Top 40 Blockchain Applications And Where They Matter Most
- BLOG
- Blockchain
- October 16, 2025
You have probably noticed something interesting. Every time a business problem comes up, someone in the room whispers “blockchain” like it is a magic spell. Yet the real story is far more practical. Many blockchain applications are already working quietly in the background, fixing issues most systems still struggle with.
They track products, secure transactions, verify identities and keep records that cannot mysteriously “go missing.” Industries use them not because they are trendy but because they reduce confusion, errors and endless back-and-forth between teams.
Here, you explore where these applications matter and how they work across industries as blockchain applications in real world scenarios continue to grow for businesses.
Contents
- 1 What is a Blockchain Application?
- 2 Key Benefits of Blockchain Applications for Modern Businesses
- 3 Build smarter blockchain solutions with Webisoft today.
- 4 Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain Applications by Industry
- 4.1 Finance and Banking
- 4.2 Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
- 4.3 Supply Chain and Logistics
- 4.4 Real Estate and Property Based Sectors
- 4.5 Media, Digital Goods and Intellectual Property
- 4.6 Public Sector and Governance
- 4.7 Energy, Sustainability and Infrastructure
- 4.8 Cryptocurrency and Digital Money
- 4.9 Insurance
- 4.10 Manufacturing and Industrial Operations
- 4.11 Education and Academic Verification
- 4.12 Retail and E Commerce
- 4.13 Agriculture and Food Safety
- 5 Limitations of Blockchain Applications and When They Fail
- 6 What It Takes to Build a Blockchain Application: Before You Begin
- 6.1 Define a Clear Business Problem and Use Case
- 6.2 Choose the Right Blockchain Type and Platform
- 6.3 Design Smart Contracts and Architecture Carefully
- 6.4 Plan for Integration with Existing Systems & User Interfaces
- 6.5 Allocate for Security, Compliance, and Long-Term Maintenance
- 6.6 Estimate Time, Cost and Resource Requirements Realistically
- 7 How Webisoft Helps You Plan and Build Blockchain Applications
- 7.1 Support Choosing the Right Use Case and Architecture
- 7.2 Development That Matches Your Vision End to End
- 7.3 Custom Networks Designed Around Your Needs
- 7.4 Infrastructure Management You Do Not Need to Handle Alone
- 7.5 Ecosystem Features Built for Your Product Goals
- 7.6 Scalability Planning for Your Long Term Growth
- 7.7 Compliance Guidance That Supports Your Sector
- 8 Build smarter blockchain solutions with Webisoft today.
- 9 Conclusion
- 10 Frequently Asked Question
What is a Blockchain Application?
A blockchain application is a software system built on a blockchain: a decentralized, distributed ledger maintained across many computers (nodes) rather than a central server. Unlike traditional apps that store data in centralized databases, blockchain application store transactions or records in cryptographically linked “blocks.”
Once confirmed, these blocks become immutable and transparent to all participants. Such apps often use smart contracts: self-executing code on the blockchain that enforces rules automatically, enabling trustless, tamper-resistant interactions.
Key Benefits of Blockchain Applications for Modern Businesses
 You work with systems that handle sensitive data, multiple stakeholders, or frequent transactions. Blockchain application strengthen these areas by improving how information is shared, secured, and validated across your operations. Especially as blockchain applications beyond cryptocurrency continue to expand into core business workflows.
You work with systems that handle sensitive data, multiple stakeholders, or frequent transactions. Blockchain application strengthen these areas by improving how information is shared, secured, and validated across your operations. Especially as blockchain applications beyond cryptocurrency continue to expand into core business workflows.
