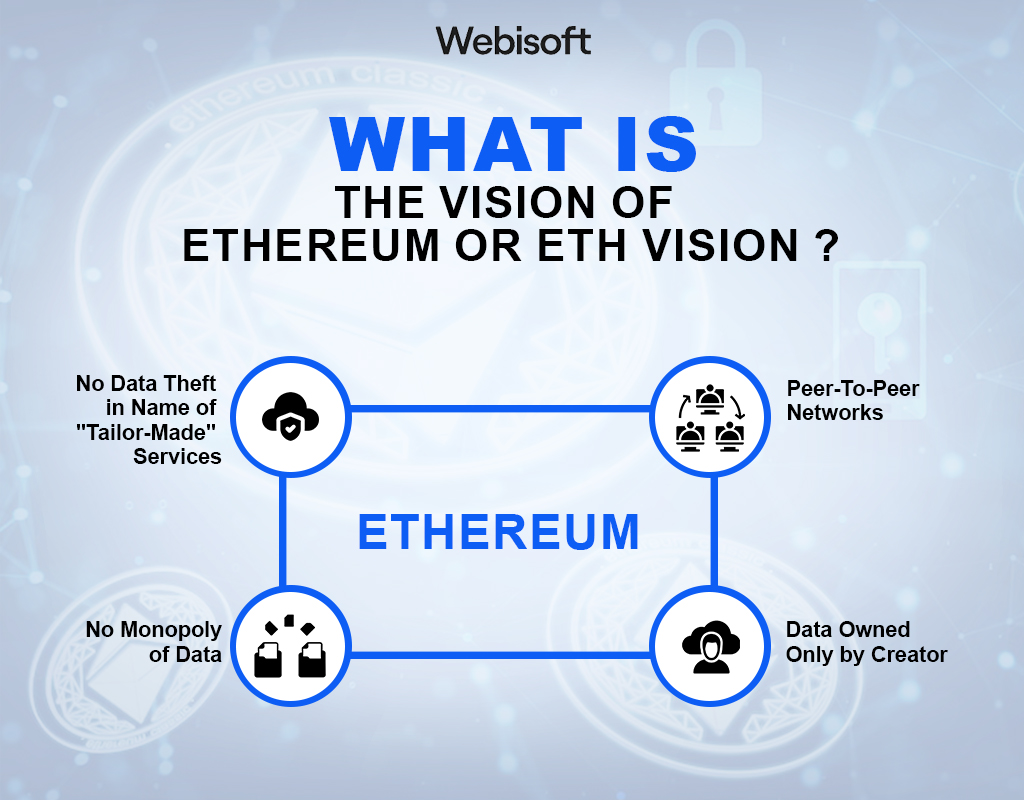
Ethereum’s vision is ambitious and transformative. It aims to create a ‘new internet,’ a concept that reimagines the structure and function of today’s Internet. Here’s a breakdown of what this vision entails:
1. Decentralization
At the heart of Ethereum platform, the vision is the principle of decentralization. As it was initially conceived, the Internet was meant to be a decentralized network.
However, over time, it has become increasingly centralized, with a handful of powerful entities controlling significant portions of the online world. Ether seeks to return the Internet to its decentralized roots. If you want to buy ethereum it becomes easier through the internet.
2. Peer-to-Peer Networks
ETH envisions an internet where peer-to-peer networks replace the current client-server model. Each participant (or ‘peer’) has the same capabilities in this model, and either party can initiate a communication session.
This contrasts with the client-server model, where a centralized server provides services to multiple clients. A peer-to-peer network is more resilient and less prone to censorship.
3. Data Ownership
In Ethereum’s vision of the Internet, data is owned solely by its creator. This is a stark departure from the current state of the Internet, where users often need control over their data.
Ethereum’s technology allows for the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) where users retain full control over their data.
4. No Data Monopoly
ETH aims to eliminate data monopolies. Today, a few large tech companies have a near-monopoly on data, which they often use to their advantage. Ethereum’s decentralized nature prevents any single entity from monopolizing data.
5. No Data Theft
Ethereum envisions an internet where applications don’t steal data under the guise of providing ‘tailor-made’ services. With ETH, users can control their data and choose who they share it with.
6. Democratization of the Internet
Ethereum strives to democratize the Internet. This means making the Internet a place where everyone has equal access and opportunities. Using blockchain technology, Ethereum aims to create a more open, accessible, and fair internet.
7. World Computer
Lastly, Ethereum wants to build a ‘world computer’ for beginners. This is a metaphor for a global network of nodes, each running Ethereum’s open-source software. This network would operate as a single, massive, decentralized computer.
This’ world computer’ could run a wide range of applications, from financial services to social networks, all without any central authority.
Ethereum’s vision is to create a new kind of Internet. An internet that is decentralized, where users have control over their data, and where peer-to-peer networks replace centralized servers.
It’s a vision that could transform how we interact online, making the Internet more fair, secure, and open.
What Are Various Aspects Of Ethereum DAO?