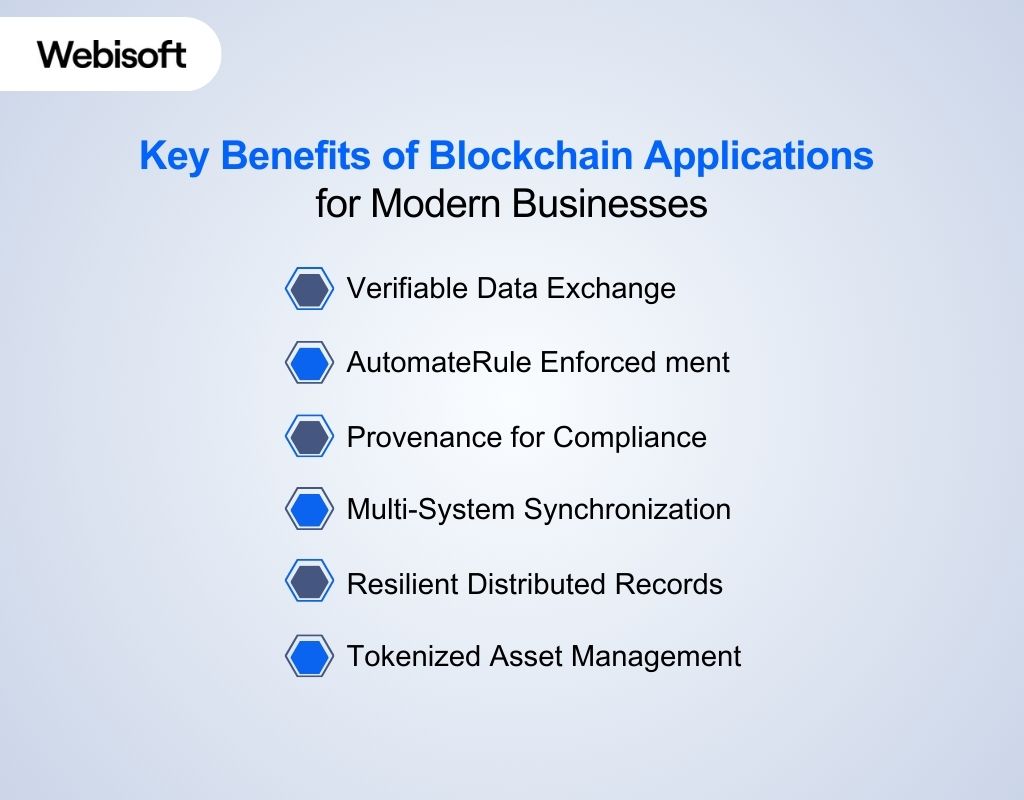
Verifiable Data Exchange
Blockchain applications allow different departments or partners to exchange information with built-in validation. Each update carries cryptographic proof, reducing reconciliation cycles and improving the reliability of shared workflows.
AutomateRule Enforced ment
Smart contracts apply conditions without manual checks. This helps you enforce service-level terms, settlement conditions, or access controls consistently, especially in processes where timing and accuracy matter.
Provenance for Compliance
Blockchain application create a complete data lineage. You see every modification, transfer, or approval. This helps satisfy regulatory audits and supports quality control in sectors like supply chain, health, and manufacturing.
Multi-System Synchronization
Blockchain acts as a neutral coordination layer when several systems or organizations must stay aligned. You avoid mismatches between databases, reduce duplicate records, and lower dependency on centralized middleware.
Resilient Distributed Records
Because blockchain operates across many nodes, your critical records remain available even if one environment fails. This increases operational continuity in high-availability or multi-party environments.
Tokenized Asset Management
Blockchain enables digital representations of physical or digital assets. You can create controlled access, fractional permissions, or on-chain rights management without redesigning your core systems.
Build smarter blockchain solutions with Webisoft today.
Get expert help to plan, design and launch secure blockchain systems effectively.
Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain Applications by Industry
 Across industries, blockchain enhances transparency, trust and data coordination, adding to a useful list of blockchain applications that support modern business needs. These examples show how blockchain applications in real life solve challenges that traditional systems struggle to handle.
Across industries, blockchain enhances transparency, trust and data coordination, adding to a useful list of blockchain applications that support modern business needs. These examples show how blockchain applications in real life solve challenges that traditional systems struggle to handle.
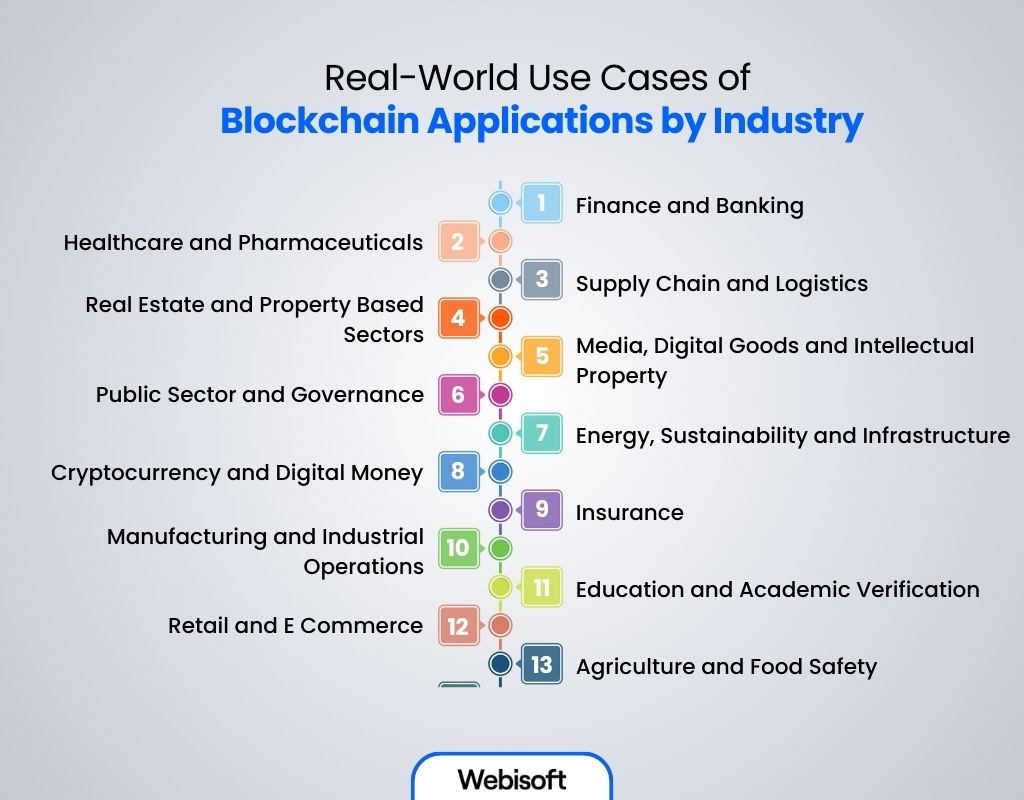
Finance and Banking
 Financial ecosystems rely on trust, speed and accurate reconciliation. Blockchain supports these goals by offering shared records, automated settlement logic and transparent asset structures. As a result, blockchain in finance continues to grow across banks and fintech companies.
Financial ecosystems rely on trust, speed and accurate reconciliation. Blockchain supports these goals by offering shared records, automated settlement logic and transparent asset structures. As a result, blockchain in finance continues to grow across banks and fintech companies.
1. Instant and Low Cost Cross Border Transfers (Ripple)
Traditional cross-border transfers take days due to layered intermediaries. Blockchain allows banks to settle payments on a shared ledger, reducing delays and fees. Ripple enables partner banks to process global transfers in near real time while maintaining transaction traceability.
2. Smart Contract Automation for Loans and Trading (JPMorgan)
Loan approvals, collateral checks and repo trades require multiple verifications. Smart logic automates these workflows, cutting back-office effort and reducing settlement risk. JPMorgan uses its Onyx platform to execute intraday repos with improved efficiency and accurate rule enforcement.
3. Asset Tokenization and Digital Securities (Securitize)
Tokens convert real assets such as shares or property into digital forms that can be issued, managed and traded more flexibly. Securitize supports regulated tokenization for companies seeking a more efficient method of raising capital and offering compliant digital securities.