Ethereum is a complex and multifaceted platform. It’s not just a single technology but a suite of related technologies and concepts that work together to create a robust and flexible platform for decentralized applications. Let’s delve into some of these key aspects:
1. Ethereum Smart Contracts
One of the most significant aspects of Ethereum DAO is its extensive use of smart contracts. These are self-executing contracts. But these come with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They are a crucial element of Ethereum and other blockchain technologies.
Smart contracts are computer programs. These contacts verify, facilitate, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. They eliminate the need for intermediaries, as they uphold their sanctity and ensure enforcement through mathematical algorithms.
This means that once the contract conditions are met, the actions outlined in the contract are automatically triggered.
2. Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is another core component of Ethereum. It’s the runtime environment where smart contracts are executed.
The EVM is completely isolated from the main Ethereum network, which makes it a perfect sandbox for testing smart contracts. It is what gives Ethereum its much-honored ‘programmability.’
It allows developers to create applications that leverage the security and decentralization of the cryptocurrencies Ethereum with a high degree of customization.
Developers can create various applications, from games to financial services, all running on the Ethereum blockchain.
3. Blockchain Validation
Blockchain validation is a critical aspect of Ethereum and blockchain technology in general. In a traditional financial system, trusted intermediaries like banks are needed to validate transactions.
However, Ethereum eliminates the need for these intermediaries. But how do we know that a transaction is valid without intermediaries? The answer lies in blockchain validation.
In Ethereum, transactions are validated by a network of ‘nodes.’ These nodes use a consensus algorithm to agree on the state of the Blockchain.
Once most nodes agree that a transaction is valid, it is added to the Blockchain. This process ensures that all transactions are transparent and cannot be tampered with.
These are just a few of the many aspects of Ethereum. Each plays a crucial role in making Ethereum a powerful platform for decentralized applications. By understanding these aspects, one can better appreciate the potential and versatility of Ethereum.
What Is Proof-of-Stake?

Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is a key concept in blockchain technology. It’s a consensus algorithm that blockchain networks use to achieve agreement and consent among all participating nodes.
- Consensus Algorithm: In a blockchain network, a consensus algorithm is a way to ensure that all nodes, or participants, agree on the validity of transactions. This agreement is crucial for maintaining the development, integrity and security of the network.
- Proof-of-Stake vs. Proof-of-Work: PoS is an alternative to the Proof-of-Work (PoW) system. In PoW, participants are also known as miners. This process requires significant computational power and energy. PoS, on the other hand, takes a different approach.
- How PoS Works: In a PoS-based blockchain, in a deterministic way, the creator of a new block is chosen. The ‘stake’ refers to the number of coins or tokens the participant holds. The more stake a participant has, the higher their chances of being chosen to create a new block.
- Benefits of PoS: PoS offers several advantages over PoW. It’s more energy-efficient, not requiring participants to perform complex calculations. It also offers better security, as an attacker must own most of the network’s stake to carry out a successful attack. This makes attacks prohibitively expensive and unlikely.
- Use in Cryptocurrencies: PoS is used in many cryptocurrencies, including Ethereum, transitioning from PoW to PoS to improve scalability and energy efficiency.
Proof-of-Stake is a crucial component of many modern blockchain networks. It offers a more sustainable and secure way to achieve consensus, making it a popular choice for new crypto.
What Are the Use Cases Of Ethereum Tutorial?

Ether’s versatility and robustness have led to its use in various applications across various industries. Here are some of the key use cases:
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
One of the most prominent use cases of Ethereum is in the field of Decentralized Finance, or DeFi. Using blockchain technology, DeFi aims to recreate and improve traditional financial systems, such as loans, insurance, and asset trading.
Ethereum’s smart contracts play a crucial role in automating financial transactions and agreements, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing costs.
2. Supply Chain Management
Supply chains can be complex and opaque, making it difficult to track the journey of a product from its origin to the consumer. Ether can bring transparency and efficiency to this process.
By recording every transaction on the Blockchain, Ethereum can provide a tamper-proof product history, ensuring its authenticity and traceability. This can help prevent fraud and counterfeiting.
3. Identity Verification
In today’s digital world, identity verification is more important than ever. Ethereum can be used to create decentralized digital identities, giving users control over their data. This can be used in various applications, from secure login systems to digital signatures.
4. Voting Systems
Voting is a fundamental process in any democratic society but it can be vulnerable to fraud and manipulation. Ethereum’s transparency and security make it ideal for creating voting systems.
Votes can be recorded on the Blockchain, creating a transparent and tamper-proof record. This can eliminate the risk of fraud and ensure the integrity of the voting process.
5. Real Estate
Buying and selling property can be complex and costly, with numerous intermediaries involved. Ethereum can simplify this process by eliminating intermediaries and reducing costs.
Property ownership can be represented as a token on the Ethereum blockchain, and smart contracts can carry out transactions. This can make the process more efficient, transparent, and accessible.
6. Gaming
Ethereum is also making waves in the gaming industry. Games built on Ethereum can offer players true ownership of in-game assets, represented as tokens on the Ethereum blockchain. This can create new economic models and player experiences in games.
7. Insurance
Ethereum can also be used to generate decentralized insurance platforms. Smart contracts can automate the claim process, making it faster and more efficient. This can reduce costs and improve the customer experience.
These are just a few examples of the many use cases of Ethereum. Its flexibility and programmability make it a powerful tool. And we can expect to see even more innovative uses in the future.
What Is The Prominent Issue Faced By Ethereum?

While Ethereum has many advantages, it also faces a significant issue: scalability.
As more people use the network, the time and resources required to process transactions increase, leading to slower transaction times and higher costs.
1. Scalability – A Hindrance To Commercial Adoption
Scalability has been a significant hindrance to the commercial adoption of Ethereum. As the network grows, it needs help to process transactions quickly and efficiently, leading to slower transaction times and higher costs.
2. Ethereum Merge
Ethereum is undergoing a major upgrade known as the Ethereum Merge to address the scalability issue. This upgrade will transition Ethereum from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.
Conclusion
Ethereum represents a significant advancement in blockchain technology, offering a platform for decentralized applications and smart contracts.
While it faces challenges such as scalability, ongoing upgrades like the Ethereum Merge are addressing these issues, paving the way for broader adoption.
Whether you’re a developer looking to build on Ethereum or a beginner interested in investing, understanding Ethereum is key to navigating the future of the digital world.