4. Fraud Reduction and Audit Ready Records (Digital Asset)
Financial institutions benefit from tamper resistant histories that simplify audits and lower fraud exposure. Digital Asset supplies blockchain infrastructure that helps banks maintain consistent data across entities while supporting faster reporting cycles.
Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
 Healthcare systems require trustworthy data and careful privacy control. Blockchain simplifies record exchange, enhances data integrity and helps manufacturers protect medical supply chains. These uses highlight growing blockchain applications in healthcare.
Healthcare systems require trustworthy data and careful privacy control. Blockchain simplifies record exchange, enhances data integrity and helps manufacturers protect medical supply chains. These uses highlight growing blockchain applications in healthcare.
5. Secure and Interoperable Patient Records (Medicalchain)
Disconnected systems often lead to inconsistent records. Blockchain allows providers to share verified patient data while preserving privacy controls. Medicalchain enables patients to grant access permissions and ensures clinicians receive consistent, authenticated records.
6. Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Tracking (MediLedger)
Drug authenticity is essential for safety and regulatory compliance. Blockchain tracks each product from production to pharmacy, ensuring clear origin and preventing counterfeits. MediLedger collaborates with pharmaceutical companies to maintain verifiable product histories.
7. Clinical Trial Data Integrity (Pfizer)
Research trials generate sensitive information that requires proof of authenticity. Blockchain timestamps and secures trial data so results cannot be altered retroactively. Pfizer participates in initiatives that use blockchain to maintain transparent research documentation.
Supply Chain and Logistics
 Complex supply chains depend on accurate shared information. Blockchain improves visibility and coordination among manufacturers, carriers and retailers, creating strong blockchain applications in supply chain management.
Complex supply chains depend on accurate shared information. Blockchain improves visibility and coordination among manufacturers, carriers and retailers, creating strong blockchain applications in supply chain management.
8. End to End Product Traceability (Walmart)
Retailers monitor the entire movement of food and goods through blockchain entries. Walmart uses this method to identify contamination sources quickly, reducing investigation times from days to seconds in some pilot tests.
9. Authenticity and Anti Counterfeit Verification (Carrefour)
Consumers want assurance about product quality and sourcing. Carrefour uses blockchain to store verifiable origin, farming and processing information so shoppers can confirm authenticity through simple QR code scans.
10. Shared Operational Data Across Stakeholders (Maersk and IBM)
Global shipping requires synchronized documentation. Maersk and IBM use blockchain to give ports, customs officials and carriers access to consistent logistics records, reducing bottlenecks caused by mismatched paperwork.
Real Estate and Property Based Sectors
 Real estate transactions involve heavy documentation and trust requirements. Blockchain improves transparency and reduces friction by storing property information securely.
Real estate transactions involve heavy documentation and trust requirements. Blockchain improves transparency and reduces friction by storing property information securely.
11. Fractional Ownership Through Tokenization (RealT)
Tokenization allows investors to purchase fractional property shares rather than entire buildings. RealT sells compliant digital tokens backed by real estate, offering a lower entry point and increasing market liquidity.
12. Transparent and Tamper Proof Land Registries (Sweden Land Registry)
Land ownership disputes arise from inaccurate or tampered records. Sweden’s land authority tested blockchain to maintain secure registries, enabling faster verification and reducing fraud risk.
13. Automated Lease and Contract Management (Propy)
Real estate agreements benefit from automated rule execution. Propy uses blockchain to record contracts and facilitate digital transactions with verifiable documentation for buyers and sellers.
Media, Digital Goods and Intellectual Property
 Media industries need tools that protect creators and confirm provenance. This is where real world blockchain applications can provide trustworthy ownership records and transparent usage tracking.
Media industries need tools that protect creators and confirm provenance. This is where real world blockchain applications can provide trustworthy ownership records and transparent usage tracking.
14. Digital Rights and Royalty Distribution (Spotify and Mediachain)
Rights management is often fragmented. Spotify acquired Mediachain to explore blockchain based systems that match creators to their works accurately and improve royalty distribution transparency.
15. NFT Based Asset Verification (OpenSea)
Digital artworks and collectibles require reliable proof of authenticity. OpenSea enables creators to issue verifiable digital items where ownership is recorded publicly.
16. Content Provenance and Anti Piracy Measures (Reuters Prototype)
News outlets need authenticated source tracking. Reuters tested blockchain to secure metadata and verify whether images or articles have been altered.
Public Sector and Governance
 Governments require transparency and accurate data retention. Blockchain supports secure citizen services, identity management and public record handling.
Governments require transparency and accurate data retention. Blockchain supports secure citizen services, identity management and public record handling.
17. Transparent and Verifiable Voting Systems (Estonia)
Digital voting requires security and citizen trust. Estonia explores blockchain backed election models where votes are stored in secure, verifiable structures that prevent tampering.
18. Decentralized Digital Identity Management (ID2020 Alliance)
Identity programs built on blockchain give users more control over their information. The ID2020 Alliance supports decentralized identity solutions for verification across services.
19. Secure Storage of Public Records (Dubai Government)
Government agencies benefit from preserving records that cannot be altered. Dubai works on placing permits, licenses and certificates on blockchain to improve service reliability.
Energy, Sustainability and Infrastructure
 Energy markets need accurate tracking for consumption, production and environmental impact. Blockchain supports reliable settlement and transparent reporting.
Energy markets need accurate tracking for consumption, production and environmental impact. Blockchain supports reliable settlement and transparent reporting.
20. Peer to Peer Energy Trading (Powerledger)
Residents with solar panels trade surplus energy locally using blockchain to record and settle transactions. Powerledger enables communities to manage energy flows transparently.
21. Carbon Credit and Emission Tracking (Veridium Labs and IBM)
Environmental reporting improves when emission data cannot be changed. IBM and Veridium collaborate to tokenize carbon credits, making sustainability tracking more accurate and auditable.
22. Secure Coordination for IoT Devices (Bosch)
Connected devices require verified identities. Bosch researches blockchain frameworks to authenticate devices and support secure machine to machine communication, a concept explored further in IoT and blockchain guide.
Cryptocurrency and Digital Money
 Digital currencies show one of the earliest and most significant blockchain applications examples. This remains the strongest application of blockchain in cryptocurrency.
Digital currencies show one of the earliest and most significant blockchain applications examples. This remains the strongest application of blockchain in cryptocurrency.
23. Secure and Transparent Payment Processing (Bitcoin Network)
Bitcoin records payments on a decentralized ledger where transactions cannot be altered. This enables global transfers supported by transparent public verification.
24. Secure Wallet and Custody Systems (Ledger)
Users protect crypto assets with encrypted hardware devices. Ledger offers wallets that store private keys offline for enhanced security.
25. Decentralized Trading Platforms (Uniswap)
Trading digital assets becomes more efficient with peer to peer swaps. Uniswap uses smart logic to match trades and manage liquidity without relying on intermediaries.
Insurance
 Insurance depends on verified claims and accurate policy records. Blockchain makes both easier to maintain and audit.
Insurance depends on verified claims and accurate policy records. Blockchain makes both easier to maintain and audit.
26. Automated Claims and Payout Validation (Lemonade Foundation)
Smart logic checks conditions before releasing payouts. The Lemonade Foundation researches blockchain based models that minimize processing delays and errors.
27. Shared Policy Data for Brokers and Underwriters (Aon and Allianz)
Insurance partners access consistent policy information stored on blockchain. Aon and Allianz participate in shared networks that improve underwriting accuracy.
28. Fraud Detection Using Immutable Records (Nationwide Pilot)
Tamper resistant records help detect repeat or suspicious claims. Nationwide tested blockchain to strengthen fraud identification.
Manufacturing and Industrial Operations
 Manufacturers require verifiable supply information and trustworthy machine data. Blockchain enhances visibility and coordination across plants.
Manufacturers require verifiable supply information and trustworthy machine data. Blockchain enhances visibility and coordination across plants.
29. Part Tracking From Origin to Assembly (Renault)
Component history is stored securely from supplier to factory. Renault uses blockchain to increase traceability within its automotive supply chain.
30. Secure Machine Data Storage (Siemens)
Machine output and sensor data must remain accurate for maintenance. Siemens explores blockchain to secure industrial data and support predictive oversight.
31. Coordinated Planning for Distributed Plants (Foxconn)
Multiple factories rely on consistent operational records. Foxconn has evaluated blockchain to improve collaboration across distributed production networks.
Education and Academic Verification
 Academic institutions use blockchain to strengthen verification processes and simplify credential sharing.
Academic institutions use blockchain to strengthen verification processes and simplify credential sharing.
32. Certificate and Transcript Verification (MIT)
Blockchain diplomas allow instant authenticity checks. MIT issues digital certificates that employers can verify without contacting the institution.
33. Secure Student Identity Profiles (Learning Machine)
Students maintain blockchain based identity records with verified achievements. Learning Machine supports universities in issuing tamper proof credentials.
34. International Credential Portability (University of Nicosia)
Students move academic records across borders more easily with blockchain. The University of Nicosia enables global portability for degrees and transcripts.
Retail and E Commerce
 Retailers need transparent sourcing and reliable customer data handling. Blockchain helps strengthen both.
Retailers need transparent sourcing and reliable customer data handling. Blockchain helps strengthen both.
35. Ethical Sourcing and Product Transparency (Starbucks)
Customers can trace supply origins through blockchain entries. Starbucks uses blockchain to let buyers view coffee production details from farm to cup.
36. Modern Blockchain Loyalty Programs (Lolli)
Reward systems run more securely on blockchain. Lolli offers Bitcoin rewards for purchases, providing a blockchain backed loyalty model.
37. Better Protection of Customer Data (Alibaba)
Retail platforms manage consent and data updates more safely using blockchain. Alibaba tests such systems to strengthen privacy compliance.
Agriculture and Food Safety
 Producers need verified information about crops, livestock and food handling. Blockchain improves transparency across agricultural supply chains.
Producers need verified information about crops, livestock and food handling. Blockchain improves transparency across agricultural supply chains.
38. Farm to Shelf Product Tracking (Nestlé)
Food items are traced through each handling stage. Nestlé uses blockchain to track selected product lines and provide detailed transparency to consumers.
39. Crop Condition and Input Monitoring (AgriDigital)
Crop data, storage details and delivery confirmations are stored securely. AgriDigital helps farmers manage supply chain transactions with verifiable records.
40. Verified Livestock and Health Records (BeefChain)
Blockchain stores animal identity and health history, helping buyers confirm authenticity. BeefChain supports ranchers in validating livestock practices.
Limitations of Blockchain Applications and When They Fail
 You should know that blockchain is not suitable for every use case. Some conditions expose significant constraints that affect scalability, flexibility, or compliance. Understanding these limitations helps you decide whether blockchain supports your real business needs.
You should know that blockchain is not suitable for every use case. Some conditions expose significant constraints that affect scalability, flexibility, or compliance. Understanding these limitations helps you decide whether blockchain supports your real business needs.
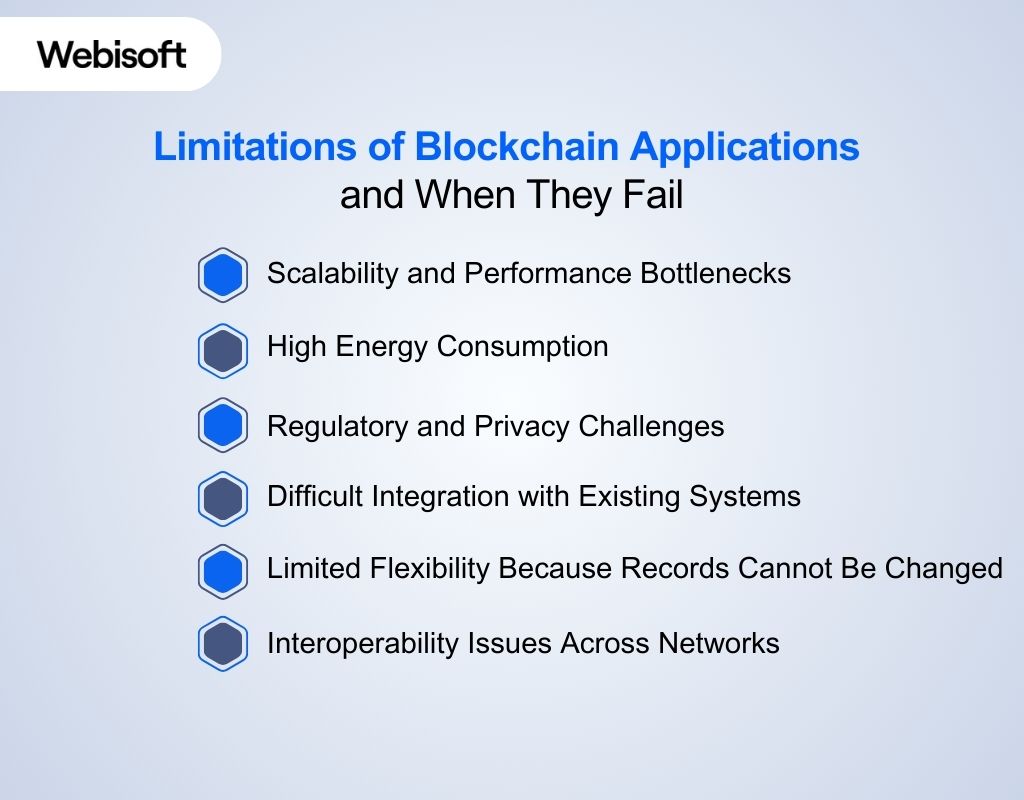
Scalability and Performance Bottlenecks
Many blockchains struggle with high transaction volumes or real time demands. As activity increases, throughput can drop and latency can rise, which limits applications that require fast processing or large scale usage.
High Energy Consumption
Some consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work require substantial computational power. This leads to higher energy usage and creates concerns for businesses with sustainability goals or regulatory pressure around environmental impact.
Regulatory and Privacy Challenges
Blockchain immutability can conflict with data protection laws such as requests for data removal. Decentralized storage also complicates compliance because organizations may not have full control over sensitive information.
Difficult Integration with Existing Systems
Connecting blockchain solutions to traditional infrastructure can require major architectural changes. Legacy systems often are not designed for decentralized models, which leads to higher integration costs and extended implementation time.
Limited Flexibility Because Records Cannot Be Changed
Once information is added to a blockchain, it cannot be edited. Errors in data entry or evolving business rules are difficult to address, which reduces flexibility compared to systems that allow controlled updates.
Interoperability Issues Across Networks
Many blockchain networks operate independently. Without reliable cross chain communication, building solutions that span multiple platforms becomes complex and can slow adoption in ecosystems where coordination matters.
What It Takes to Build a Blockchain Application: Before You Begin
 Some situations reveal where blockchain fits and where it struggles, and many teams document these insights in a blockchain application PDF for internal planning. Before moving into development, you need a clear view of the foundational conditions that influence how well a blockchain application can perform in a real environment.
Some situations reveal where blockchain fits and where it struggles, and many teams document these insights in a blockchain application PDF for internal planning. Before moving into development, you need a clear view of the foundational conditions that influence how well a blockchain application can perform in a real environment.
Define a Clear Business Problem and Use Case
Identify a concrete problem or inefficiency that blockchain can solve (e.g. shared data across parties, audit trail, automated agreements). Without a strong use case, standard databases and traditional apps may work better.
Choose the Right Blockchain Type and Platform
Decide whether you need a public, private or consortium blockchain. And select a platform that matches performance, privacy, cost and governance needs (e.g. Ethereum, Hyperledger, Solana, etc.). You can explore this further in our How to Build a Blockchain Network Using Hyperledger Fabric guide.
Design Smart Contracts and Architecture Carefully
Smart contracts will handle logic and agreements, they must be secure, efficient, and tested thoroughly. Architecture must accommodate data flows, network nodes, consensus mechanisms, and integration with existing systems.
Plan for Integration with Existing Systems & User Interfaces
Blockchain alone rarely suffices. You’ll need frontend/backend infrastructure, API or user interface, wallet or identity integration, and a bridge between blockchain and off-chain data.
Allocate for Security, Compliance, and Long-Term Maintenance
Expect audits, security testing, ongoing maintenance, and compliance checks (especially in regulated sectors). Blockchain apps require continuous oversight, not a “set-and-forget” deployment.
Estimate Time, Cost and Resource Requirements Realistically
Building a blockchain application involves both blockchain-specific work (contracts, nodes, network) and traditional dev work (frontend/back-end). A simple app may take months; a full-scale system needs significantly more.
You do not need to navigate blockchain development alone. Contact Webisoft to get expert guidance, clear planning support and a team that helps you turn ideas into secure solutions without unnecessary delays.
How Webisoft Helps You Plan and Build Blockchain Applications
 You’re set to build your application, yet blockchain work can turn complicated quicker than expected. Webisoft guides each phase with careful planning and strong technical execution so you can build secure, scalable applications that serve your business objectives effectively.
You’re set to build your application, yet blockchain work can turn complicated quicker than expected. Webisoft guides each phase with careful planning and strong technical execution so you can build secure, scalable applications that serve your business objectives effectively.
Support Choosing the Right Use Case and Architecture
Webisoft helps you evaluate whether blockchain fits your objectives. Our team guides you through choosing the right architecture such as public, private or consortium networks while aligning design choices with compliance and operational needs.
Development That Matches Your Vision End to End
Our developers build every layer of your application including smart contracts, backend logic and user interfaces. This ensures your blockchain system functions seamlessly across all components and remains ready for real world usage.
Custom Networks Designed Around Your Needs
If your project requires privacy, performance or strict control, Webisoft designs custom private or hybrid blockchain networks. This is part of our Blockchain Development Services. These solutions support regulated environments where data protection and precise governance structures are essential.
Infrastructure Management You Do Not Need to Handle Alone
Webisoft sets up your blockchain infrastructure and keeps it running reliably. This includes node configuration, hosting, monitoring and continuous updates so your application remains stable and secure over time.
Ecosystem Features Built for Your Product Goals
Whether you need tokens, wallets, dApps or specialized modules, Webisoft builds the surrounding ecosystem required to support your application. This helps you achieve a complete blockchain solution from one team.
Scalability Planning for Your Long Term Growth
Webisoft develops solutions that grow with your business. Your blockchain application can expand from a small pilot to a full enterprise launch without compromising performance or security.
Compliance Guidance That Supports Your Sector
Our team follows secure development practices and supports regulatory requirements. This includes preparing your blockchain application for audits and ensuring it meets industry standards for safety and accountability.
Build smarter blockchain solutions with Webisoft today.
Get expert help to plan, design and launch secure blockchain systems effectively.
Conclusion
When you look at the full blockchain applications list, it becomes obvious that this technology is no longer a futuristic buzzword. It is the quiet problem solver businesses rely on when spreadsheets, emails and “quick fixes” finally give up.
And if you want support turning these capabilities into something useful for your business, Webisoft is ready to help. You get a team that understands the tech, simplifies the complexity and builds solutions you can rely on, not just talk about.
Frequently Asked Question
What are the 4 types of blockchain?
There are four main types: public, private, consortium and hybrid blockchains. Each offers different levels of access, control and transparency, allowing businesses to choose the structure that fits their operational and regulatory requirements.
Is Bitcoin a blockchain?
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency that runs on its own blockchain, which records all transactions in a decentralized and tamper resistant ledger. The Bitcoin blockchain was the first widely adopted example of this technology.
What is the future of blockchain?
The future of blockchain includes wider enterprise adoption, improved scalability, stronger cross-chain interoperability and deeper integration with AI and IoT systems. Businesses will use it for trusted data, automation and secure multi-party collaboration across industries.


